Question: Case Problem Some Financial Ratios Are Real Eye-Openers Jack Arnold is a resident of Lubbock, Texas, where he is a prosperous rancher and businessman. He
Case Problem
Some Financial Ratios Are Real Eye-Openers
Jack Arnold is a resident of Lubbock, Texas, where he is a prosperous rancher and businessman. He has also built up a sizable portfolio of common stock, which, he believes, is due to the fact that he thoroughly evaluates each stock he invests in. As Jack says, You cant be too careful about these things! Anytime I plan to invest in a stock, you can bet Im going to learn as much as I can about the company. Jack prefers to compute his own ratios even though he could easily obtain analytical reports from his broker at no cost. (In fact, Bob Smith, his broker, has been volunteering such services for years.) Recently Jack has been keeping an eye on a small chemical stock. The firm, South Plains Chemical Company, is big in the fertilizer businesswhich is something Jack knows a lot about. Not long ago, he received a copy of the firms latest financial statements (summarized here) and decided to take a closer look at the company.

Questions
a. Using the South Plains Chemical Company figures, compute the following ratios.
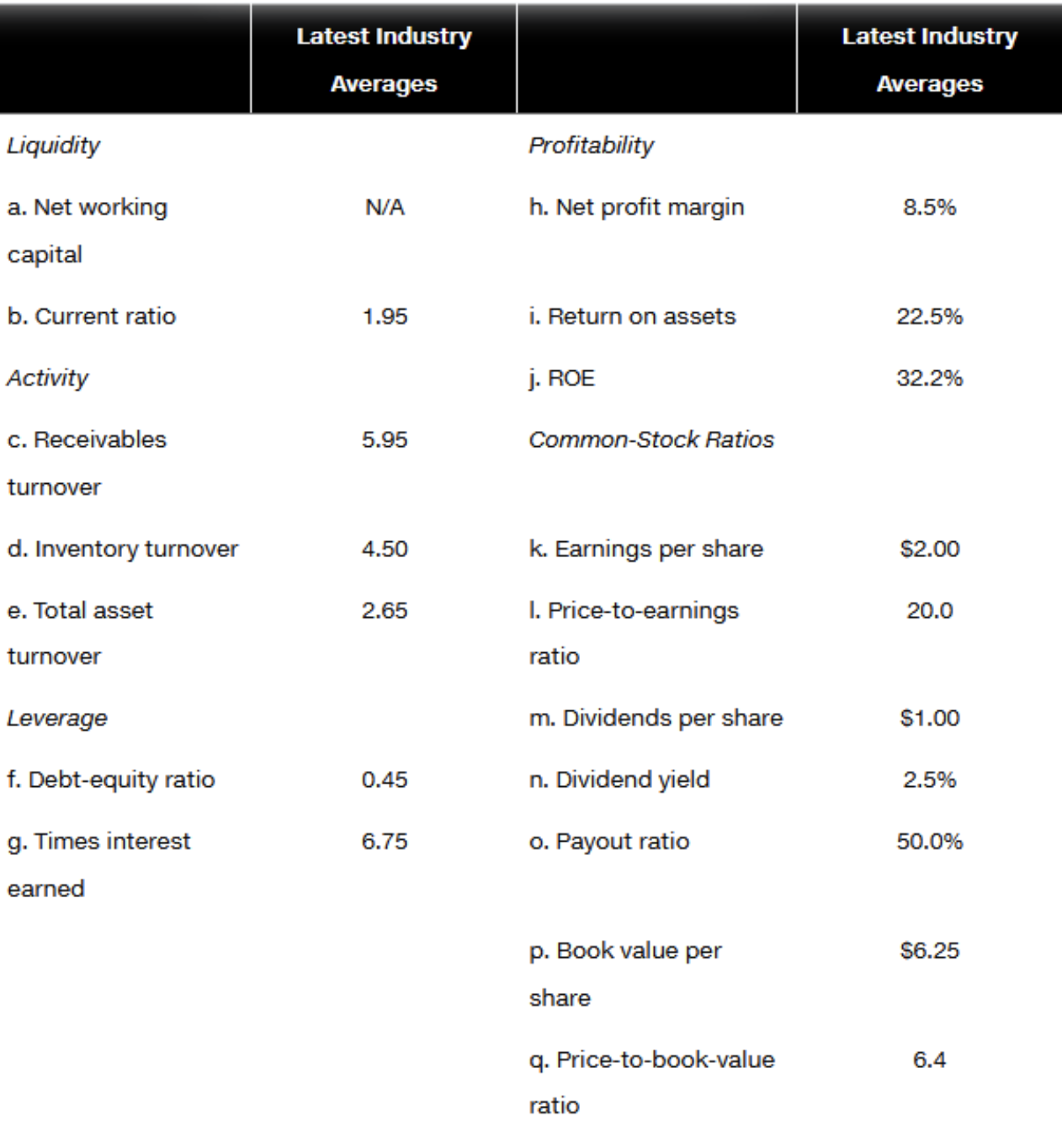
b. Compare the company ratios you prepared to the industry figures given in part a. What are the companys strengths? What are its weaknesses? c. What is your overall assessment of South Plains Chemical? Do you think Jack should continue with his evaluation of the stock? Explain.
South Plains Chemical Company Balance Sheet (\$ thousands) \begin{tabular}{lrlr} Cash & $1,250 & & \\ Accounts receivable & $8,000 & Current liabilities & $10,000 \\ Inventory & $12,000 & Long-term debt & $8,000 \\ Current assets & $21,250 & Stockholders' equity & $12,000 \\ \hline Fixed and other assets & $8,750 & Total liabilities and & \\ \hline Total assets & $30,000 & stockholders' equity & $30,000 \\ \hline \end{tabular} South Plains Chemical Company Income Statement (\$ thousands) Sales Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Operating profit Interest expense Taxes Net profit Dividends paid to common stockholders (\$ in thousands) Number of common shares outstanding Recent market price of the common stock $50,000 $25,000 \begin{tabular}{c} $15,000 \\ \hline$10,000 \\ $2,500 \\ $2,500 \\ \hline$5,000 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} $1,250 5 million $25 Latest Industry Averages Liquidity a. Net working capital b. Current ratio Activity c. Receivables turnover d. Inventory turnover e. Total asset turnover Leverage f. Debt-equity ratio g. Times interest earned Latest Industry Averages Profitability h. Net profit margin 8.5% 1.95 i. Return on assets 22.5% j. ROE 32.2% 5.95 Common-Stock Ratios 4.50 k. Earnings per share $2.00 2.65 I. Price-to-earnings 20.0 ratio m. Dividends per share $1.00 n. Dividend yield 2.5% o. Payout ratio 50.0% p. Book value per $6.25 share q. Price-to-book-value 6.4 ratio
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


