Question: chapter 17 focuses on the linkages between purchasing and selecting the correct mode of transportation. There are many variables involved in selecting the correct mode
chapter 17 focuses on the linkages between purchasing and selecting the correct mode of transportation. There are many variables involved in selecting the correct mode of transportation and logistics system that affect costs. Review the five criteria used to measure transportation performance and the five transportation modes. Then review the relative ranking chart of domestic transportation modes. Select two modes of transportation and an example product appropriate for each mode. Using your example product, discuss why the mode of transportation you selected received the ranking as indicated in the chart for each criteria. Be specific in your responses.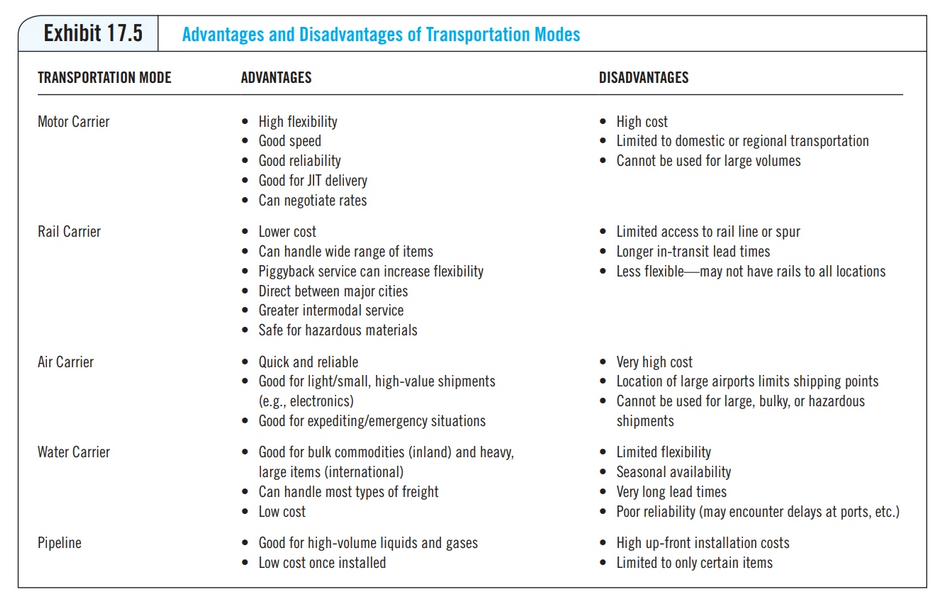
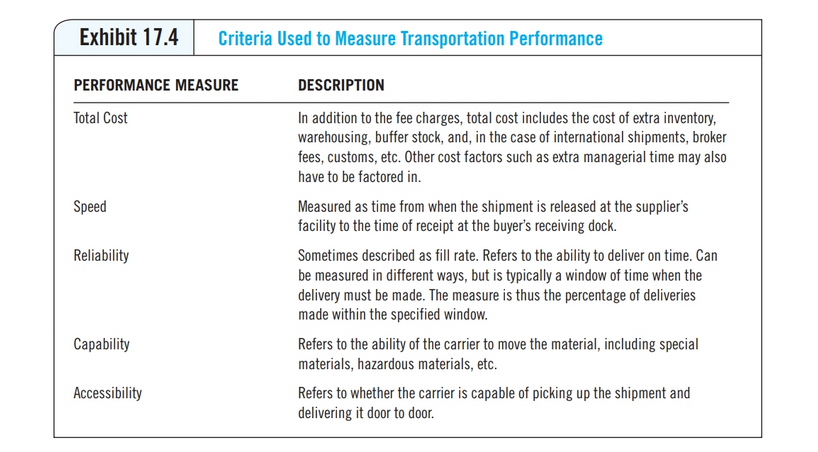
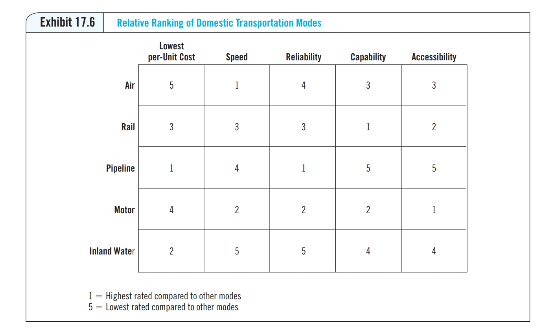
Exhibit 17.5 Advantages and Disadvantages of Transportation Modes TRANSPORTATION MODE ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES Motor Carrier High cost Limited to domestic or regional transportation Cannot be used for large volumes Rail Carrier Limited access to rail line or spur Longer in-transit lead times Less flexiblemay not have rails to all locations High flexibility Good speed Good reliability Good for JIT delivery Can negotiate rates Lower cost Can handle wide range of items Piggyback service can increase flexibility Direct between major cities Greater intermodal service Safe for hazardous materials Quick and reliable . Good for light/small, high-value shipments (e.g., electronics) Good for expediting/emergency situations Good for bulk commodities (inland) and heavy, large items (international) Can handle most types of freight Low cost Good for high-volume liquids and gases Low cost once installed Air Carrier Water Carrier Very high cost Location of large airports limits shipping points Cannot be used for large, bulky, or hazardous shipments Limited flexibility Seasonal availability Very long lead times Poor reliability (may encounter delays at ports, etc.) High up-front installation costs Limited to only certain items Pipeline Exhibit 17.4 Criteria Used to Measure Transportation Performance PERFORMANCE MEASURE Total Cost Speed Reliability DESCRIPTION In addition to the fee charges, total cost includes the cost of extra inventory, warehousing, buffer stock, and, in the case of international shipments, broker fees, customs, etc. Other cost factors such as extra managerial time may also have to be factored in. Measured as time from when the shipment is released at the supplier's facility to the time of receipt at the buyer's receiving dock. Sometimes described as fill rate. Refers to the ability to deliver on time. Can be measured in different ways, but is typically a window of time when the delivery must be made. The measure is thus the percentage of deliveries made within the specified window. Refers to the ability of the carrier to move the material, including special materials, hazardous materials, etc. Refers to whether the carrier is capable of picking up the shipment and delivering it door to door Capability Accessibility Exhibit 17.6 Relative Ranking of Domestic Transportation Modes Lowest per-Unit Cost Speed Reliability Capability Accessibility Air 5 . 4 3 3 Rail 3 3 3 1 2 Pipeline 1 4 5 5 5 Motor 4 2 2 2 1 Inland Water 2 2 5 5 1 - Highest rated compared to other modes 5-Lowest rated compared to other modes






