Question: can you please explain how to solve this question? Example 22.4 The electric potential energy of a phosphate anion Phosphate, which is critical to the
can you please explain how to solve this question?
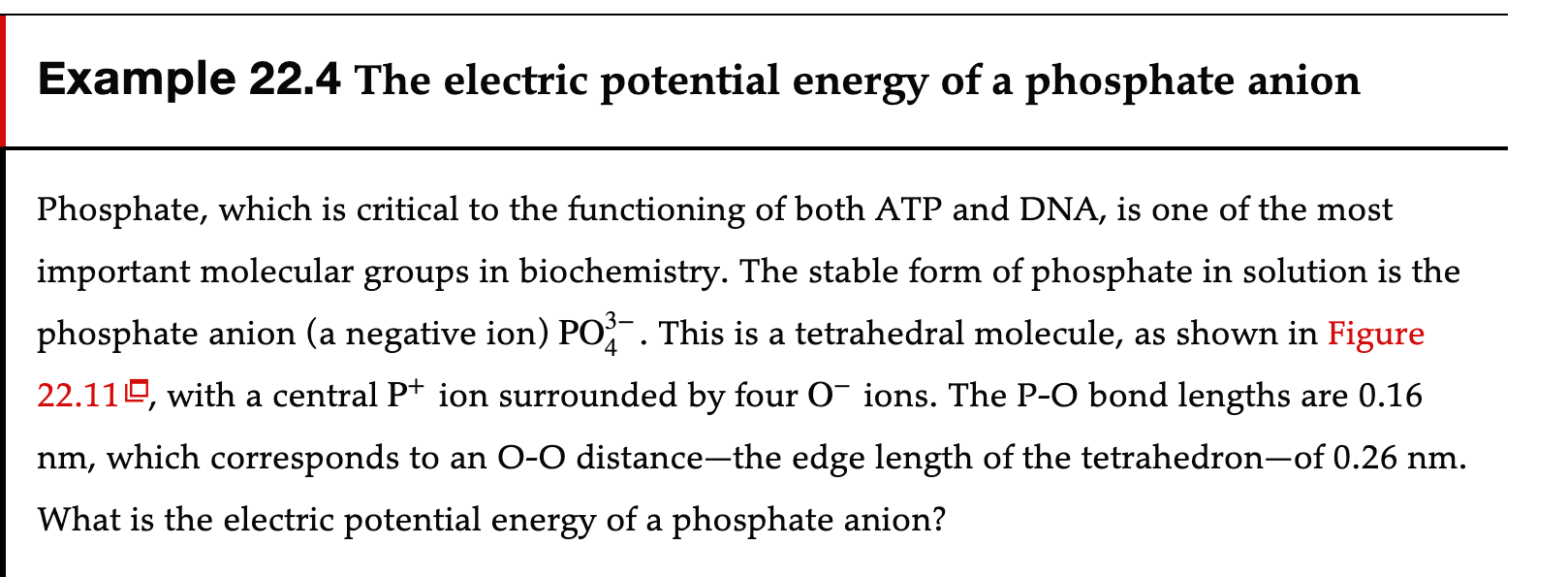
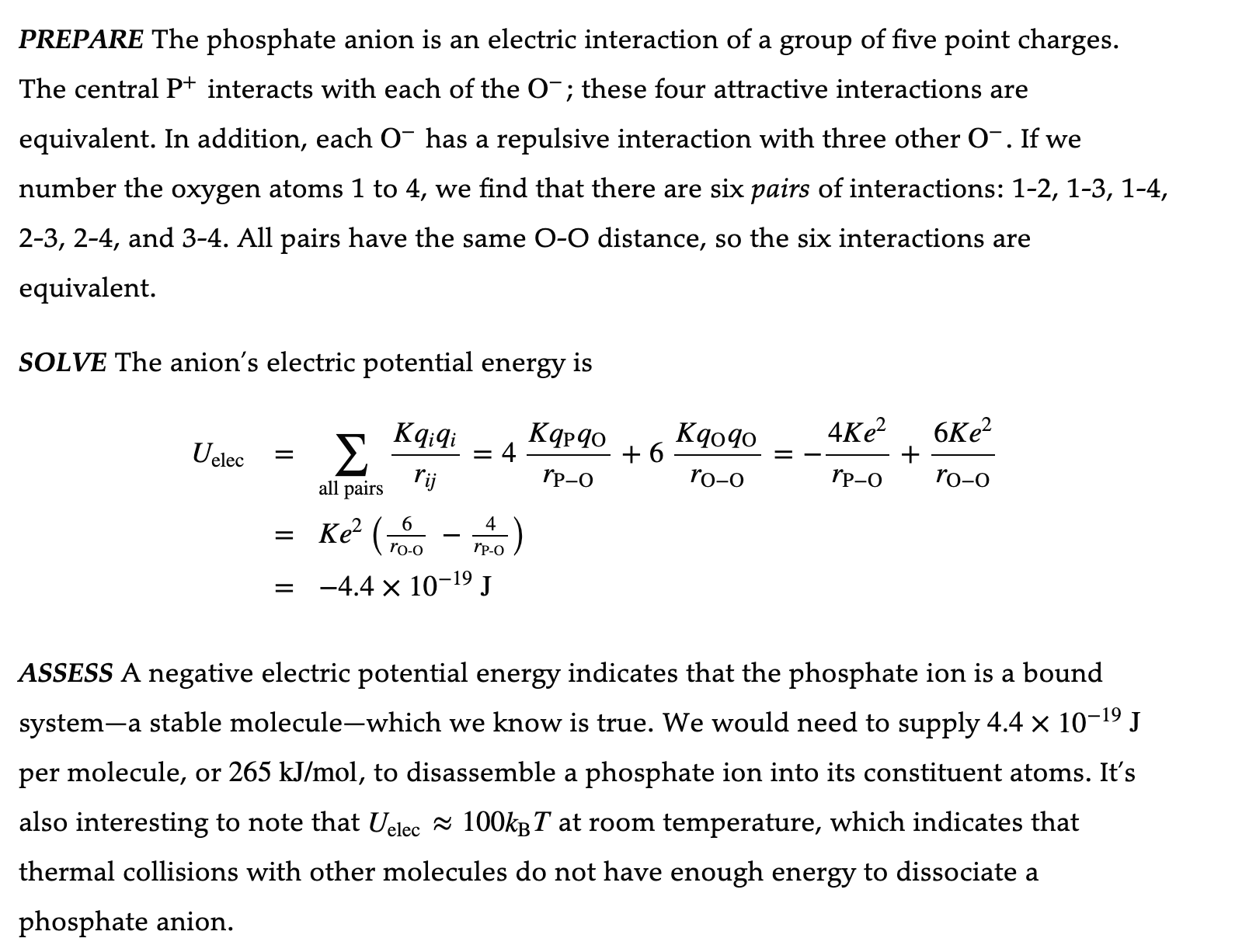
Example 22.4 The electric potential energy of a phosphate anion Phosphate, which is critical to the functioning of both ATP and DNA, is one of the most important molecular groups in biochemistry. The stable form of phosphate in solution is the phosphate anion (a negative ion) POf. This is a tetrahedral molecule, as shown in Figure 22.11 IE', with a central P+ ion surrounded by four 0' ions. The P-O bond lengths are 0.16 nm, which corresponds to an 00 distancethe edge length of the tetrahedronof 0.26 nm. What is the electric potential energy of a phosphate anion? PREPARE The phosphate anion is an electric interaction of a group of five point charges. The central P+ interacts with each of the O' ; these four attractive interactions are equivalent. In addition, each 0' has a repulsive interaction with three other 0'. If we number the oxygen atoms 1 to 4, we nd that there are six pairs of interactions: 1-2, 13, 1-4, 23, 2-4, and 3-4. All pairs have the same O-O distance, so the six interactions are equivalent. SOLVE The anion's electric potential energy is K ,- ,- K K 4K 2 6K 2 U61\" = z qq =4 qPCI0+6 61040=_ e + e 311pr y "Po Too rPO roo _ 6 4 - K92 (70.0 _E) = 4.4x10-19J ASSESS A negative electric potential energy indicates that the phosphate ion is a bound systema stable moleculewhich we know is true. We would need to supply 4.4 X 10'19 J per molecule, or 265 kJ/mol, to disassemble a phosphate ion into its constituent atoms. It's also interesting to note that Uelec z IOOkBT at room temperature, which indicates that thermal collisions with other molecules do not have enough energy to dissociate a phosphate anion
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


