Question: Can you please help me with these college physics questions. The questions are in the screenshots and dow below: 1. A 0.400-kg object is attached












Can you please help me with these college physics questions. The questions are in the screenshots and dow below:
1. A 0.400-kg object is attached to a spring with spring constant k = 10.0 N/m and moves with simple harmonic motion over a horizontal frictionless surface. At the instant that it is displaced from equilibrium by ?0.0550 m, what is its acceleration? a. 2 200 m/s2 b. ?220 m/s2 c. 0.220 m/s2 d. 1.38 m/s2 e. 0.550 m/s2
2. A 0.30-kg object is oscillating on a spring with a spring constant of k = 22.0 N/m. What is the potential energy of the system when the object displacement is 0.035 m, exactly half the maximum amplitude? a. zero b. 0.027 J c. 0.013 J d. 0.39 J e. 11 J
3. A runaway railroad car, with mass 45.0 104 kg, coasts across a level track at 3.80 m/s when it collides with a spring-loaded bumper at the end of the track. If the spring constant of the bumper is 3.80 106 N/m, what is the maximum compression of the spring during the collision? (Assume the collision is elastic.) a. 1.31 m b. 1.85 m c. 0.925 m d. 2.10 m e. 2.62 m
4. A 0.20-kg mass is oscillating on a spring over a horizontal frictionless surface. When it is at a displacement of 2.3 cm for equilibrium it has a kinetic energy of 1.5 J and a spring potential energy of 2.3 J. What is the maximum speed of the mass during its oscillation? a. 4.4 m/s b. 0.16 m/s c. 6.2 m/s d. 4.8 m/s e. 3.0 m/s
5. A mass on a spring vibrates in simple harmonic motion at a frequency of 4.20 Hz and an amplitude of 7.50 cm. If the mass of the object is 0.260 kg, what is the spring constant? a. 6.86 N/m b. 696 N/m c. 181 N/m d. 24.1 N/m e. 339 N/m
6. A simple pendulum has a period of 4.40 s. What is the pendulum length? (g = 9.80 m/s2) a. 19.2 m b. 15.1 m c. 4.81 m d. 0.208 m e. 0.0520 m
Chapter 14: 7. The wavelength of a traveling wave can be calculated if one knows the: a. frequency. b. speed and amplitude. c. amplitude and frequency. d. frequency and speed.
8. A musical tone, sounded on a piano, has a frequency of 460 Hz and a wavelength in air of 0.50 m. What is the wave speed? a. 920 m/s b. 270 m/s c. 230 m/s d. 109 m/s e. 115 m/s
9. Bats can detect small objects such as insects that are of a size approximately that of one wavelength. If bats emit a chirp at a frequency of 60 kHz, and the speed of sound waves in air is 335 m/s, what is the smallest size insect they can detect? a. 4.6 mm b. 3.6 mm c. 5.6 mm d. 6.6 mm e. 7.6 mm
10. A 2.00-m long piano string of mass 10.0 g is under a tension of 320 N. Find the speed with which a wave travels on this string. a. 506 m/s b. 253 m/s c. 126 m/s d. 358 m/s e. 80.0 m/s
11. The frequency separating audible waves and ultrasonic waves is considered to be 15.0 kHz. What wavelength in air at room temperature is associated with this frequency? (Assume the speed of sound to be 225 m/s.) a. 1.50 cm b. 33.8 cm c. 22.5 cm d. 33.8 cm e. 33.8 cm
12. Which of the following best describes a sound level of intensity 1 W/m2? a. extremely loud b. about that of a power mower c. normal conversation d. like a whisper
13. What is the intensity of sound from a band with a sound level of 129 dB? (I0 = 10?12 W/m2) a. 7.94 W/m2 b. 1.29 W/m2 c. 79.4 W/m2 d. 12.9 W/m2 e. 129 W/m2
14. You stand by the railroad tracks as a train passes by. You hear a 1 020-Hz frequency when the train approaches, which changes to 760 Hz as it goes away. How fast is the train moving? The speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. a. 30.2 m/s b. 34.5 m/s c. 40.1 m/s
d. 49.7 m/s e. 45.6 m/s
15. A 550-Hz whistle is moved toward a listener at a speed of 25.0 m/s. At the same time, the listener moves at a speed of 35.0 m/s in a direction away from the whistle. What is the apparent frequency heard by the listener? (The speed of sound is 340 m/s.) a. 510 Hz b. 533 Hz c. 655 Hz d. 460 Hz e. 594 Hz
16. A 1.30-m string is held fixed at both ends. When driven by a 140-Hz source, the string vibrates in 4 distinct segments. What is the natural fundamental frequency of the string? a. 35.0 Hz b. 70.0 Hz c. 215 Hz d. 431 Hz e. 45.5 Hz
17. The lower A on a piano has a frequency of 30.0 Hz. If the tension in the 2.00-m-long string is 316 N and one-half wavelength occupies the string, what is the mass of the string? a. 61.4 g b. 21.9 g c. 17.6 g d. 43.9 g e. 91.1 g
Chapter 15: 18. A 6.6-C charge is placed at the origin and a second charge is placed on the x-axis at x = 0.1 m. If the resulting force on the second charge is 5.7 N in the positive x-direction, what is the value of its charge? a. 1.0 C b. 1.0 nC c. -1.0 C d. -1.0 nC e. 0 C
19. Two point charges each have a value of 35.5 mC and are separated by a distance of 4.0 cm. What is the electric field midway between the two charges? (ke = 8.99 109 Nm2/C2) a. 7.1E+8 N/C b. 3.5E+8 N/C c. 1.8E+8 N/C d. zero e. 2.0E+8 N/C
Chapter 16: 20. Find the electrical potential at 0.25 m from a point charge of 7.0 C. (ke = 8.99 109N?m2/C2) a. 3.4 104 V b. 2.5 105 V c. 3.2 106 V d. 3.2 107 V e. 3.4 105 V
21. Two point charges of values +3.6 and +6.9 C are separated by 0.40 m. What is the electrical potential at the point midway between the two point charges? (ke = 8.99 109 N?m2/C2) a. +0.47 MV b. ?0.24 MV c. +0.24 MV d. +0.97 MV e. ?0.47 MV
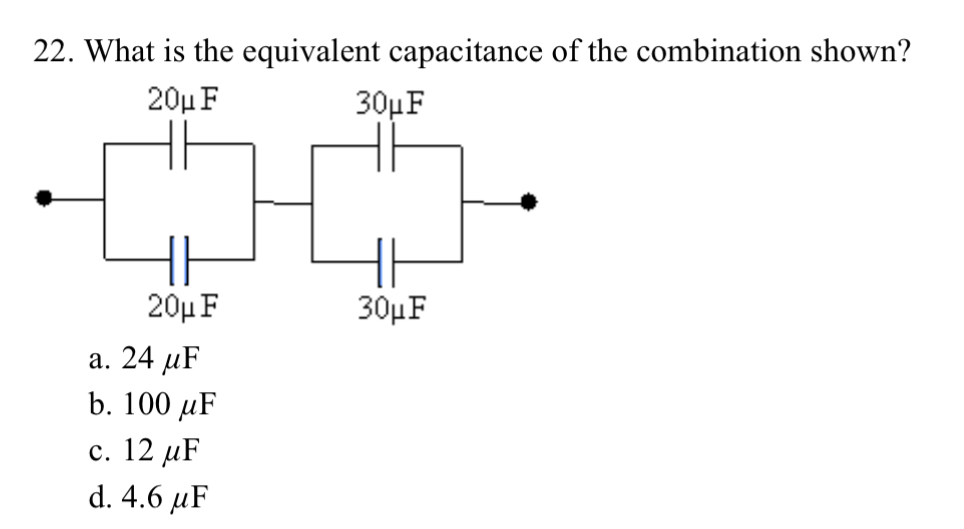
#22 (in screenshot down below)
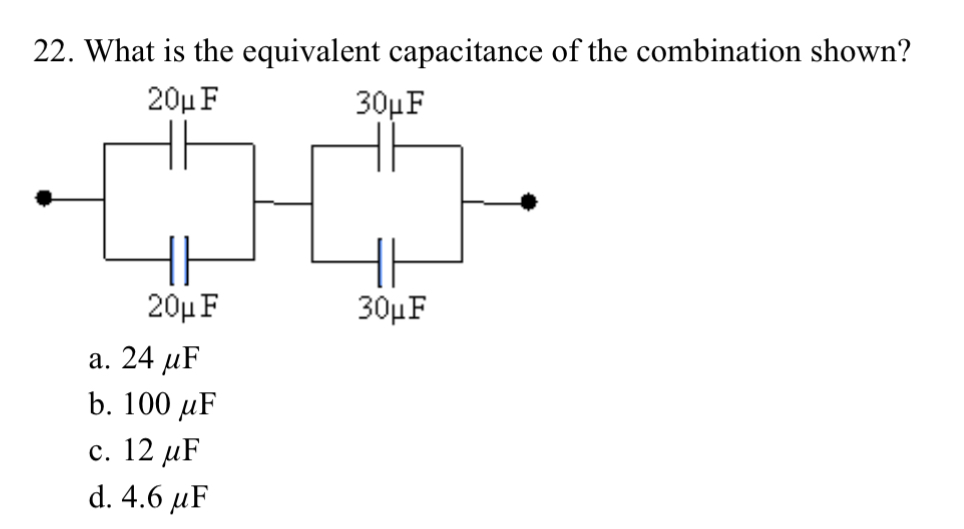








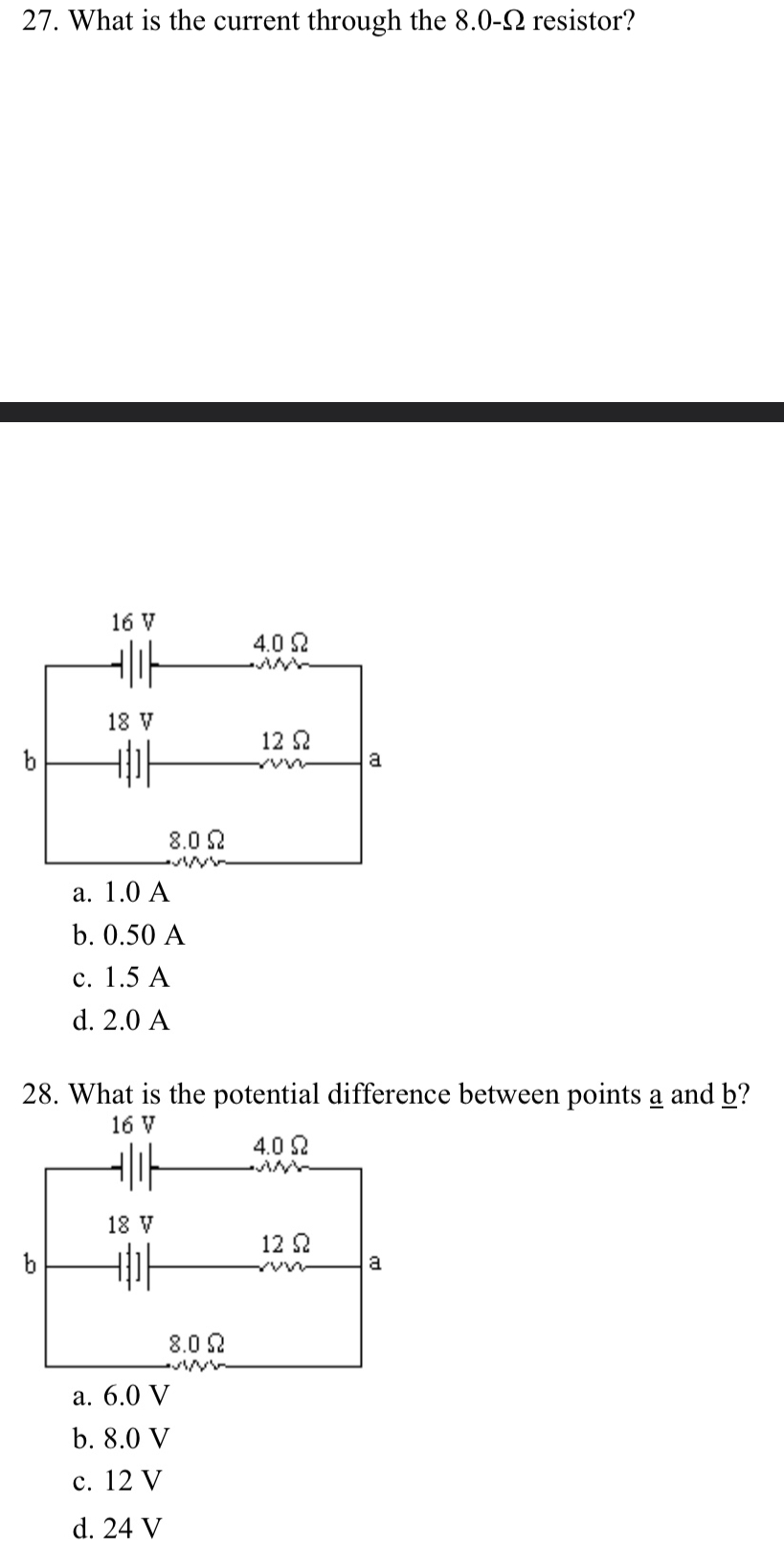




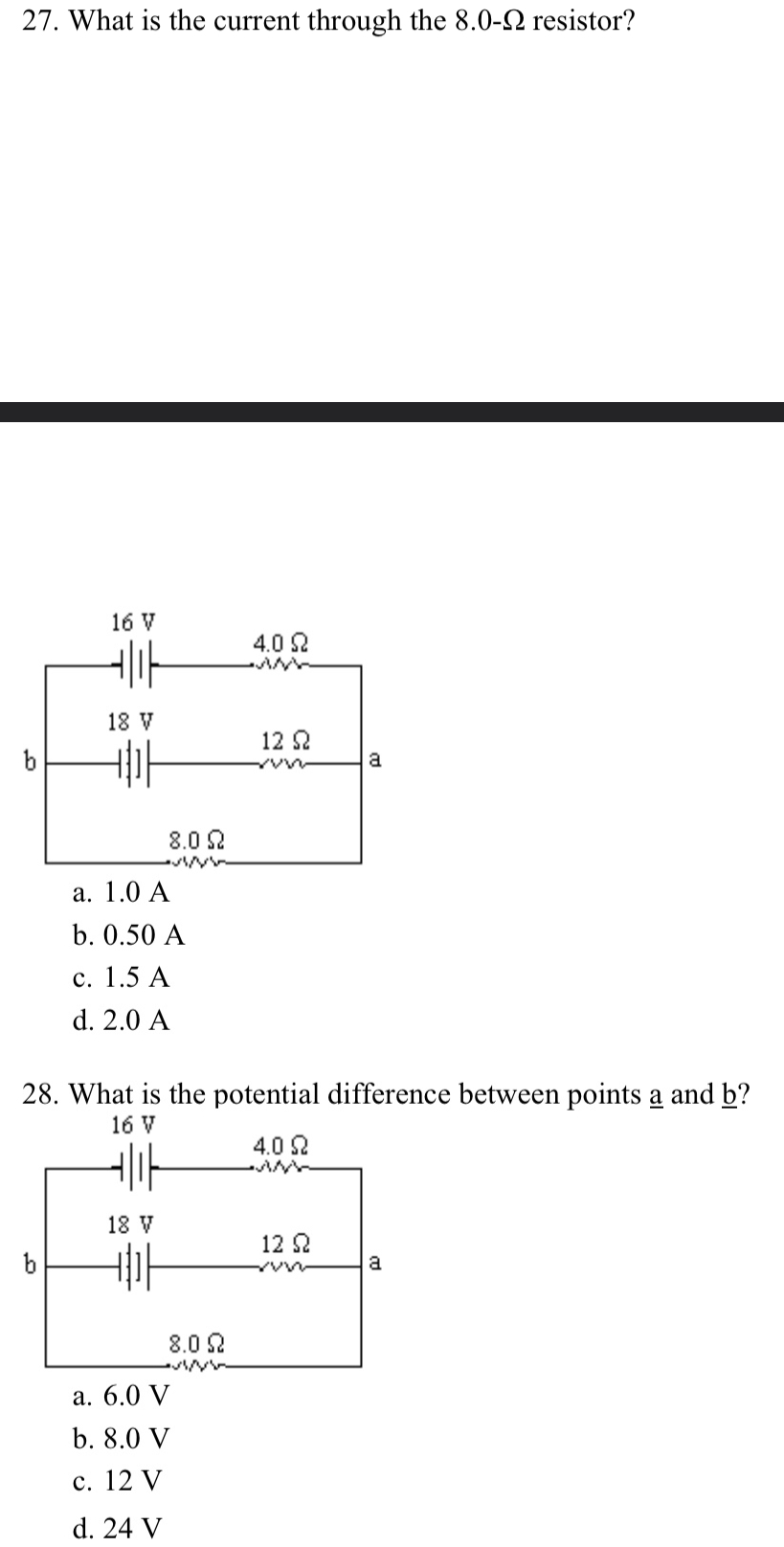
22. What is the equivalent capacitance of the combination shown? 20u F 30UF 20u F 30UF a. 24 uF b. 100 uF c. 12 uF d. 4.6 uFChapter 18: 26. Three resistors connected in parallel have individual values of 4.0, 6.0, and 10.0 0, respectively. If this combination is connected in series with a 12-V battery and a 2.0-2 resistor what is the current in the 10.0-2 resistor? 200 12 VI $4.09 36.09 $10.00 a. 0.55 A b. 1.0 A c. 1 1 A d. 16 A 27. What is the current through the 8.0-2 resistor? 16 V 4.0 92 18 V 12 92 8.0 9 a. 1.0 A b. 0.50 A C. 1.5 A d. 2.0 A 28. What is the potential difference between points a and b? 16 V 4.0 92 18 V 12 Q a 8.0 92 a. 6.0 V b. 8.0 V c. 12 V d. 24 V 29. If & = 9.0 V, what is the current in the 15-2 resistor? 20 Q $ 15 Q $ 30 C a. 0.20 A b. 0.30 A c. 0.10 A d. 0.26 AChapter 13: 1. A 0.400-kg object is attached to a spring with spring constant = 10.0 N/m and moves with simple harmonic motion over a horizontal frictionless surface. At the instant that it is displaced from equilibrium by 0.0550 m, what is its acceleration? a. 2200 m/s' b. 220 m/s' c. 0.220 m/s' d. 1.38 m/s' e. 0.550 m/s\" 2. A 0.30-kg object is oscillating on a spring with a spring constant of = 22.0 N/m. What is the potential energy of the system when the object displacement is 0.035 m, exactly half the maximum amplitude? a. zero b. 0.027J c. 0.0131] d.0.39] e. 111J 3. A runaway railroad car, with mass 45.0 x 10" kg, coasts across a level track at 3.80 m/s when it collides with a spring-loaded bumper at the end of the track. If the spring constant of the bumper is 3.80 x 10 N/m, what is the maximum compression of the spring during the collision? (Assume the collision is elastic.) a. 13l m b. 1.85m c. 0925 m d.210m e. 2.62m 4. A 0.20-kg mass is oscillating on a spring over a horizontal frictionless surface. When it is at a displacement of 2.3 ccm for equilibrium it has a kinetic energy of 1.5 J and a spring potential energy of 2.3 J. What is the maximum speed of the mass during its oscillation? a. 44 m/s b. 0.16 m/s c. 6.2m/s d. 4.8 m/s e. 3.0 m/s 5. A mass on a spring vibrates in simple harmonic motion at a frequency of 4.20 Hz and an amplitude of 7.50 cm. If the mass of the object is 0.260 kg, what is the spring constant? a. 6.86 N/m b. 696 N/m c. 181 N/m d. 24.1 N/m e. 339 N/m 6. A simple pendulum has a period of 4.40 s. What is the pendulum length? (g = 9.80 m/s?) a. 192 m b. 15.1m c. 48l m d. 0.208 m e. 0.0520 m Chapter 14: 7. The wavelength of a traveling wave can be calculated if one knows the: a. frequency. b. speed and amplitude. c. amplitude and frequency. d. frequency and speed. 8. A musical tone, sounded on a piano, has a frequency of 460 Hz and a wavelength in air of 0.50 m. What is the wave speed? a. 920 m/s b. 270 m/s c. 230 m/s d. 109 m/s e. 115 m/s 9. Bats can detect small objects such as insects that are of a size approximately that of one wavelength. If bats emit a chirp at a frequency of 60 kHz, and the speed of sound waves in air is 335 m/s, what is the smallest size insect they can detect? a. 4.6 mm b. 3.6 mm . 5.6 mm d. 6.6 mm e. 7.6 mm 10. A 2.00-m long piano string of mass 10.0 g is under a tension of 320 N. Find the speed with which a wave travels on this string. a. 506 m/s b. 253 m/s c. 126 m/s d. 358 m/s e. 80.0 m/s 11. The frequency separating audible waves and ultrasonic waves is considered to be 15.0 kHz. What wavelength in air at room temperature is associated with this frequency? (Assume the speed of sound to be 225 m/s.) a. 1.50 cm b.33.8 cm c.22.5cm d. 33.8 cm . 33.8 cm 12. Which of the following best describes a sound level of intensity 1 W/m? a. extremely loud b. about that of a power mower c. normal conversation d. like a whisper 13. What is the intensity of sound from a band with a sound level of 129 dB? (1, = 10"* W/m?) a. 7.94 W/m? b.1.29 W/m c. 79.4 W/m? d. 12.9 W/m? e. 129 W/m? 14. You stand by the railroad tracks as a train passes by. You hear a 1 020-Hz frequency when the train approaches, which changes to 760 Hz as it goes away. How fast is the train moving? The speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. a. 30.2 m/s b. 34.5 m/s c. 40.1 m/s d. 49.7 m/s e. 45.6 m/s 15. A 550-Hz whistle is moved toward a listener at a speed of 25.0 m/s. At the same time, the listener moves at a speed of 35.0 m/s in a direction away from the whistle. What is the apparent frequency heard by the listener? (The speed of sound is 340 m/s.) a. 510 Hz b. 533 Hz c. 655 Hz d. 460 Hz e. 594 Hz 16. A 1.30-m string is held fixed at both ends. When driven by a 140-Hz source, the string vibrates in 4 distinct segments. What is the natural fundamental frequency of the string? a. 35.0 Hz b. 70.0 Hz c. 215 Hz d. 431 Hz e. 45.5 Hz 17. The lower A on a piano has a frequency of 30.0 Hz. If the tension in the 2.00-m-long string is 316 N and one-half wavelength occupies the string, what is the mass of the string? a. 61.4 g b. 21.9 g c. 17.6 g d. 43.9 g e. 91.1 g Chapter 15: 18. A 6.6-uC charge is placed at the origin and a second charge is placed on the x-axis at x = 0.1 m. If the resulting force on the second charge is 5.7 N in the positive x-direction, what is the value of its charge? a. 1.0 JC b. 1.0 nC c. -1.0 JC d. -1.0 nc e. O uC19. Two point charges each have a value of 35.5 mC and are separated by a distance of 4.0 cm. What is the electric field midway between the two charges? (ke = 8.99 x 10' N.m-/CZ) a. 7.1E+8 N/C b. 3.5E+8 N/C c. 1.8E+8 N/C d. zero e. 2.0E+8 N/C Chapter 16: 20. Find the electrical potential at 0.25 m from a point charge of 7.0 uC. (ke = 8.99 x 109 N.m /C2) a. 3.4 x 104 V b. 2.5 x 10' V c. 3.2 x 10' V d. 3.2 x 10' V e. 3.4 x 10' V 21. Two point charges of values +3.6 and +6.9 uC are separated by 0.40 m. What is the electrical potential at the point midway between the two point charges? (ke = 8.99 x 109 N . my/C2) a. +0.47 MV b. -0.24 MV c. +0.24 MV d. +0.97 MV e. -0.47 MV22. What is the equivalent capacitance of the combination shown? 20u F 30UF 20u F 30UF a. 24 uF b. 100 uF c. 12 MF d. 4.6 uF Chapter 17: 23. A wire carries a steady current of 0.30 A over a period of 20 s. What total charge passes through the wire in this time interval? a. 67 C b. 20 C c. 6.0 C d. 0.015 C e. 0.30 C 24. You measure a 20-V potential difference across a 7.0-2 resistor. What is the current flowing through it? a. 140 A b. 2.9 A c. 27 A d. 13 A 5.2 A24. You measure a 20-V potential difference across a 7.0-2 resistor. What is the current flowing through it? a. 140 A b. 2.9 A c. 27 A d. 13 A e. 5.2 A 25. A metallic conductor has a resistivity of 35 x 10- 2 m. What is the resistance of a piece that is 20 m long and has a uniform cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10- m-? a. 0.44 Q b. 180 Q c. 2.3 0 d. 7.0 0 e. 2 800 0 Chapter 18: 26. Three resistors connected in parallel have individual values of 4.0, 6.0, and 10.0 0, respectively. If this combination is connected in series with a 12-V battery and a 2.0-2 resistor, what is the current in the 10.0-2 resistor? 2.00 12 V - $4.00 36.00 $10.09 a. 0.55 A b. 1.0 A c. 11 A d. 16 A27. What is the current through the 8.0-2 resistor? 16 V 4.0 92 18 V 12 92 b a 8.0 2 a. 1.0 A b. 0.50 A c. 1.5 A d. 2.0 A 28. What is the potential difference between points a and b? 16 V 4.0 92 18 V 12 9 b a 8.0 9 a. 6.0 V b. 8.0 V c. 12 V d. 24 V29. If =9.0 V, what is the current in the 15-Q resistor? 00 15Q $30C b g ll a. 020 A b.0.30 A c. 0.10 A d. 026 A Chapter 19: 30. A deuteron, with the same charge but twice the mass of a proton, moves with a speed of 6.00 x 10 m/s perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.0525 T. Which of the paths described below would it follow? (g, = 1.60 x 10~"" C and m, = 3.34 x 10" kg) a. a straight-line path b. a circular path of 61.1 cm radius c. a circular path of 23.9 cm radius d. a circular path of 2.14 cm radius e. a circular path of 1.70 cm radius 31. A proton moving at a speed of 4.2 x 10 m/s cuts across the lines of a magnetic field at an angle of 78. The strength of the field is 0.91 x 10* T. What is the magnitude of the force acting on the proton? (g, = 1.6 x 10-"" C) a. 1.3E-17N b.3.1E-17N c. 6.0E-17N d. 72E-9N e. 9.6E-36 N 32. A copper wire of length 25.0 cm is in a magnetic field of 0.36 T. If it has a mass of 11.0 g, what 1s the minimum current through the wire that would cause a magnetic force equal to its weight? a. 12 A b. 048 A L2-A d33A e.0.75A Chapter 22: 33. A ray of light strikes a thick sheet of glass (n = 1.5) at an angle of 22 with the normal. Find the angle of the ray reflected off the glass surface with respect to the normal. 3. 33 b. 50 c. 14 ge22" e 157 34. A light ray in air is incident on an air-to-glass boundary at an angle of 33.0 and is refracted in the glass at an angle of 18.5 with the normal. Find the index of refraction of the glass. a. 1.78 b. 2.89 c. 2.95 g 172 e. 1.58 Chapter 23: 35. A concave mirror forms a real image at 35.2 cm from the mirror surface along the principal axis. If the corresponding object is at a 12.6-cm distance, what is the mirror's focal length? a. 22.6 cm b. 47.8 cm c. 10.8 cm d. 9.28 cm e. 19.6 cm 36. Which of the following best describes the image for a thin convex lens that forms whenever the object is at a distance less than one focal length from the lens? a. inverted, enlarged and real b. upright, enlarged and virtual c. upright, diminished and virtual d. inverted, diminished and real 37. Two thin lenses with 6.80-cm focal lengths at are mounted at opposite ends of a 18.8-cm long tube. An object is located 20.4 cm from one end of the tube. How far from the opposite end is the final image? (For additional practice: draw the ray diagram for this situation, EC will be awarded) a. 8.88 cm b.32.5cm c. 4.54 cm d. 8.60 cm e. 204 cm 38. A real object is place a distance d from a converging lens. The object is then moved to a distance 2d from the converging lens. Which of the following statements is false? (For additional practice: draw the ray diagram for this situation, EC will be awarded) a. The image in the first case with the object at distance d can be the larger one. b. The image in the second case with the object at distance 2d can be the larger one. c. If both images are real, the image in the second case is smaller. d. If the image in the first case is real, the image in the second case is upright. 39. Sally places an object 12.6 cm from a thin convex lens along its axis. The lens has a focal length of 14.8 cm. What are the respective values of the image distance and magnification? (For additional practice: draw the ray diagram for this situation, EC will be awarded) a. -84.8 cm and + 6.73 b. 84.8 cm and + 6.73 c. 6.81 cm and + 5.73 d. -84.8 cm and -6.73 e. 84.8 cm and -6.73 Chapter 25: 40. A microscope has a tube length of 15.0 cm, an objective focal length of 0.95 cm, and an eyepiece focal length of 2.50 cm. What is the magnification of the microscope? Assume it is adjusted so that the eye is relaxed. a. 122 b. 132 c. 148 d. 12
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


