Question: Carlo integration The aim here is to write a function to estimate integrals over rectangles in any number of variables (dimensions) via the Monte Carlo

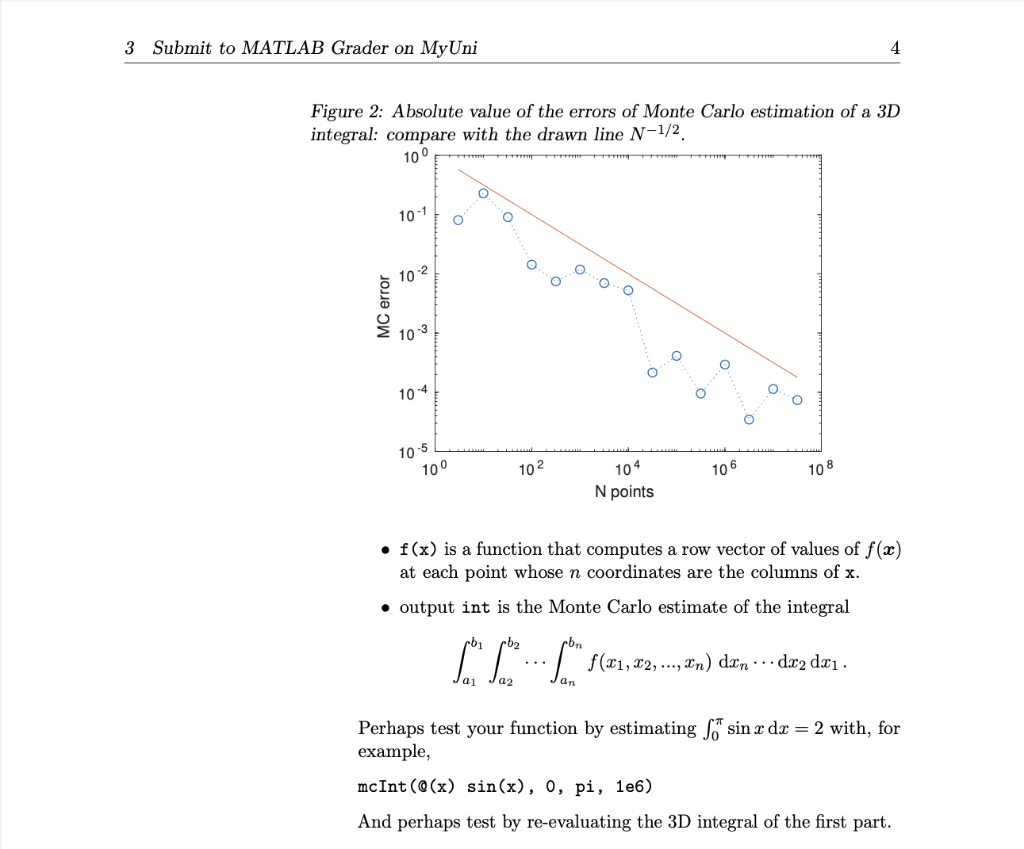
Carlo integration The aim here is to write a function to estimate integrals over rectangles in any number of variables (dimensions) via the Monte Carlo method. 1. Consider the 3D Example 4.6 (p.133) by Quarteroni, Saleri \& Gervasio et al. (2014), I3D=010101sin(x)cos(y)sin(z)dxdydz, which has exact value zero. Write a script that uses the Monte Carlo method to estimate the value of the integral (2.1). The script mcsin.m on MyUni might be a good place to start. Your script should: (a) Estimate the integral for N=10k/2 points, where k= 1,2,,15. (b) Store the xyz-coordinates of each random point in each column of a 3N array (in part 2 you will extend this to d variables, in which case you will create a dN array). (c) Vectorize the Monte Carlo code as it is "embarrassingly parallel". (d) Create a log-log plot of the error, including the line N1/2 for comparison, as in Figure 2. 2. Now adapt your script to create a function function int =mcInt(f,a,b,N) that computes a Monte Carlo estimate of a multi-dimensional integral of the supplied function f. - N is the number of random points to use. - a and b are column vectors, say of length n : the i th components delimit the domain of the integral in the i th variable, ai xibi. Figure 2: Absolute value of the errors of Monte Carlo estimation of a 3D integral: compare with the drawn line N1/2. - f(x) is a function that computes a row vector of values of f(x) at each point whose n coordinates are the columns of x. - output int is the Monte Carlo estimate of the integral a1b1a2b2anbnf(x1,x2,,xn)dxndx2dx1 Perhaps test your function by estimating 0sinxdx=2 with, for example, mcInt(@(x)sin(x),0, pi, 1e6) And perhaps test by re-evaluating the 3D integral of the first part. Carlo integration The aim here is to write a function to estimate integrals over rectangles in any number of variables (dimensions) via the Monte Carlo method. 1. Consider the 3D Example 4.6 (p.133) by Quarteroni, Saleri \& Gervasio et al. (2014), I3D=010101sin(x)cos(y)sin(z)dxdydz, which has exact value zero. Write a script that uses the Monte Carlo method to estimate the value of the integral (2.1). The script mcsin.m on MyUni might be a good place to start. Your script should: (a) Estimate the integral for N=10k/2 points, where k= 1,2,,15. (b) Store the xyz-coordinates of each random point in each column of a 3N array (in part 2 you will extend this to d variables, in which case you will create a dN array). (c) Vectorize the Monte Carlo code as it is "embarrassingly parallel". (d) Create a log-log plot of the error, including the line N1/2 for comparison, as in Figure 2. 2. Now adapt your script to create a function function int =mcInt(f,a,b,N) that computes a Monte Carlo estimate of a multi-dimensional integral of the supplied function f. - N is the number of random points to use. - a and b are column vectors, say of length n : the i th components delimit the domain of the integral in the i th variable, ai xibi. Figure 2: Absolute value of the errors of Monte Carlo estimation of a 3D integral: compare with the drawn line N1/2. - f(x) is a function that computes a row vector of values of f(x) at each point whose n coordinates are the columns of x. - output int is the Monte Carlo estimate of the integral a1b1a2b2anbnf(x1,x2,,xn)dxndx2dx1 Perhaps test your function by estimating 0sinxdx=2 with, for example, mcInt(@(x)sin(x),0, pi, 1e6) And perhaps test by re-evaluating the 3D integral of the first part
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


