Question: central axis r = 1.0 m 01.0 kg central axis r = 2.0 m 0 25 kg it depends on the rate of spin both
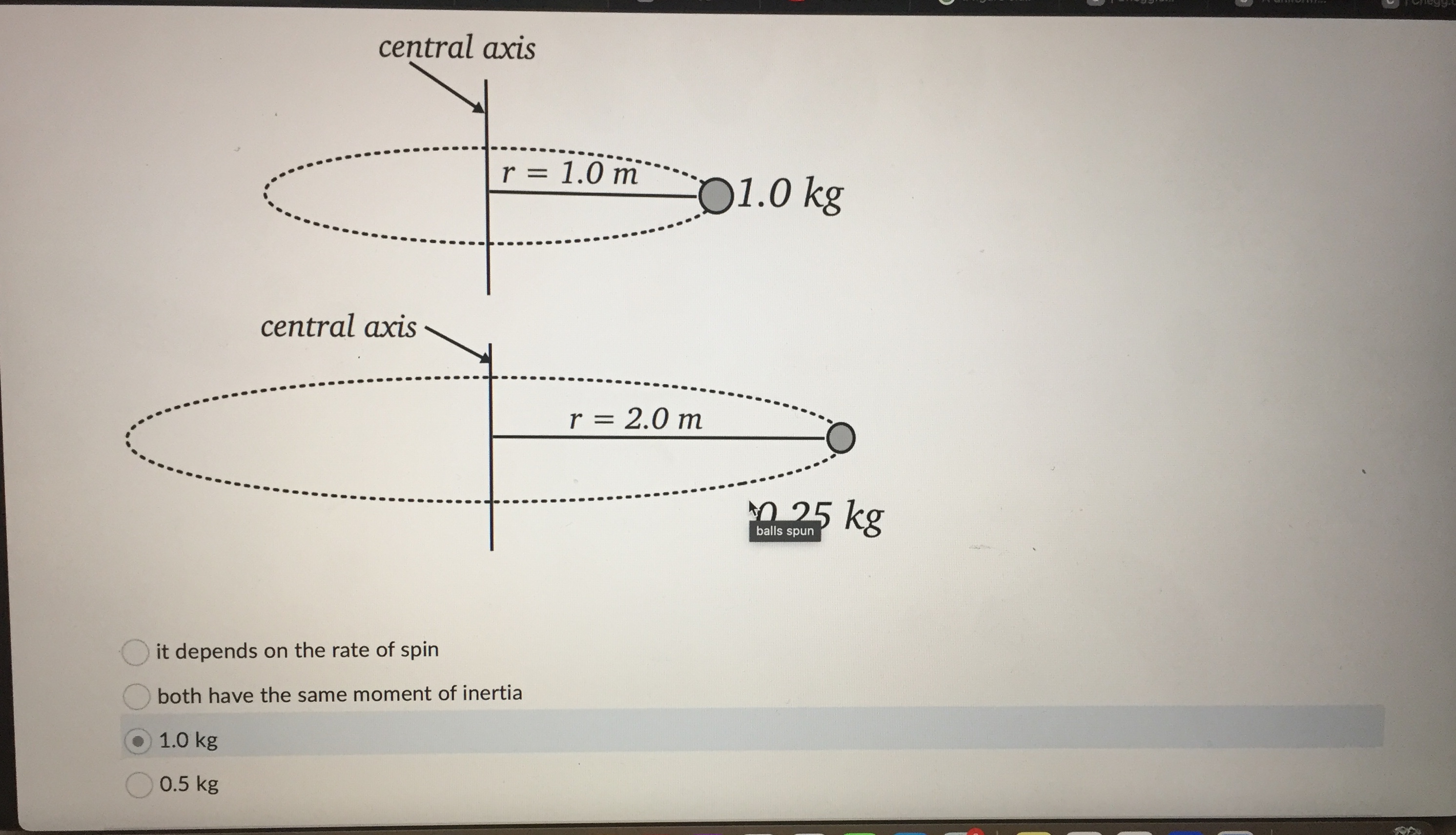

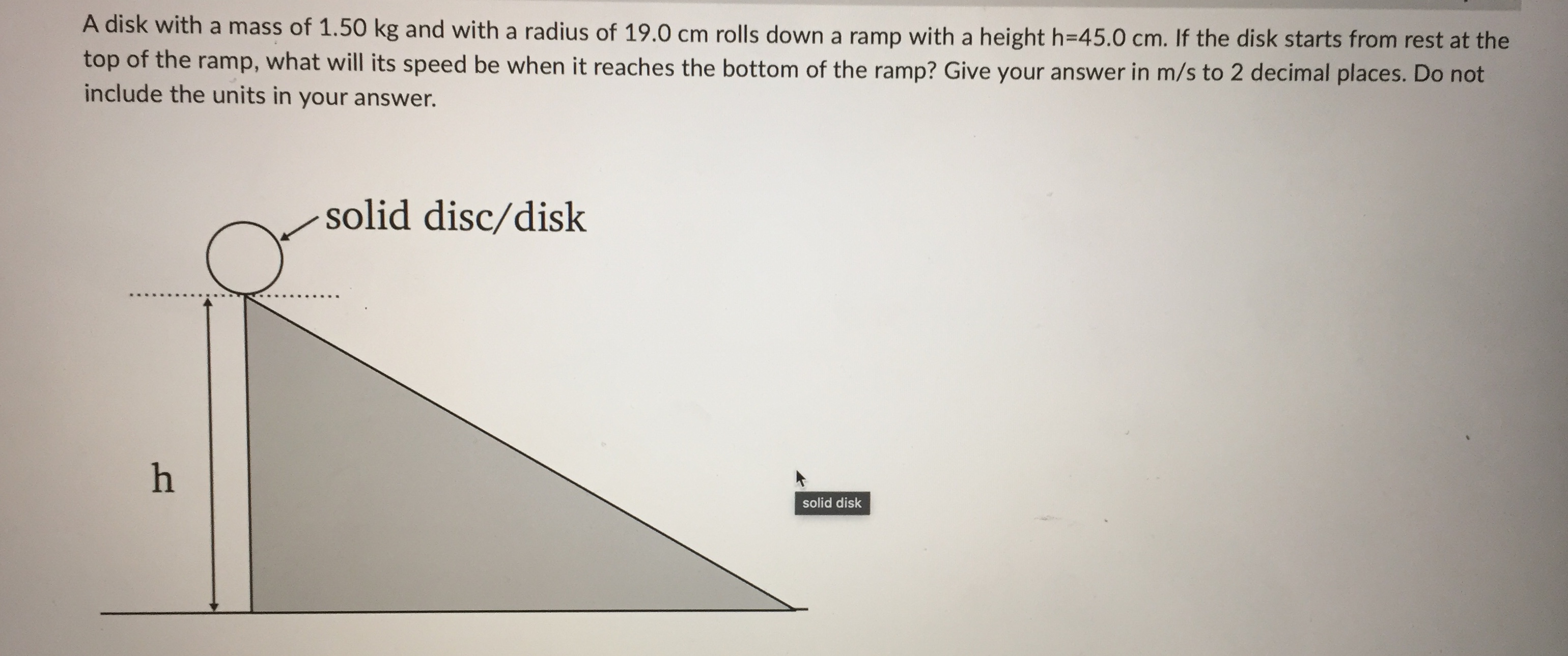


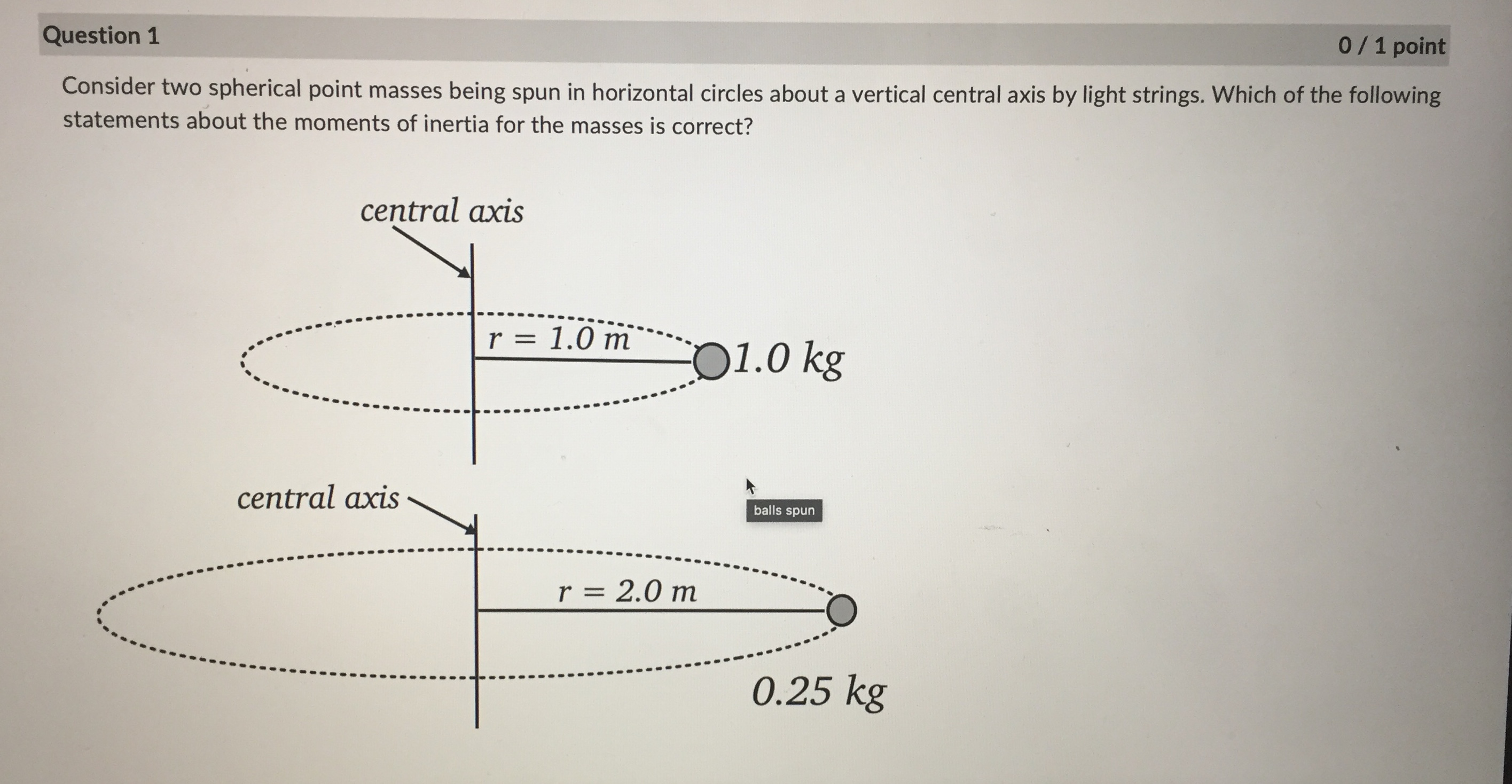
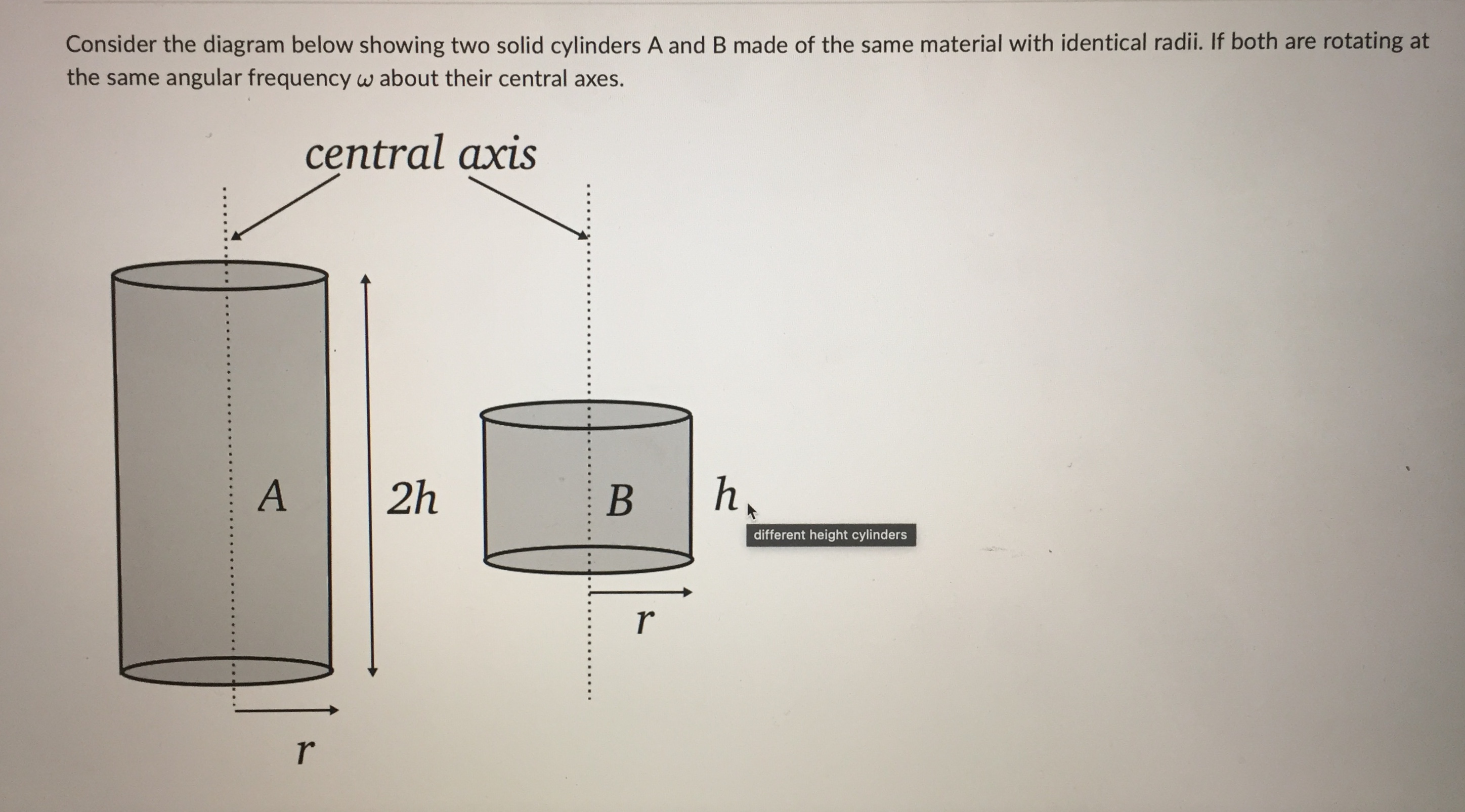
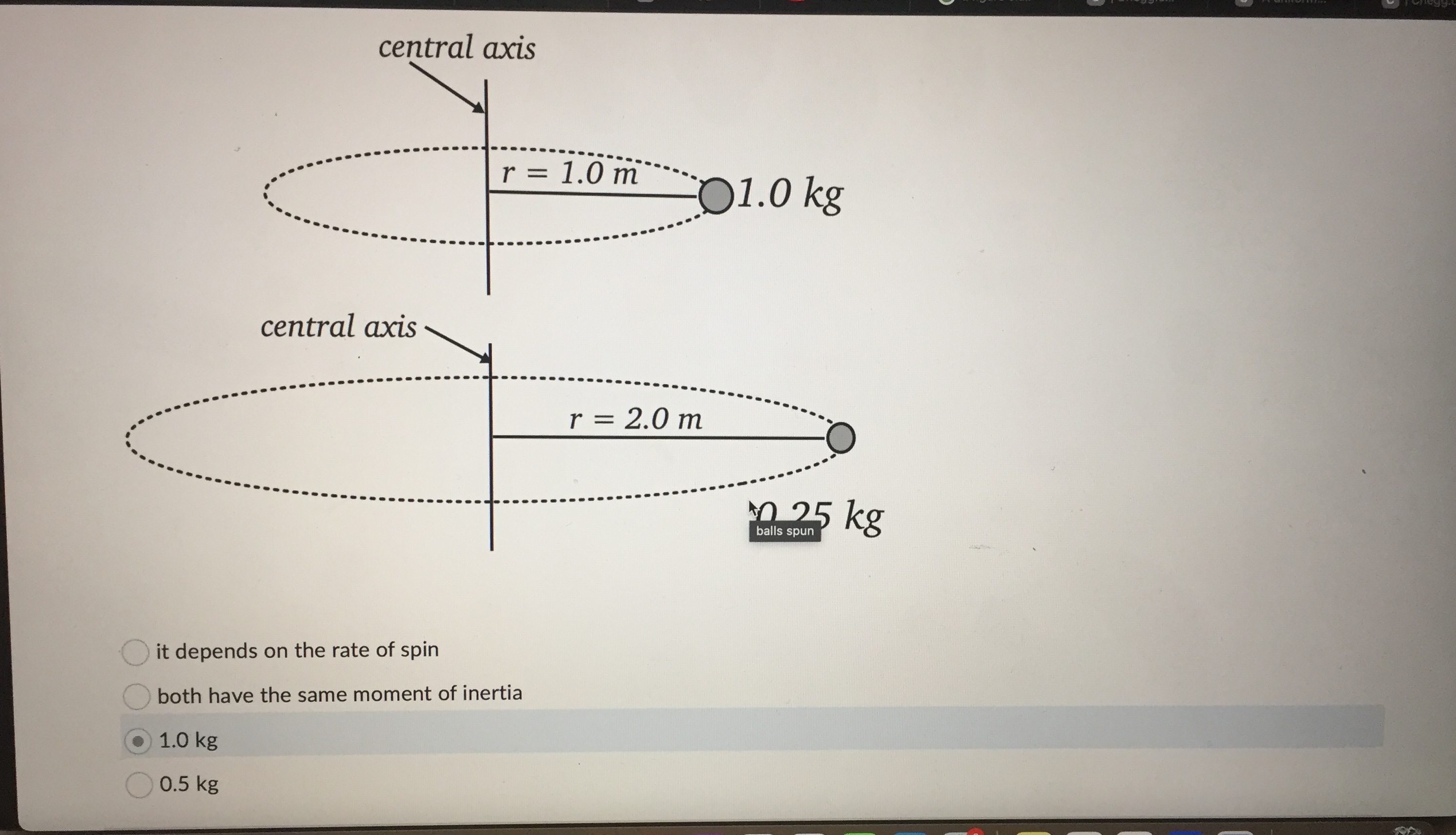

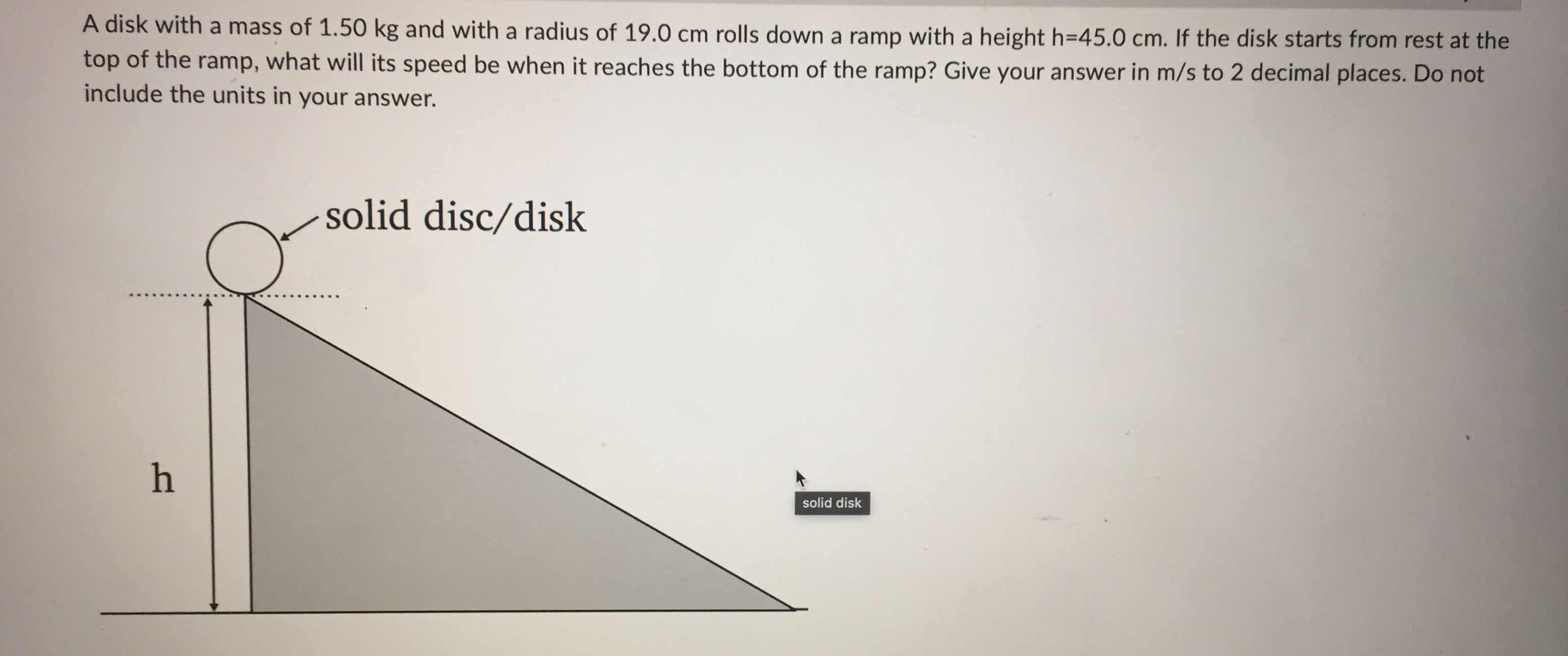


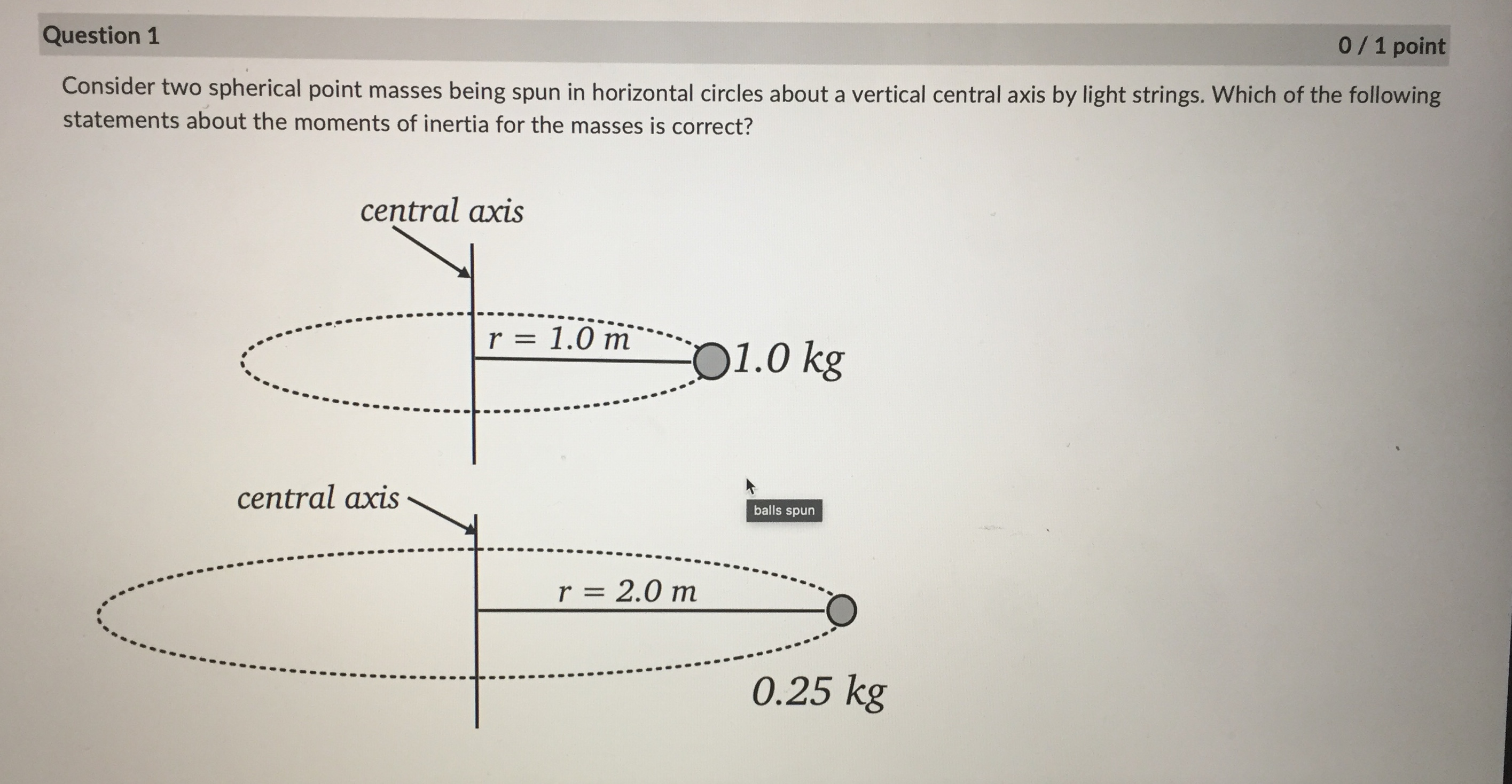
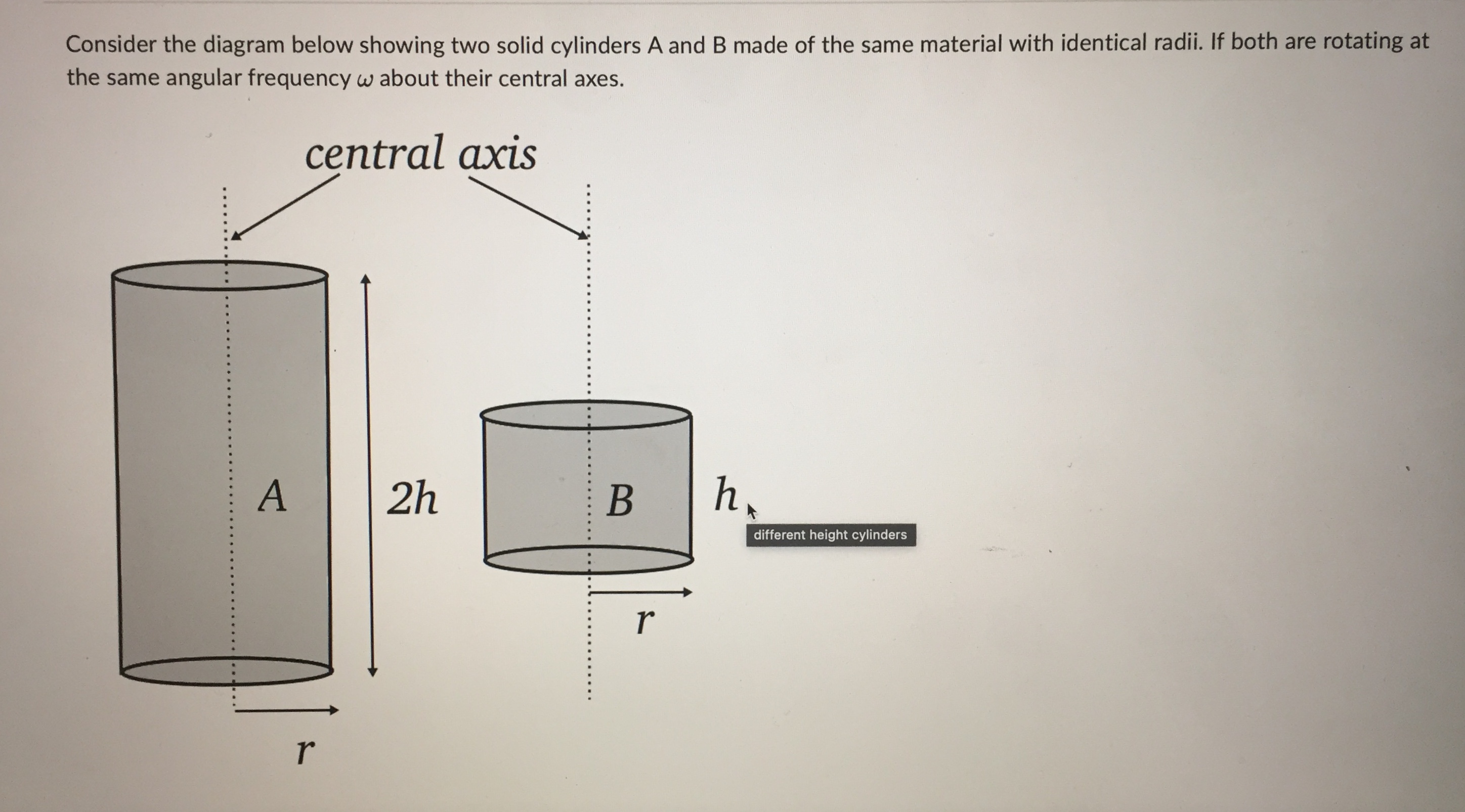
central axis r = 1.0 m 01.0 kg central axis r = 2.0 m 0 25 kg it depends on the rate of spin both have the same moment of inertia 1.0 kg 0.5 kgQuestion 2 0 / 1 point You have a hollow thin walled cylinder of mass 1.40 kg and radius 0.200 m, which is subject to a constant counterclockwise torque 1.20 Nm about its central axis. If the cylinder starts out with an angular velocity of 13.0 rad/s, what is its angular velocity after 8.00 s? (Provide you answer in rad/s to 1 decimal place. Do NOT include the units in the answer!) Your Answer: Question 3 0 / 1 pointA disk with a mass of 1.50 kg and with a radius of 19.0 cm rolls down a ramp with a height h=45.0 cm. If the disk starts from rest at the top of the ramp, what will its speed be when it reaches the bottom of the ramp? Give your answer in m/s to 2 decimal places. Do not include the units in your answer. solid disc/disk - . .. h solid diskA 1.50 kg ball on a massless string is being spun around in a horizontal circle. The distance from the axis of rotation to the centre of mass of the ball is r = 1.24 m. If the ball has an angular momentum of 6.90 kg . m /s, how long does it take to complete 15.0 rotations? Give your answer in units of seconds to 1 decimal place, but do NOT include your units in the answer. axis of rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .| Chegg.c... Rotational... a figure sk... C | Chegg.c... C A uniform.. C | Chegg.c... A 2h B h . . . . . r . . . . . . . . .. . O the angular momentum of A is the same as the angular momentum of B and the rotational kinetic energy of B is twice the rotational kinetic energy of A the angular momentum of A is the same as the angular momentum of B and the rotational kinetic energy of A is twice the rotational kinetic energy of B the angular momentum of A is the twice the angular momentum of B and the rotational kinetic energy of A is twice the rotational kinetic energy of B C the angular momentum of A is the same as the angular momentum of B and the rotational kinetic energy of A is the same as the rotational kinetic energy of BQuestion 1 0 / 1 point Consider two spherical point masses being spun in horizontal circles about a vertical central axis by light strings. Which of the following statements about the moments of inertia for the masses is correct? central axis - -. r = 1.0m O1.0 kg central axis balls spun r = 2.0 m 0.25 kgConsider the diagram below showing two solid cylinders A and B made of the same material with identical radii. If both are rotating at the same angular frequency w about their central axes. central axis . . . . . . . .. . . . .. . . .... . . . . . . . .f . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A 2h . . . . . . . . . B h, different height cylinders - . . . . . . . . . . . .. . r . . . . . . . . . . . r
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


