Question: CHAPTER 13 CASE FLOW BUDGETING This problem involves working out a cash flow budget for next year. The following information should be all that is


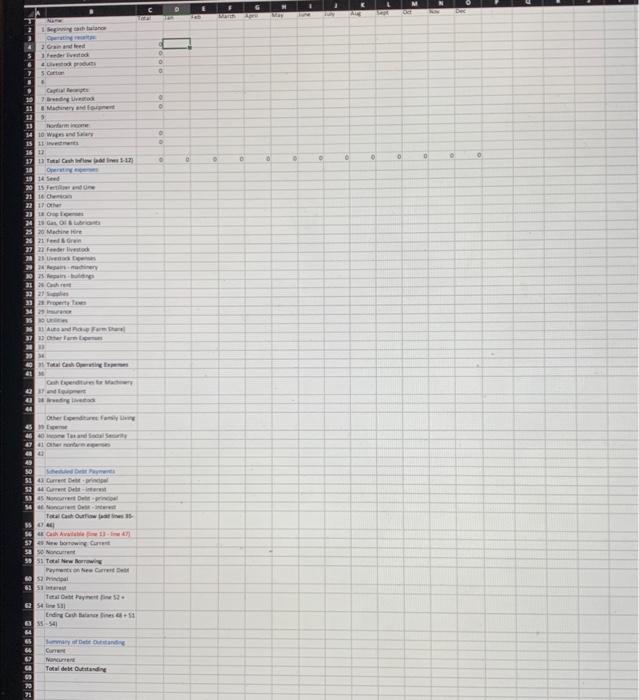
CHAPTER 13 CASE FLOW BUDGETING This problem involves working out a cash flow budget for next year. The following information should be all that is needed to complete this problem. The information is in no particular order so carefully check to be sure you have used it all before finishing the problem. Round everything to the nearest whole dollar. Complete a cash flow budget on the form provided. Beginning inventory (January 1): Wheat, 8,500 bu. to sell in January Beef cows, 140 head Prices to use: Beef calves -70 cents per pound Yields: 90% calf crop Wheat$3.40perbushelCotton72centsperpound32bu.peracre575lbs.peracre Additional Information 1. Sells all calves in August at average weight of 450 lbs. (Assume no replacements kept.) 2. Will raise 300 acres of cotton and 450 acres of wheat in 2008 . 3. Plans to trade for a new pickup in March, paying $18,500 cash difference. There will be a new intermediate term loan of $14,000 to help pay for it. 4. The new intermediate loan on the pickup will have a semi-annual payment due in August of $2,300 for principal and $750 for interest. 5. Will sell a bull in April for $800 and buy a replacement in May for $2,000. 6. Income and Social Security tax of $15,200 due in March. 7. Family living expenses of $3,000 per month. 8. Personal life insurance premium of $2,000 due in April. 9. Cash on hand January 1,$12,000. 10. Assume all cotton is sold at harvest in October and all wheat produced is stored for sale in the following year. 11. Spouse's non-farm job nets $1,500 per month after all deductions. 12. All new borrowing needed will be "current" borrowing except as indicated in \#3 above. To simplify calculations, borrow and repay loans in even $100 units. 13. Interest rate is 12% per year or 1% per month on current borrowing. Repay oldest current borrowing first and pay interest only on the amount of principal repaid. 14. Maintain $1000 monthly minimum balance (anything between $950 and $1050 is okay). Estimated Expenses for the year 1. Hired labor \$18,000 per year, equal amount each month. 2. Feed and grain $6,000 per year, 1/2 in March, 1/2 in December 3. Chemicals $14,400 per year, 1/2 in April, 1/2 in August 6. Building repairs S4,000 in November 7. Livestock expenses $4,800 per year, equal amount each month 8. Fertilizer $14,000 in February 9. Gas, fuel, oil $7,200 per year, 1/2 in April, 1/2 September 10. Property taxes $1,400 per year, 1/2 in June, 1/2 in November 11. Insurance for farm $3,000 in February 12. Farm share of auto and pickup $4,800 per year, equal amount each month 13. Utilities $3,600 per year, equal amount each month 14. Miscellaneous $2,400 per year, equal amount each month 15. Seed $5,400 in February Debt Situation as of January 1 Payment Due this year Current loans Noncurrent loans $205,000 \begin{tabular}{lll} Princ. & Interest & Month due \\ \hline$25,000 & $2,000 & February \\ $15,500 & $16,400 & May \end{tabular} CHAPTER 13 CASE FLOW BUDGETING This problem involves working out a cash flow budget for next year. The following information should be all that is needed to complete this problem. The information is in no particular order so carefully check to be sure you have used it all before finishing the problem. Round everything to the nearest whole dollar. Complete a cash flow budget on the form provided. Beginning inventory (January 1): Wheat, 8,500 bu. to sell in January Beef cows, 140 head Prices to use: Beef calves -70 cents per pound Yields: 90% calf crop Wheat$3.40perbushelCotton72centsperpound32bu.peracre575lbs.peracre Additional Information 1. Sells all calves in August at average weight of 450 lbs. (Assume no replacements kept.) 2. Will raise 300 acres of cotton and 450 acres of wheat in 2008 . 3. Plans to trade for a new pickup in March, paying $18,500 cash difference. There will be a new intermediate term loan of $14,000 to help pay for it. 4. The new intermediate loan on the pickup will have a semi-annual payment due in August of $2,300 for principal and $750 for interest. 5. Will sell a bull in April for $800 and buy a replacement in May for $2,000. 6. Income and Social Security tax of $15,200 due in March. 7. Family living expenses of $3,000 per month. 8. Personal life insurance premium of $2,000 due in April. 9. Cash on hand January 1,$12,000. 10. Assume all cotton is sold at harvest in October and all wheat produced is stored for sale in the following year. 11. Spouse's non-farm job nets $1,500 per month after all deductions. 12. All new borrowing needed will be "current" borrowing except as indicated in \#3 above. To simplify calculations, borrow and repay loans in even $100 units. 13. Interest rate is 12% per year or 1% per month on current borrowing. Repay oldest current borrowing first and pay interest only on the amount of principal repaid. 14. Maintain $1000 monthly minimum balance (anything between $950 and $1050 is okay). Estimated Expenses for the year 1. Hired labor \$18,000 per year, equal amount each month. 2. Feed and grain $6,000 per year, 1/2 in March, 1/2 in December 3. Chemicals $14,400 per year, 1/2 in April, 1/2 in August 6. Building repairs S4,000 in November 7. Livestock expenses $4,800 per year, equal amount each month 8. Fertilizer $14,000 in February 9. Gas, fuel, oil $7,200 per year, 1/2 in April, 1/2 September 10. Property taxes $1,400 per year, 1/2 in June, 1/2 in November 11. Insurance for farm $3,000 in February 12. Farm share of auto and pickup $4,800 per year, equal amount each month 13. Utilities $3,600 per year, equal amount each month 14. Miscellaneous $2,400 per year, equal amount each month 15. Seed $5,400 in February Debt Situation as of January 1 Payment Due this year Current loans Noncurrent loans $205,000 \begin{tabular}{lll} Princ. & Interest & Month due \\ \hline$25,000 & $2,000 & February \\ $15,500 & $16,400 & May \end{tabular}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


