Question: Case - Low Nail Company After making some wise short-term investments at a race track, Chris Low had some additional cash to invest in a
Case - Low Nail Company After making some wise short-term investments at a race track, Chris Low had some additional cash to invest in a business. The most promising opportunity at the time was in building supplies, so Low bought a business that specialized in sales of one size of nail. The annual volume of nails was 2,200 kegs, and they were sold to retail customers in an even flow. Low was uncertain how many nails to order at any time. Initially, only two costs concerned him: order-processing costs, which were $52 per order without regard to size, and warehousing costs, which were $1.52 per year per keg space. This meant that Low had to rent a constant amount of warehouse space for the year, and it had to be large enough to accommodate an entire order when it arrived. Low was not worried about maintaining safety stocks, mainly because the outward flow of goods was so even. Low bought his nails on a delivered basis. Questions
1. Using the EOQ methods outlined in the chapter, how many kegs of nails should Low order at one time? Compute the corresponding Orders per year, Annual processing cost, Annual warehousing cost, and the Total inventory-related cost.
2. Assume all conditions in Question 1 hold, except that Lows supplier now offers a quantity discount in the form of absorbing all or part of Lows order-processing costs. For orders of 750 or more kegs of nails, the supplier will absorb all the order-processing costs; for orders between 250 and 749 kegs, the supplier will absorb half. Use the provided cost table to estimate Lows new EOQ. Should he take the full rebate? Should he take the partial rebate? Should he avoid the rebate? Compare the savings in Total inventory-related costs from #1 to convince Mr. Low of your recommendation.
3. Temporarily, ignore your work on Question 2. Assume that Lows warehouse offers to rent Low space on the basis of the average number of kegs Low will have in stock, rather than on the maximum number of kegs Low would need room for whenever a new shipment arrived. The storage charge per keg remains the same. Does this change the answer to Question 1? If so, what is the new answer? Should Mr. Low take the new warehouse offer? What is your new recommendation for EOQ? Compare the savings in Total inventory-related costs from #1 to convince Mr. Low of your recommendation.
4. Take into account the answer to Question 1 and the suppliers new policy outlined in Question 2 and the warehouses new policy in Question 3. What is your new recommendation for EOQ? Convince Mr. Low to take the supplier rebate, new warehouse offer, both or neither.
5. Temporarily, ignore your work on Questions 2, 3, and 4. Lows luck at the race track is over; he now must borrow money to finance his inventory of nails. Looking at the situation outlined in Question 1, assume that the wholesale cost of nails is $42 per keg and that Low must pay interest at the rate of 1.3% per month on unsold inventory. What is his new EOQ and how has his Total inventory costs changed? Discuss how this situation is different from when you used company cash-on-hand to purchase inventory in the past.
6. Taking into account all the factors listed in Questions 1, 2, 3, and 5, calculate Lows EOQ for kegs of nails. Given the new Cost of Capital, should Mr. Low still take t rebate and new warehouse offer? How much do these now save him? he supplier Which of these 6 EOQs Murphy, P . are correct? What is your final recommendation to 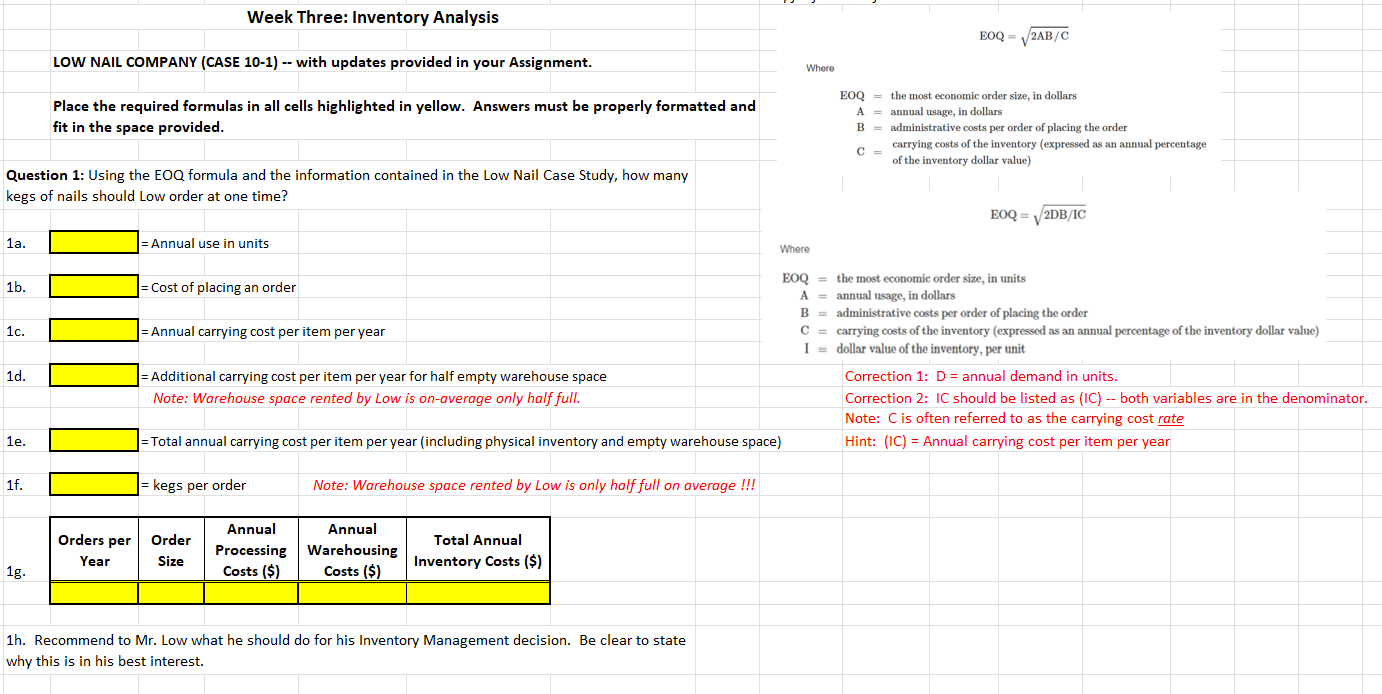
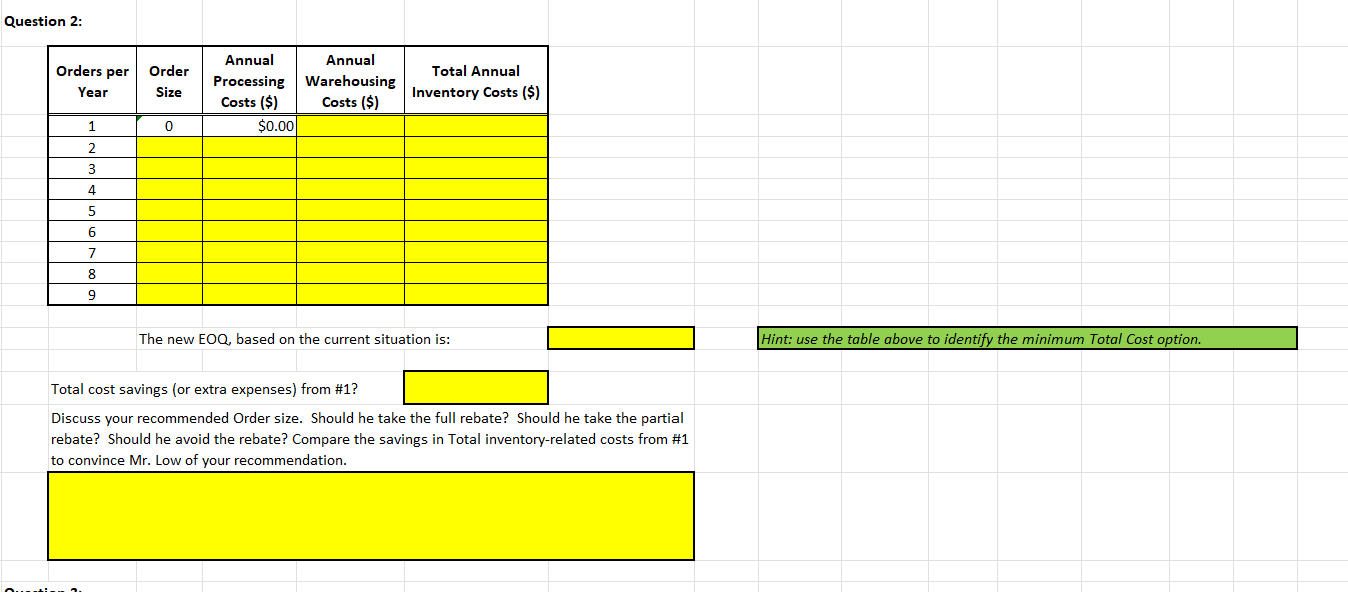
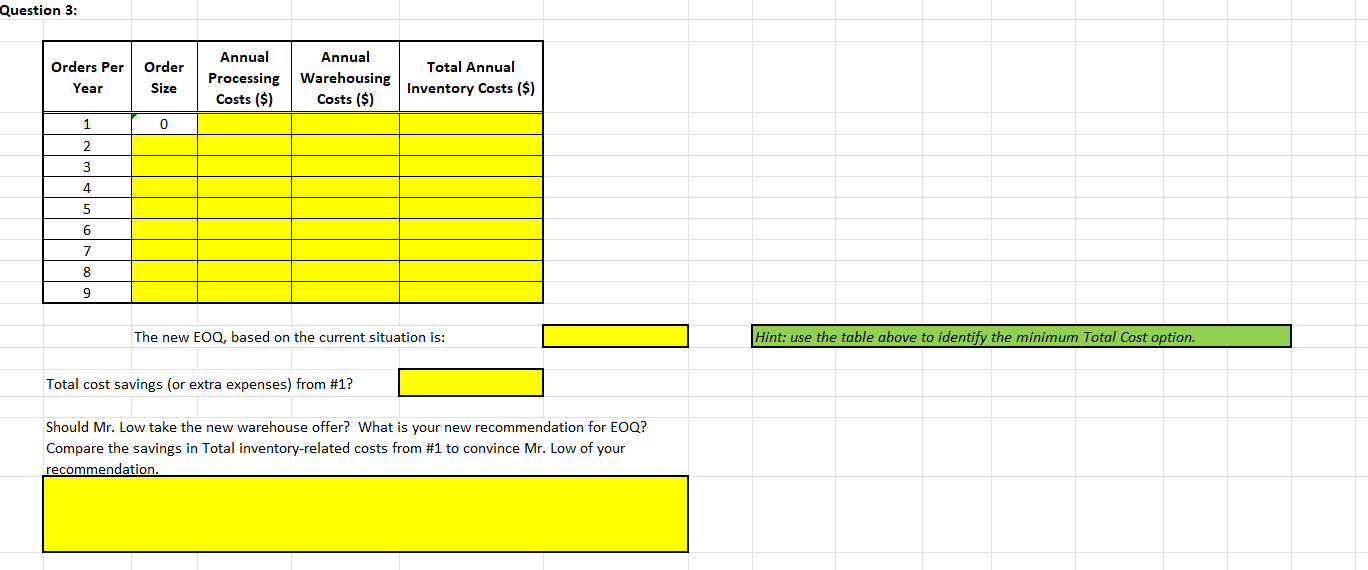
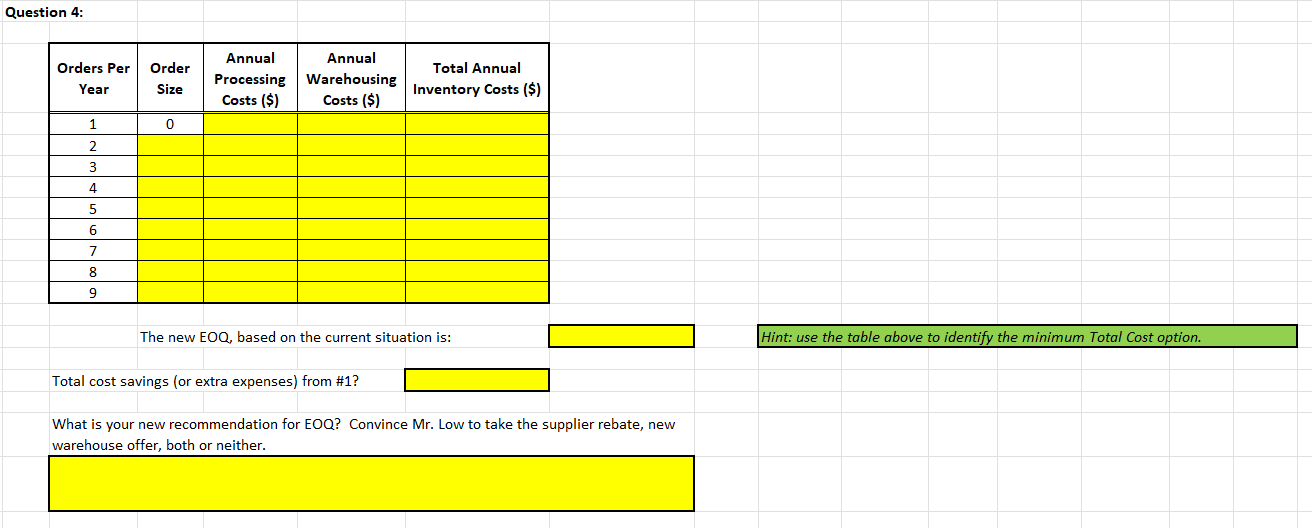
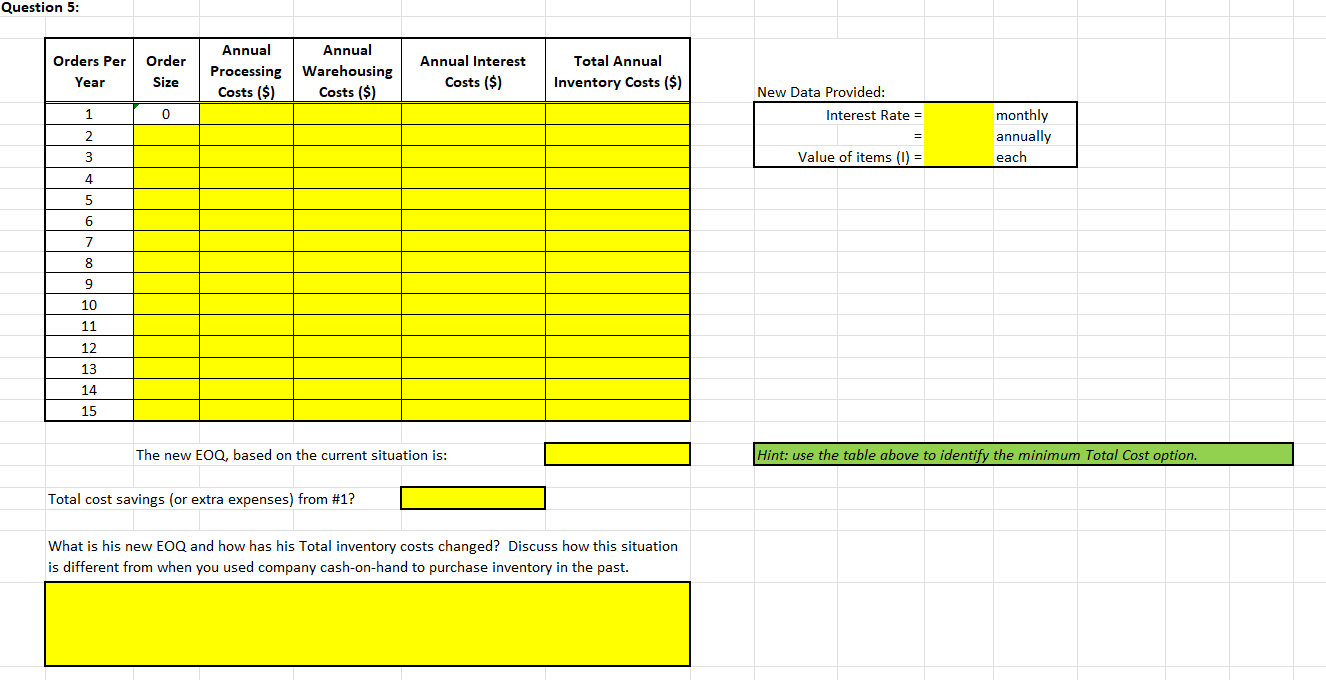
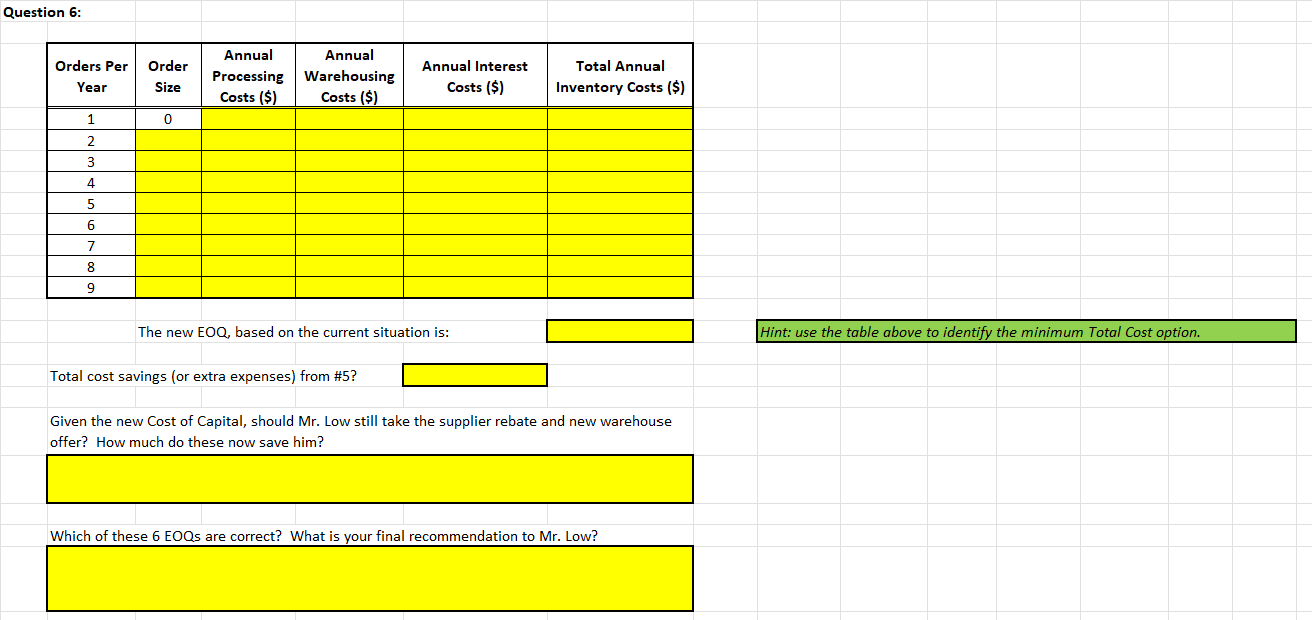
Week Three: Inventory Analysis EOQ - 2AB/C LOW NAIL COMPANY (CASE 10-1) -- with updates provided in your Assignment. Where Place the required formulas in all cells highlighted in yellow. Answers must be properly formatted and fit in the space provided. EOQ = the most economic order size, in dollars A = annual usage, in dollars B = administrative costs per order of placing the order carrying costs of the inventory (expressed as an annual percentage of the inventory dollar value) CE Question 1: Using the EOQ formula and the information contained in the Low Nail Case Study, how many kegs of nails should Low order at one time? EOQ = 2DB/IC 1a. Annual use in units Where 1b. 1c. EOQ = the most economic order size, in units Cost of placing an order A = annual usage, in dollars B = administrative costs per order of placing the order = Annual carrying cost per item per year C = carrying costs of the inventory (expressed as an annual percentage of the inventory dollar value) I = dollar value of the inventory, per unit - Additional carrying cost per item per year for half empty warehouse space Correction 1: D = annual demand in units. Note: Warehouse space rented by Low is on-average only half full. Correction 2: IC should be listed as (IC) -- both variables are in the denominator. Note: C is often referred to as the carrying cost rate Total annual carrying cost per item per year (including physical inventory and empty warehouse space) Hint: (C) = Annual carrying cost per item per year 1d. 1e. 1f. kegs per order Note: Warehouse space rented by Low is only half full on average !!! Orders per Order Size Annual Processing Costs ($) Annual Warehousing Costs ($) Year Total Annual Inventory Costs ($) 1g. 1h. Recommend to Mr. Low what he should do for his Inventory Management decision. Be clear to state why this is in his best interest. Question 2: Orders per Year Order Size Annual Annual Processing Warehousing Costs ($) Costs ($) $0.00 Total Annual Inventory Costs ($) 1 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The new EOQ, based on the current situation is: Hint: use the table above to identify the minimum Total Cost option. Total cost savings (or extra expenses) from #1? Discuss your recommended Order size. Should he take the full rebate? Should he take the partial rebate? Should he avoid the rebate? Compare the savings in Total inventory-related costs from #1 to convince Mr. Low of your recommendation. Question 3: Orders Per Year Order Size Annual Annual Processing Warehousing Costs ($) Costs ($) Total Annual Inventory Costs ($) 1 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The new EOQ, based on the current situation is: Hint: use the table above to identify the minimum Total Cost option. Total cost savings (or extra expenses) from #1? Should Mr. Low take the new warehouse offer? What is your new recommendation for EOQ? Compare the savings in Total inventory-related costs from #1 to convince Mr. Low of your recommendation Question 4: Orders Per Year Order Size Annual Processing Costs ($) Annual Warehousing Costs ($) Total Annual Inventory Costs ($) 1 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The new EOQ, based on the current situation is: Hint: use the table above to identify the minimum Total Cost option. Total cost savings (or extra expenses) from #1? What is your new recommendation for EOQ? Convince Mr. Low to take the supplier rebate, new warehouse offer, both or neither. Question 5: Orders Per Year Order Size Annual Annual Processing Warehousing Costs ($) Costs ($) Annual Interest Costs ($) Total Annual Inventory Costs ($) New Data Provided: Interest Rate = 0 1 2 3 monthly annually each Value of items (1) = 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 The new EOQ, based on the current situation is: Hint: use the table above to identify the minimum Total Cost option. Total cost savings (or extra expenses) from #1? What is his new EOQ and how has his Total inventory costs changed? Discuss how this situation is different from when you used company cash-on-hand to purchase inventory in the past. Question 6: Annual Interest Orders Per Year Order Size Annual Annual Processing Warehousing Costs ($) Costs ($) Costs ($) Total Annual Inventory Costs ($) 1 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The new EOQ, based on the current situation is: Hint: use the table above to identify the minimum Total Cost option. Total cost savings (or extra expenses) from #5? Given the new Cost of Capital, should Mr. Low still take the supplier rebate and new warehouse offer? How much do these now save him? Which of these 6 EOQs are correct? What is your final recommendation to Mr. Low









