Question: Case context In Australia, activity - based funding ( ABF ) is used to fund the healthcare system, where hospitals receive payment based on the
Case context
In Australia, activitybased funding ABF is used to fund the healthcare system, where hospitals
receive payment based on the number and type of patients they treat. Hospitals are funded more if
they treat a higher volume of patients. ABF also adjusts for the complexity of cases, recognising that
some patients are more complicated to treat than others. Activitybased costing ABC is an essential
component of ActivityBased Funding ABF This costing method identifies the activities within an
organisation and allocates the costs of each activity to the products andor services based on their
actual resource consumption.
Given the increasing costs of patient care in Westmead Hospital in Sydney, New South Wales,
Jenelle Perera General Manager of Westmead Hospital called for a strategy meeting. At the
meeting, she requested the current Director of Finance and Performance, Preet Matic, to carry out an
ABC study to determine the costs for different types of cardiology patients. The cardiology unit at
the Westmead Hospital is one of the busiest departments within the state hospital with high resource
usage.
The current costing system treats all cardiology patients as requiring the same type of patient care,
allocating costs based on a single cost driver number of patient days. However, the management
and accounting teams know that some patients with complicated cardiac surgeries require more
intensive care than patients who require basicnormal care. Thus, there is a belief within the hospital
that the current costing system does not provide an accurate indication of resources consumed by
different types of cardiology patients.
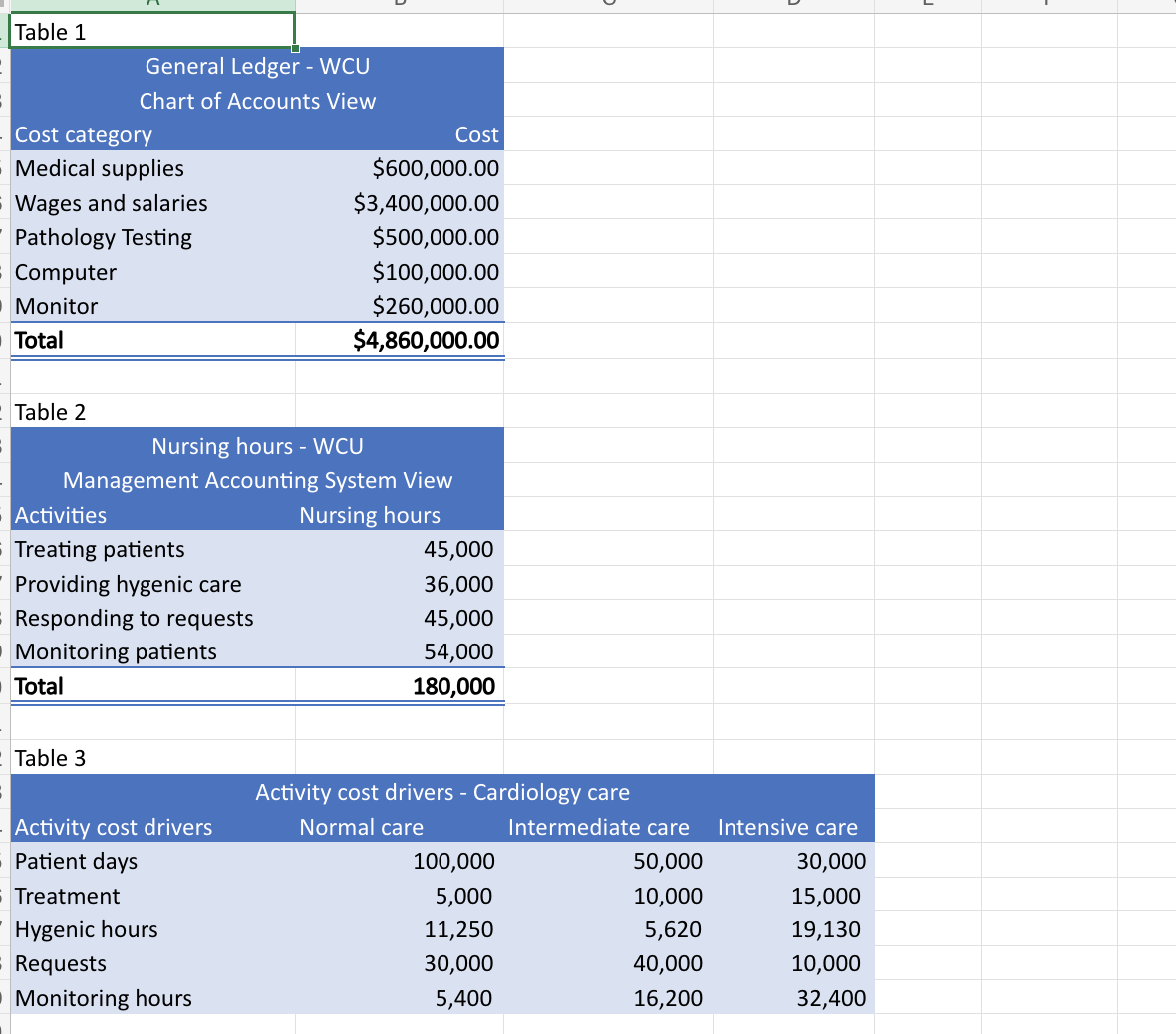
After the meeting, Preet began work on designing an activitybased costing system for Westmead
Cardiology Unit hereafter WCU Based on her analysis of the annual figures from the previous year
in the general ledger, she first identified five main cost categories see Table She then recalled,
from her accounting studies at UTS, that there were six main steps in implementing an ABC system:
Identify the relevant cost object
Identify activities
Assign costs to activitybased cost pools
For each ABC cost pool, choose a cost driver
For each ABC cost pool, calculate a cost driver rate
For each ABC cost pool, allocated activity costs to the cost objects
She decided to split the steps into two stages. Stage would include identifying and classifying
activities and then determining the cost of each activity Steps to Stage would require the
identification of activity drivers, an activity rate for each activity and finally calculating and
allocating the consumption of activities by cost objects Step to
To accomplish Stage Preet conducted an interview with the WCU nursing manager, David Lam.
The interview transcript is provided in Appendix After the interview, Preet extracted key
information she required for the ABC system from the hospitals Management Accounting System
MAS and placed them into Table which provides information about the previous years nursing
hours used by each of the four activity centres identified during the interview. She also gathered
information about the total annual estimates of the activity cost drivers and the three different patient
types that she hoped she could use for WCUs ABC system see Table Table
Table
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


