Question: Capillary rise (10 points) Two identical flat macroscopic surfaces 2.5 cm high and 7.5 cm long (i.e. microscope slides) are chemically modified with hydrophobic silane
Capillary rise (10 points) Two identical flat macroscopic surfaces 2.5 cm high and 7.5 cm long (i.e. microscope slides) are chemically modified with hydrophobic silane in such way that the left half of the plane is fully wetting (contact angle, = 0 degree) and the right half is non-wetting ( = 110 degree). The two surfaces are placed parallel facing each other (that is, the wetting half on one microscope slide faces the other slide wetting half, see figure below) and are to be immersed at the right angle in the water ( = 72 mN/m; density = 988 kg/m3) so that the lower edges of the plates are parallel with the water surface (see figure below). Calculate the optimal separation distance between the two plates and the depth of immersion at which the measurement of capillary rise and capillary depression would utilize the full height of the plate (2.5 cm) (in other words, magnitudes of capillary rise and capillary depresion should sum up to 2.5 cm). Neglect the weights of menisci. Also, neglect what happens at the area between wetting and non-wetting regions and at each end of the plates.
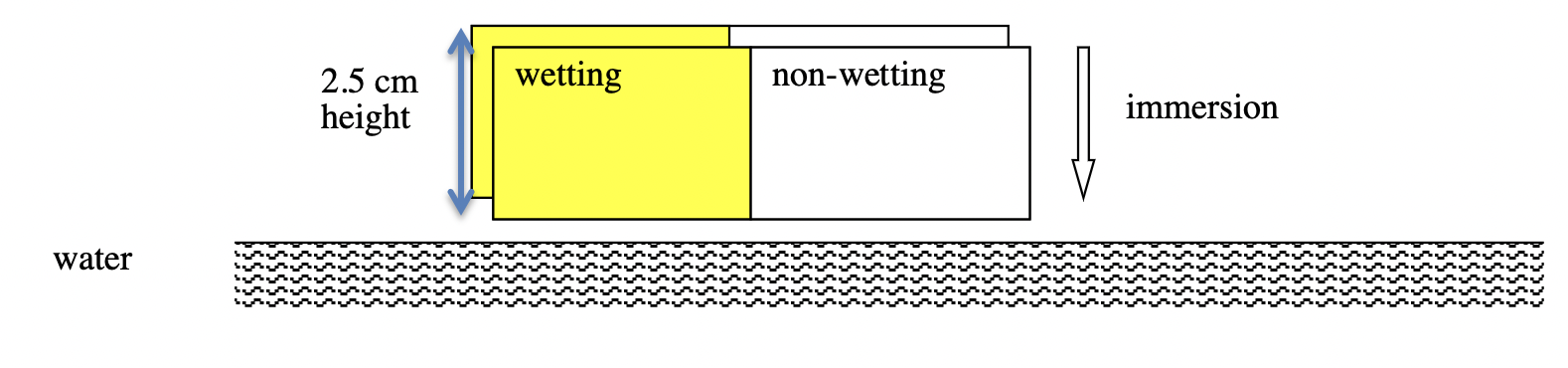
2.5 cm wetting non-wetting height immersion water
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


