Question: CASE STUDY The company analyzed in this study is SSS-ZZZ, an associated work co-operative belonging to Spains Mondragon Co-operative Corporation (the MCC). The MCC can
CASE STUDY
The company analyzed in this study is SSS-ZZZ, an associated work co-operative belonging to Spains Mondragon Co-operative Corporation (the MCC). The MCC can be considered as the world leader in co-operative working. It is made up of more than 100 co-operatives of associated businesses and employs over 42,000 workers.
SSS-ZZZ is a firm devoted to the assembly of luxury coaches. It has seen spectacular growth over the last few years (see Table 1); especially noteworthy has been its growth in average productivity of 18.4% in the 19932000 period. The firm currently has 634 workers in its Ormaiztegui factory (in the Spanish Basque country). It exports to 45 countries and has shareholdings in five other companies: SSS-ZZZ Tianjin (35%); SSS-ZZZ Maghreb (34%); Irizar Brasil (100%); SSS-ZZZ Mexico (100%) and International Hispacold (65%). It assembles six coaches every day and has a 33% share in the Spanish market with a further ten companies sharing the rest.
Table 1. Some figures for SSS-ZZZ
| Number of workers (9100) | 225 | 634 |
| Sales (9199) | $15 million | $103 million |
| Sales per person (9199) | $55,000 | $165,000 |
| Added value per | $14,000 | $61,500 |
| person (9199) Maturity time (9199) | 38 days | 14 days |
| Production rate (9300) | 1.2 coaches/ 6 coaches/ day day | |
Within its sector, it ranks first in Spain and third in Europe. Sales of luxury coaches in the European market are around 10,000 units/year, but only seven companies sell more than 600 units/year. Furthermore, the sector is strongly concentrated as a result of agreements between the bodywork and chassis makers for both coaches and trucks (Mercedes, Volvo and Scania).
SSS-ZZZ can be considered as an innovator in products, processes and in general management, where it is successful in its field. For the Economist Intelligence Unit, SSS-ZZZ is probably now the most efficient coach builder in the world (EIU, 2000: 172). These facts justify the study of the KM strategy implementation process and the factors which have made it successful.
Strategic change at SSS-ZZZ: the organizations mission and values
The KM strategy implementation began at SSS-ZZZ in 1991, a moment in which the firm was in a critical situation, having accumulated major losses almost to the point of bankruptcy. Given the situation, the new management decided, with the support of all the workers, to carry out an emergency plan. This involved changing the strategy of the firm, diversifying markets in order to succeed in a global market and focusing only on the assembly of luxury coaches (they had previously produced urban buses also).
The implementation process was supported through a global change focused on the building of a strong culture, in which all the members of the organization were to be involvedthis led to the definition of the process as a project based on people. The firms management tried to encourage the acceptance throughout the organization of some cultural principlesthese have been reinforced over time
- considered to be basic requirements of competitiveness. The effort made to obtain ISO 9001 quality certification should be emphasized; SSS-ZZZ was the first European luxury coachmaker to obtain this qualification.
- 19941997: Radical changes in the organization. A strategic reflection period took place in this year, which gave rise to the introduction of a reengineering model. The model involved a redesign of processes, and changes to the vertical and horiziontal organization charts: all work was to be organized in multi-disciplinary teams, with wide autonomy and limited supervision. The work teams periodically set objectives relating to productivity, quality, compliance with customer deadlines and other operative improvements. The strategy has made it possible to achieve compatability between incremental changes and radical improvements in a re-engineering model.
KM and innovation came to form part of the companys strategic objectives. Use of knowledge storage and distribution systems (such as databases) was generalized and major improvements were obtained at the operational level, together with significant increases in all the sales, profitability and efficiency indicators. This has continued since then.
From 1995, SSS-ZZZ adopted the EFQM (European Fundation for Quality Management) Model for Excellence, based on participation, innovation and learning. This serves as a model for the detection of improvement opportunities via overall external evaluations and detailed self-evaluation. The efforts made at the company over this period have been recognized by the receipt of a number of national and international awards.
- 19982000: Expansion of Irizar and recognition of itys work. Starting in 1998, Irizar created a business group, comprising SSS-ZZZ. Coop, with its headquarters in Spain, SSS-ZZZ Tianjin (China), SSS-ZZZ Magreb (Morocco), SSS-ZZZ Brazil and SSS-ZZZ Mexico, with a shareholding in International Hispacold, all to be able to service the growing demand in these markets.
At the same time, a systematic application of KM was put in place to establish a continuous improvement process and ensure results in the creation phases and application of the new knowledge. The achievements obtained were major, radical improvements, the development of innovations and the creation of new knowledge. The company has been in this position since 1994.
The companys work in this period was recognized by the winning of numerous prizes and awards, including ISO 14001 certification for the Environmental Management system and the maximum EFQM qualification, among others.
To reach the levels proposed by the model, different systems, practices and tools were used, related to the strategy and core features and surrounding conditions of the firm. One of the most important of these was organization of the work into teams.
Changes in work organization: multidisciplinary teams
In order to carry out its proposed strategy, SSS-ZZZ introduced major changes to its work organization, in line with a model for re-engineering based in multidisciplinary and self-management teams. This organization of work has been essential in the evolution of the firm. The work teams are understood as systems for the creation and distribution of explicit and tacit knowledge, and their functions are closely related to different stages of KM.
The organizational structure of SSS-ZZZ is built around a group of working teams. A static chart is first set up, built around a group of teams with specific tasks which remain the same for a long time, in which all the workers are included. This coexists with a dynamic chart, which includes another group of teams devoted to support jobs for the strategic objectives; their working method is much more agile, to adapt to the improvement needs required in any given situation. In addition, the work is divided into processes, including a core selfmanagement process in which more than 90% of workers take part, together with customers and suppliers. Everybody is involved in different working teams which have relations with their surrounding entities and which manage the whole process, from receipt of a customer order to the delivery of the vehicle. All are inter-related. The work teams which have been created and active from 1994 are shown in Figure 1.
The people working in the teams have more generalized skills, are less specialist and enjoy wide autonomy and development possibilities in their work. The work teams have been one of the main tools through which the company has achieved continuous, intensive co-operation between different professionals, with very different knowledge, that characterizes the process of technological innovation and the creation, accumulation and transmission of knowledge.
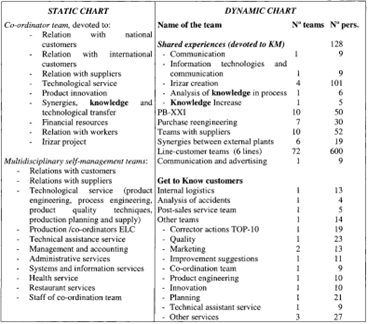
Figure 1 SSS-ZZZ chart
SUCCESS FACTORS IN THE STRATEGYS IMPLEMENTATION
The analysis of the case in question allows pointing out a group of organizational factors that can be considered essential in the success of the implementation process of this strategy.
The factors found in the case analysis can be fitted to the classic 7-S McKinsey model (Waterman, 1982) (Figure 2), the scheme used to represent the principal aspects on which a successful strategic implementation depends.
The model suggests that there are a set of factors which influence strategic change in a company, and that these should be interconnected and be internally coherent. In this case, a KM strategy is involved, focused on the building of a series of capabilities related to innovation. Corporate culture is the core factor, although it must fit with organizational structure, management of human resources, leadership style and KM systems and tools.
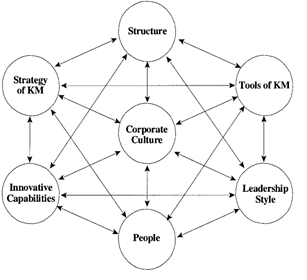
Figure 2 SSS-ZZZ Organizational success factors in the implementation of KM
- Students in individual will write the purpose of KM is to leverage knowledge to improve SSS-ZZZ organizational performance internally and externally and to address KM challenges from a leadership objectives and perspective.
- KM Strategic Approach to SSS-ZZZ Knowledge Flow.
- Modeling Enablers for SSS-ZZZ KM Success
- Role of Management and Leadership in SSS-ZZZ KM Success
- Contribution to SSS-ZZZ KM corporate culture systems (Success - factor -Description).
- Conclusion factors that reflect your objectives and the contributions to your challenge.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


