Question: Can you please solve both Problems 9-4 and 9-6? All the information and templates are provided below. Thank you! 9-4 ENTERPRISE VALUATION-TRADITIONAL WACC MODEL Canton

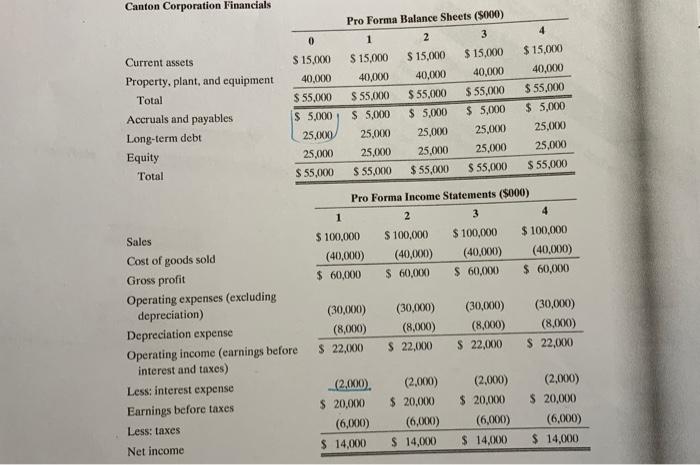




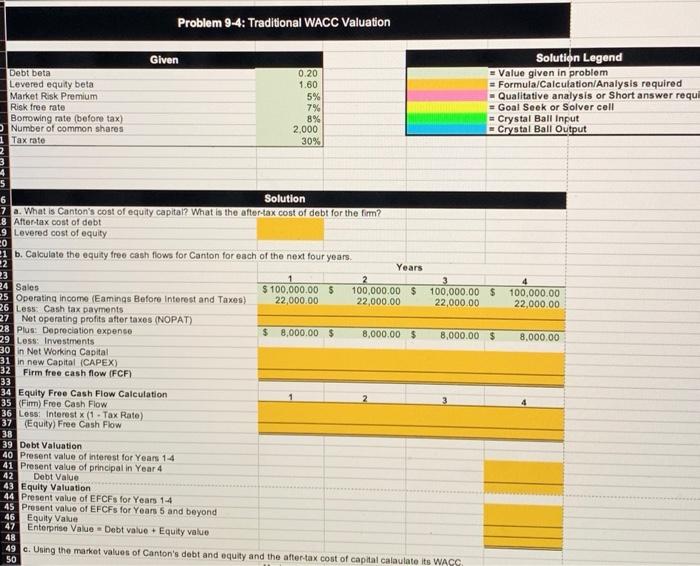
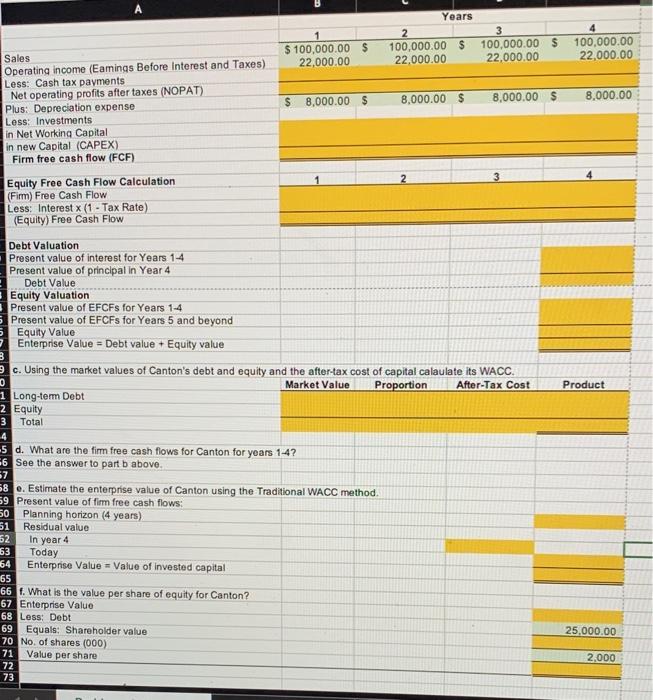
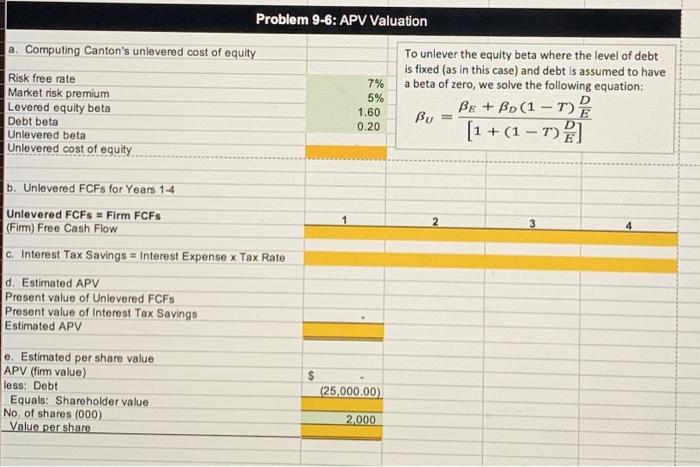
9-4 ENTERPRISE VALUATION-TRADITIONAL WACC MODEL Canton Corporation is a privately owned firm that engages in the production and sale of industrial chemicals, primarily in North America. The firm's primary product line consists of organic solvents and intermediates for pharmaceutical, agricultural, and chemical products. Canton's managers have recently been considering the possibility of taking the company public and have asked the firm's investment banker to perform some preliminary analysis of the value of the firm's equity. To support its analysis, the investment banker has prepared pro forma financial statements for each the next four years under the (simplifying) assumption that firm sales are flat (i.e., have a zero rate of growth), the corporate tax rate equals 30%, and capital expenditures are equal to the estimated depreciation expense. Canton Corporation Financials 0 Current assets Property, plant, and equipment Total Accruals and payables Long-term debt Equity Total $ 15,000 40.000 $ 55,000 $ 5,000 25,000 25,000 $ 55,000 Pro Forma Balance Sheets (5000) 1 2 3 $ 15,000 $ 15,000 $ 15,000 40,000 40,000 40,000 $ 55.000 $ 55,000 $ 55,000 $ 5,000 $ 5,000 $ 5,000 25,000 25,000 25.000 25,000 25,000 25,000 $ 55,000 $ 55,000 $ 55,000 4 $ 15,000 40,000 $ 55,000 $ 5.000 25.000 25,000 $ 55,000 Pro Forma Income Statements (5000) 1 2 3 4 $ 100,000 $ 100,000 $ 100,000 $ 100,000 (40,000) (40,000) (40,000) (40,000) $ 60,000 $ 60,000 $ 60,000 $ 60,000 Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Operating expenses (excluding depreciation) Depreciation expense Operating income (earnings before interest and taxes) Less: interest expense Earnings before taxes Less: taxes Net income (30,000) (8,000) $ 22,000 (30,000) (8,000) $ 22,000 (30,000) (8,000) $ 22,000 (30,000) (8,000) $ 22,000 (2.000). $ 20,000 (6,000) $ 14,000 (2.000) $ 20,000 (6,000) $ 14,000 (2.000) $ 20,000 (6,000) $ 14,000 (2,000) $ 20,000 (6,000) $ 14,000 In addition to the financial information on Canton, the investment banker has as- sembled the following information concerning current rates of return in the capital market: The current market rate of interest on ten-year Treasury bonds is 7%, and the mar- ket risk premium is estimated to be 5%. Canton's debt currently carries a rate of 8%, and this is the rate the firm would have to pay for any future borrowing as well. Using publicly traded firms as proxies, the estimated equity beta for Canton is 1.60. a. What is Canton's cost of equity capital? What is the after-tax cost of debt for the firm? b. Calculate the equity free cash flows for Canton for each of the next four years. Assuming that equity free cash flows are a level perpetuity for year 5 and beyond, estimate the value of Canton's equity. (Hint: Equity value is equal to the present value of the equity free cash flows discounted at the levered cost of equity.) If the market rate of interest on Canton's debt is equal to the 8% coupon, what is the cur- rent market value of the firm's debt? What is the enterprise value of Canton? (Hint: Enterprise value can be estimated as the sum of the estimated values of the firm's interest-bearing debt plus equity.) c. Using the market values of Canton's debt and equity calculated in Problem 9-56b), 9-4(b) calculate the firm's after-tax weighted average cost of capital. Hint: kwacc (1 - ) Cost of Tax Debt Value - Debt Rate Cost of Equity Value Levered Equity Enterprise Value d. What are the FCFs for Canton for years 1 through 4? e. Estimate the enterprise value of Canton using the traditional WACC model. Base your estimate on your previous answers, and assume that the FCFs after year 4 are a level perpetuity equal to the year 4 FCF. How does your estimate compare to your earlier estimate using the sum of the values of the firm's debt and equity? f. Based on your estimate of enterprise value, what is the value per share of equity for the firm if the firm has 2 million shares outstanding? Remember that your calculations up to this point have been in thousands of dollars. 9-6 ENTERPRISE VALUATION-APV MODEL This problem uses the information from Problem 9-4 about Canton Corporation to estimate the firm's enterprise value using the APV model. a. What is the firm's unlevered cost of equity? (Hint: The firm's debt beta is.20) b. What are the unlevered FCFs for Canton for years 1 through 4? (Hint: The unle- 1 vered FCFs are the same as the firm FCFs.) c. What are the interest tax savings for Canton for years 1 through 4? d. Assuming that the firm's future cash flows from operations (i.e., its FCFs) and its interest tax savings are level perpetuities for year 5 and beyond that equal their year 4 values, what is your estimate of the enterprise value of Canton? e. Based on your estimate of enterprise value, what is the value per share of equity for the firm if the firm has 2 million shares outstanding? Remember that your calcula- tions up to this point have been in thousands of dollars. Problem 9-4: Traditional WACC Valuation Given Solution Legend Debt beta 0.20 - Value given in problem Levered equity beta 1.60 = Formula/Calculation Analysis required Market Risk Premium 5% - Qualitative analysis or Short answer requl Risk free rate 7% = Goal Seek or Solver coll 8% Borrowing rate (before tax) = Crystal Ball Input Number of common shares 2.000 - Crystal Ball Output 1 Tax rate 30% 2 3 4 5 6 Solution 7 a. What is Canton's cost of equity capital? What is the after-tax cost of debt for the firm? 8 After-tax cost of debt 9 Lovered cost of equity 20 1 b. Calculate the equity free cash flows for Canton for each of the next four years, 22 Years 23 2 24 Sales $ 100,000.00 $ 100,000.00 $ 100,000.00 $ 100,000.00 25 Operating income (Eaminas Before Interest and Taxes) 22,000.00 22,000.00 22,000.00 22,000.00 26 Less Cash tax payments 27 Net operating profits after taxes (NOPAT) 28 Plus: Depreciation expense $ 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 29 Loss Investments 30 in Not Working Capital 31 in new Capital (CAPEX) 32 Firm free cash flow (FCF) 33 34 Equity Free Cash Flow Calculation 35 (Fin) Free Cash Flow 36 Loss Interest (1 . Tax Rate) 37 (Equity) Free Cash Flow 38 39 Debt Valuation 40 Present value of interest for Years 1-4 41 Present value of principal in Year 4 42 Debt Value 43 Equity Valuation 44 Present value of EFCFs for Years 1-4 45 Present value of EFCFs for Years 5 and beyond Equity Valve 47 Enterprise Value - Debt value + Equity value 48 49. Using the market values of Canton's debt and equity and the after tax cost of capital calaulate its WAGG 50 46 Years 2 100,000.00 $ 22,000.00 $ 100,000.00 $ 22,000.00 3 100,000.00 $ 22,000.00 100,000.00 22,000.00 $ 8,000.00 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 $ Sales Operating income (Eamings Before Interest and Taxes) Less: Cash tax payments Net operating profits after taxes (NOPAT) Plus: Depreciation expense Less: Investments in Net Working Capital in new Capital (CAPEX) Firm free cash flow (FCF) 3 Equity Free Cash Flow Calculation (Firm) Free Cash Flow Less: Interest x (1 - Tax Rate) (Equity) Free Cash Flow Product Debt Valuation Present value of interest for Years 1-4 Present value of principal in Year 4 Debt Value Equity Valuation Present value of EFCFs for Years 1-4 Present value of EFCFs for Years 5 and beyond Equity Value Enterprise Value = Debt value + Equity value 3 c. Using the market values of Canton's debt and equity and the after-tax cost of capital calaulate its WACC. 0 Market Value Proportion After-Tax Cost 1 Long-term Debt 2 Equity 3 Total 4 -5 d. What are the firm free cash flows for Canton for years 1-4? 6 See the answer to part b above. 37 58 e. Estimate the enterprise value of Canton using the Traditional WACC method 59 Present value of fimm free cash flows: 50 Planning horizon (4 years) 51 Residual value 52 In year 4 63 Today 64 Enterprise Value = Value of invested capital 65 66 r. What is the value per share of equity for Canton? 67 Enterprise Value 68 Less: Debt 69 Equals: Shareholder value 70 No. of shares (000) 71 Value per share 72 73 25,000.00 2,000 Problem 9-6: APV Valuation a. Computing Canton's unlevered cost of equity Risk free rate Market risk premium Levered equity beta Debt bota Unlevered beta Unlevered cost of equity 7% 5% 1.60 0.20 To unlever the equity beta where the level of debt is fixed (as in this case) and debt is assumed to have a beta of zero, we solve the following equation: Be + Bp (1 - 1) Bu [1 + (1 - ) 2 b. Unlevered FCFs for Years 1-4 Unlevered FCFS #Firm FCFS (Firm) Free Cash Flow c. Interest Tax Savings = Interest Expense x Tax Rate d. Estimated APV Present value of Unlevered FCFs Present value of Interest Tax Savings Estimated APV e. Estimated per share value APV (firm value) less: Debt Equals: Shareholder value No. of shares (000) Value per share S (25,000.00) 2,000 9-4 ENTERPRISE VALUATION-TRADITIONAL WACC MODEL Canton Corporation is a privately owned firm that engages in the production and sale of industrial chemicals, primarily in North America. The firm's primary product line consists of organic solvents and intermediates for pharmaceutical, agricultural, and chemical products. Canton's managers have recently been considering the possibility of taking the company public and have asked the firm's investment banker to perform some preliminary analysis of the value of the firm's equity. To support its analysis, the investment banker has prepared pro forma financial statements for each the next four years under the (simplifying) assumption that firm sales are flat (i.e., have a zero rate of growth), the corporate tax rate equals 30%, and capital expenditures are equal to the estimated depreciation expense. Canton Corporation Financials 0 Current assets Property, plant, and equipment Total Accruals and payables Long-term debt Equity Total $ 15,000 40.000 $ 55,000 $ 5,000 25,000 25,000 $ 55,000 Pro Forma Balance Sheets (5000) 1 2 3 $ 15,000 $ 15,000 $ 15,000 40,000 40,000 40,000 $ 55.000 $ 55,000 $ 55,000 $ 5,000 $ 5,000 $ 5,000 25,000 25,000 25.000 25,000 25,000 25,000 $ 55,000 $ 55,000 $ 55,000 4 $ 15,000 40,000 $ 55,000 $ 5.000 25.000 25,000 $ 55,000 Pro Forma Income Statements (5000) 1 2 3 4 $ 100,000 $ 100,000 $ 100,000 $ 100,000 (40,000) (40,000) (40,000) (40,000) $ 60,000 $ 60,000 $ 60,000 $ 60,000 Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Operating expenses (excluding depreciation) Depreciation expense Operating income (earnings before interest and taxes) Less: interest expense Earnings before taxes Less: taxes Net income (30,000) (8,000) $ 22,000 (30,000) (8,000) $ 22,000 (30,000) (8,000) $ 22,000 (30,000) (8,000) $ 22,000 (2.000). $ 20,000 (6,000) $ 14,000 (2.000) $ 20,000 (6,000) $ 14,000 (2.000) $ 20,000 (6,000) $ 14,000 (2,000) $ 20,000 (6,000) $ 14,000 In addition to the financial information on Canton, the investment banker has as- sembled the following information concerning current rates of return in the capital market: The current market rate of interest on ten-year Treasury bonds is 7%, and the mar- ket risk premium is estimated to be 5%. Canton's debt currently carries a rate of 8%, and this is the rate the firm would have to pay for any future borrowing as well. Using publicly traded firms as proxies, the estimated equity beta for Canton is 1.60. a. What is Canton's cost of equity capital? What is the after-tax cost of debt for the firm? b. Calculate the equity free cash flows for Canton for each of the next four years. Assuming that equity free cash flows are a level perpetuity for year 5 and beyond, estimate the value of Canton's equity. (Hint: Equity value is equal to the present value of the equity free cash flows discounted at the levered cost of equity.) If the market rate of interest on Canton's debt is equal to the 8% coupon, what is the cur- rent market value of the firm's debt? What is the enterprise value of Canton? (Hint: Enterprise value can be estimated as the sum of the estimated values of the firm's interest-bearing debt plus equity.) c. Using the market values of Canton's debt and equity calculated in Problem 9-56b), 9-4(b) calculate the firm's after-tax weighted average cost of capital. Hint: kwacc (1 - ) Cost of Tax Debt Value - Debt Rate Cost of Equity Value Levered Equity Enterprise Value d. What are the FCFs for Canton for years 1 through 4? e. Estimate the enterprise value of Canton using the traditional WACC model. Base your estimate on your previous answers, and assume that the FCFs after year 4 are a level perpetuity equal to the year 4 FCF. How does your estimate compare to your earlier estimate using the sum of the values of the firm's debt and equity? f. Based on your estimate of enterprise value, what is the value per share of equity for the firm if the firm has 2 million shares outstanding? Remember that your calculations up to this point have been in thousands of dollars. 9-6 ENTERPRISE VALUATION-APV MODEL This problem uses the information from Problem 9-4 about Canton Corporation to estimate the firm's enterprise value using the APV model. a. What is the firm's unlevered cost of equity? (Hint: The firm's debt beta is.20) b. What are the unlevered FCFs for Canton for years 1 through 4? (Hint: The unle- 1 vered FCFs are the same as the firm FCFs.) c. What are the interest tax savings for Canton for years 1 through 4? d. Assuming that the firm's future cash flows from operations (i.e., its FCFs) and its interest tax savings are level perpetuities for year 5 and beyond that equal their year 4 values, what is your estimate of the enterprise value of Canton? e. Based on your estimate of enterprise value, what is the value per share of equity for the firm if the firm has 2 million shares outstanding? Remember that your calcula- tions up to this point have been in thousands of dollars. Problem 9-4: Traditional WACC Valuation Given Solution Legend Debt beta 0.20 - Value given in problem Levered equity beta 1.60 = Formula/Calculation Analysis required Market Risk Premium 5% - Qualitative analysis or Short answer requl Risk free rate 7% = Goal Seek or Solver coll 8% Borrowing rate (before tax) = Crystal Ball Input Number of common shares 2.000 - Crystal Ball Output 1 Tax rate 30% 2 3 4 5 6 Solution 7 a. What is Canton's cost of equity capital? What is the after-tax cost of debt for the firm? 8 After-tax cost of debt 9 Lovered cost of equity 20 1 b. Calculate the equity free cash flows for Canton for each of the next four years, 22 Years 23 2 24 Sales $ 100,000.00 $ 100,000.00 $ 100,000.00 $ 100,000.00 25 Operating income (Eaminas Before Interest and Taxes) 22,000.00 22,000.00 22,000.00 22,000.00 26 Less Cash tax payments 27 Net operating profits after taxes (NOPAT) 28 Plus: Depreciation expense $ 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 29 Loss Investments 30 in Not Working Capital 31 in new Capital (CAPEX) 32 Firm free cash flow (FCF) 33 34 Equity Free Cash Flow Calculation 35 (Fin) Free Cash Flow 36 Loss Interest (1 . Tax Rate) 37 (Equity) Free Cash Flow 38 39 Debt Valuation 40 Present value of interest for Years 1-4 41 Present value of principal in Year 4 42 Debt Value 43 Equity Valuation 44 Present value of EFCFs for Years 1-4 45 Present value of EFCFs for Years 5 and beyond Equity Valve 47 Enterprise Value - Debt value + Equity value 48 49. Using the market values of Canton's debt and equity and the after tax cost of capital calaulate its WAGG 50 46 Years 2 100,000.00 $ 22,000.00 $ 100,000.00 $ 22,000.00 3 100,000.00 $ 22,000.00 100,000.00 22,000.00 $ 8,000.00 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 $ 8,000.00 $ Sales Operating income (Eamings Before Interest and Taxes) Less: Cash tax payments Net operating profits after taxes (NOPAT) Plus: Depreciation expense Less: Investments in Net Working Capital in new Capital (CAPEX) Firm free cash flow (FCF) 3 Equity Free Cash Flow Calculation (Firm) Free Cash Flow Less: Interest x (1 - Tax Rate) (Equity) Free Cash Flow Product Debt Valuation Present value of interest for Years 1-4 Present value of principal in Year 4 Debt Value Equity Valuation Present value of EFCFs for Years 1-4 Present value of EFCFs for Years 5 and beyond Equity Value Enterprise Value = Debt value + Equity value 3 c. Using the market values of Canton's debt and equity and the after-tax cost of capital calaulate its WACC. 0 Market Value Proportion After-Tax Cost 1 Long-term Debt 2 Equity 3 Total 4 -5 d. What are the firm free cash flows for Canton for years 1-4? 6 See the answer to part b above. 37 58 e. Estimate the enterprise value of Canton using the Traditional WACC method 59 Present value of fimm free cash flows: 50 Planning horizon (4 years) 51 Residual value 52 In year 4 63 Today 64 Enterprise Value = Value of invested capital 65 66 r. What is the value per share of equity for Canton? 67 Enterprise Value 68 Less: Debt 69 Equals: Shareholder value 70 No. of shares (000) 71 Value per share 72 73 25,000.00 2,000 Problem 9-6: APV Valuation a. Computing Canton's unlevered cost of equity Risk free rate Market risk premium Levered equity beta Debt bota Unlevered beta Unlevered cost of equity 7% 5% 1.60 0.20 To unlever the equity beta where the level of debt is fixed (as in this case) and debt is assumed to have a beta of zero, we solve the following equation: Be + Bp (1 - 1) Bu [1 + (1 - ) 2 b. Unlevered FCFs for Years 1-4 Unlevered FCFS #Firm FCFS (Firm) Free Cash Flow c. Interest Tax Savings = Interest Expense x Tax Rate d. Estimated APV Present value of Unlevered FCFs Present value of Interest Tax Savings Estimated APV e. Estimated per share value APV (firm value) less: Debt Equals: Shareholder value No. of shares (000) Value per share S (25,000.00) 2,000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


