Question: Chapters 7 and 9 Homework i Saved Help Save & Exit Submit Check my work Complete the following table and answer the questions below: Instructions:
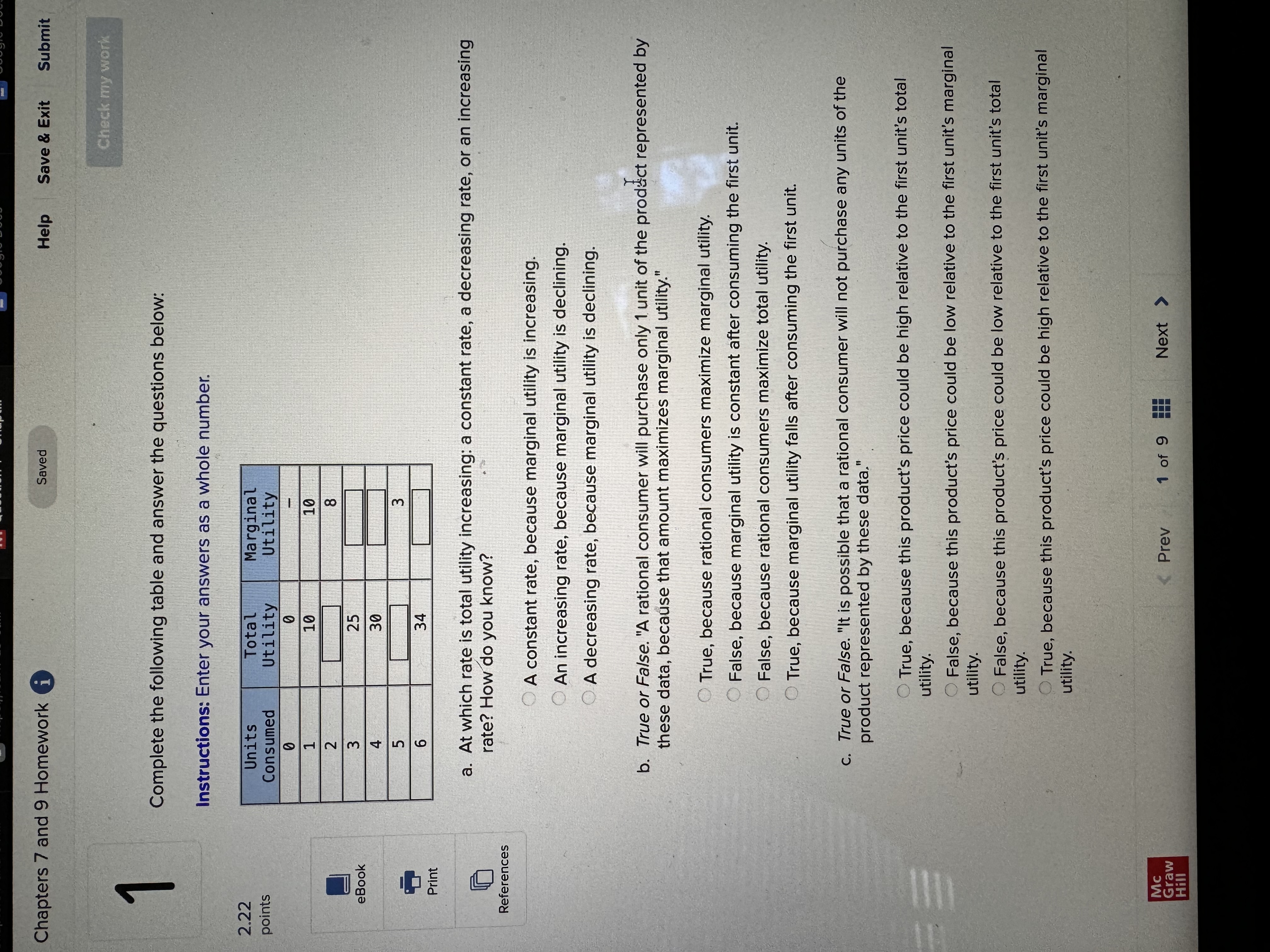
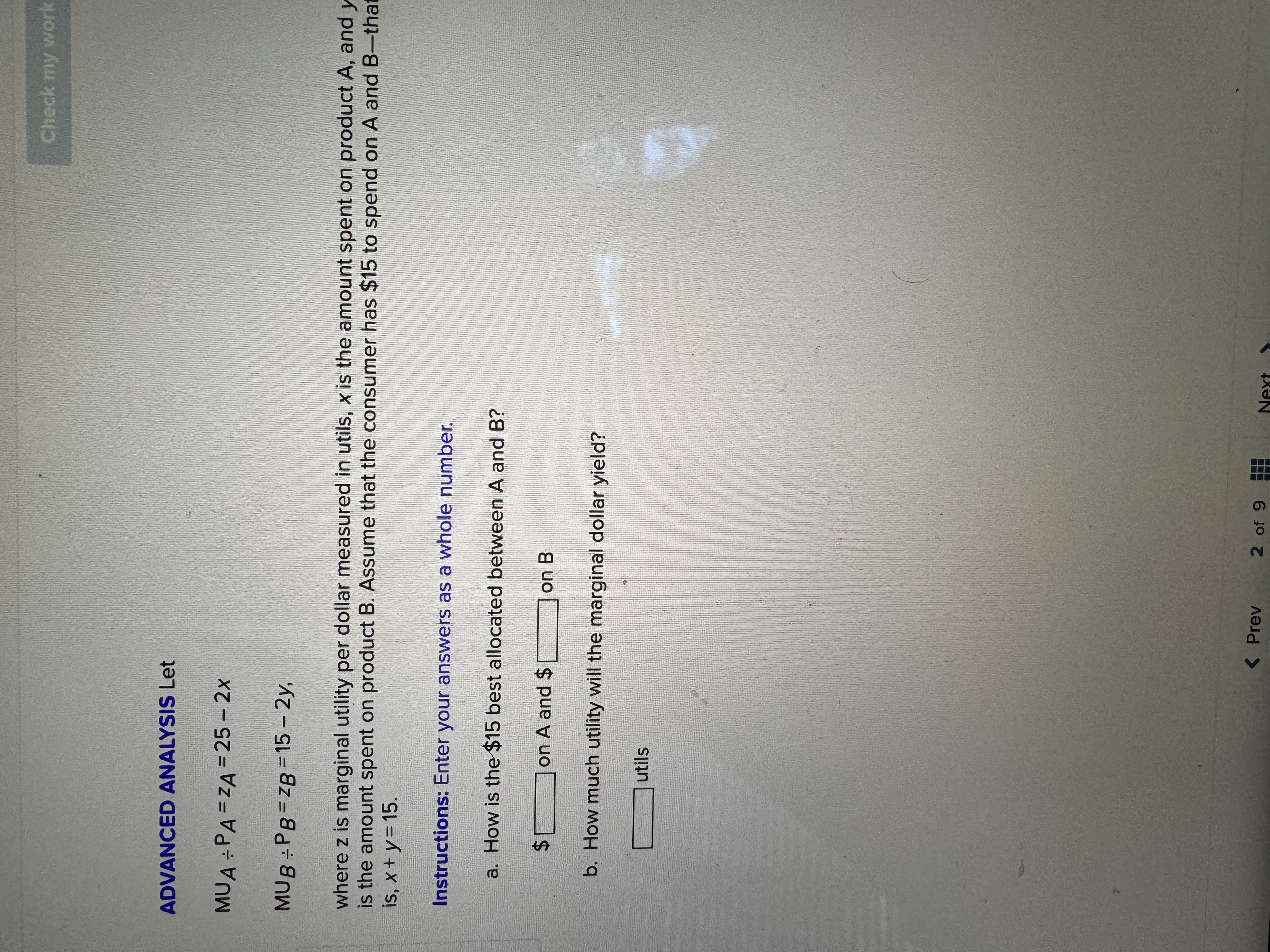
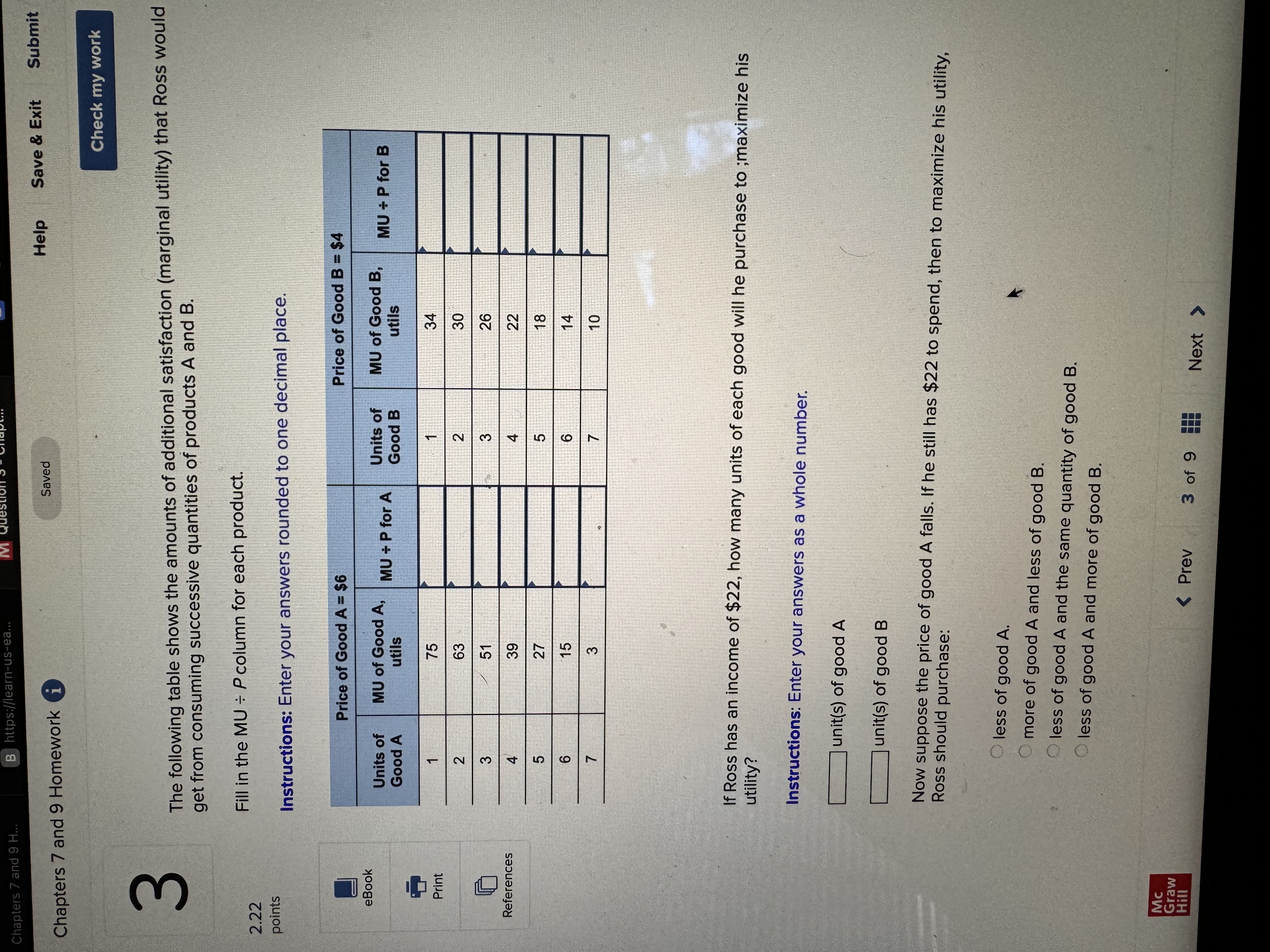
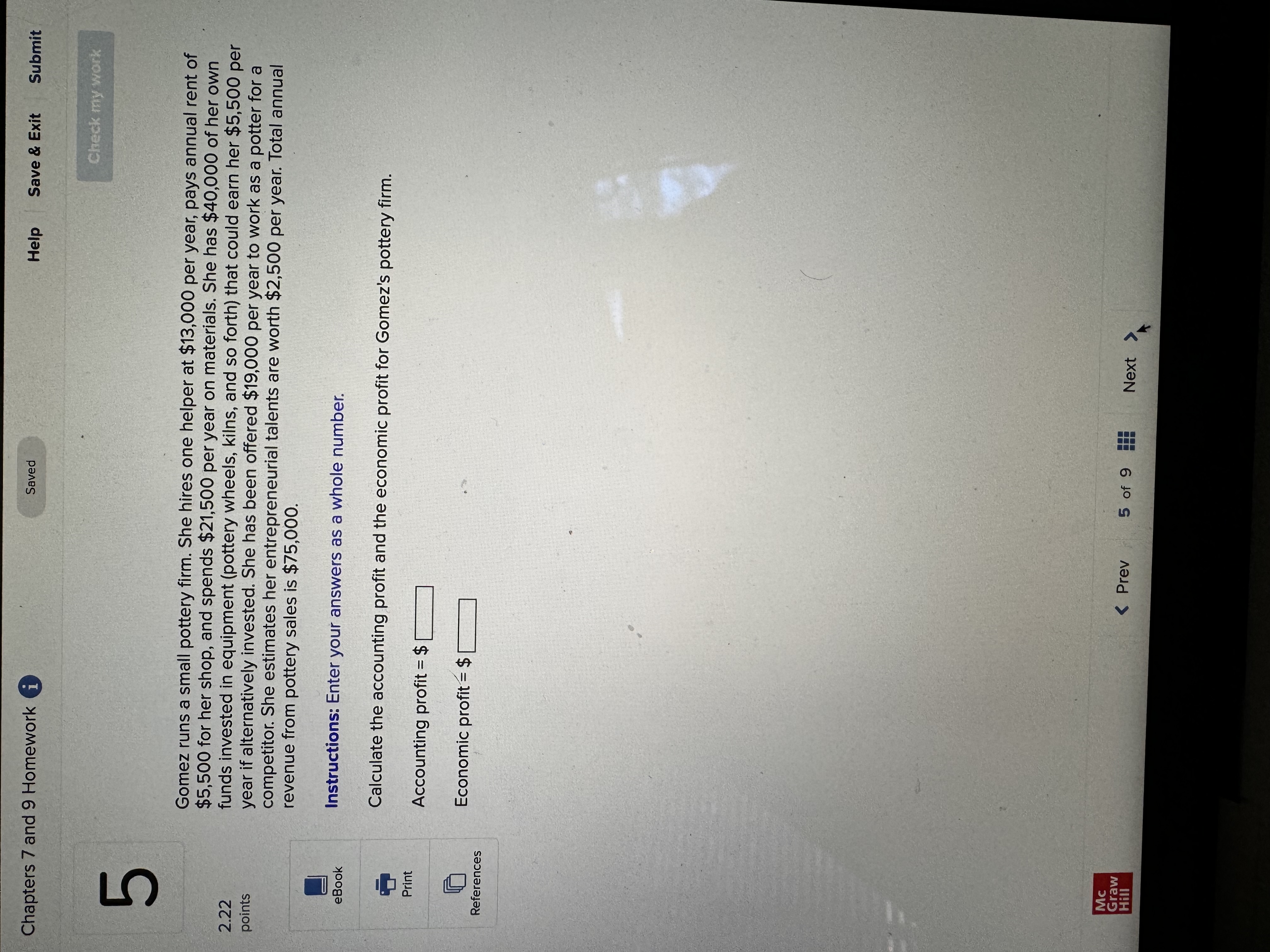
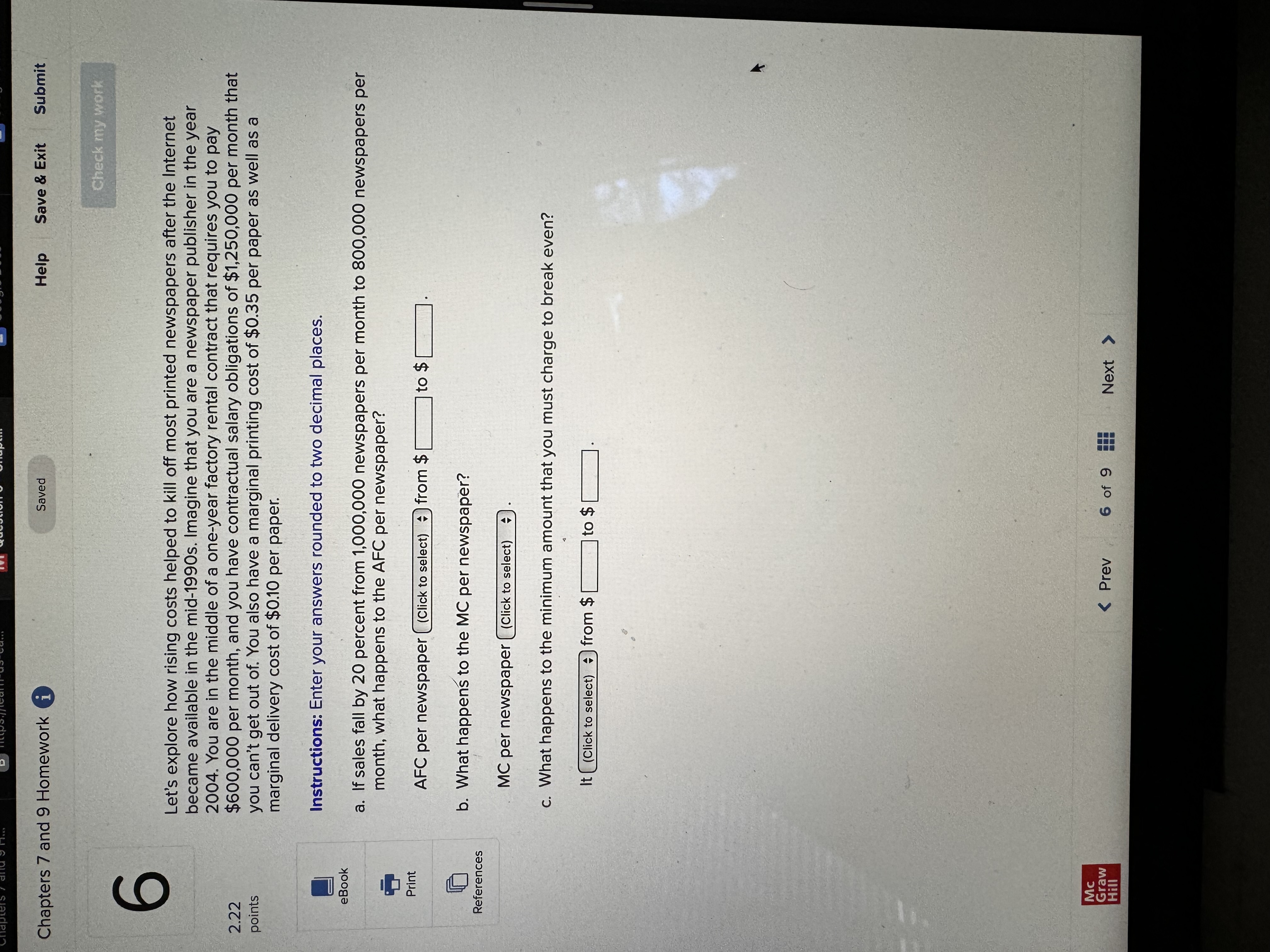
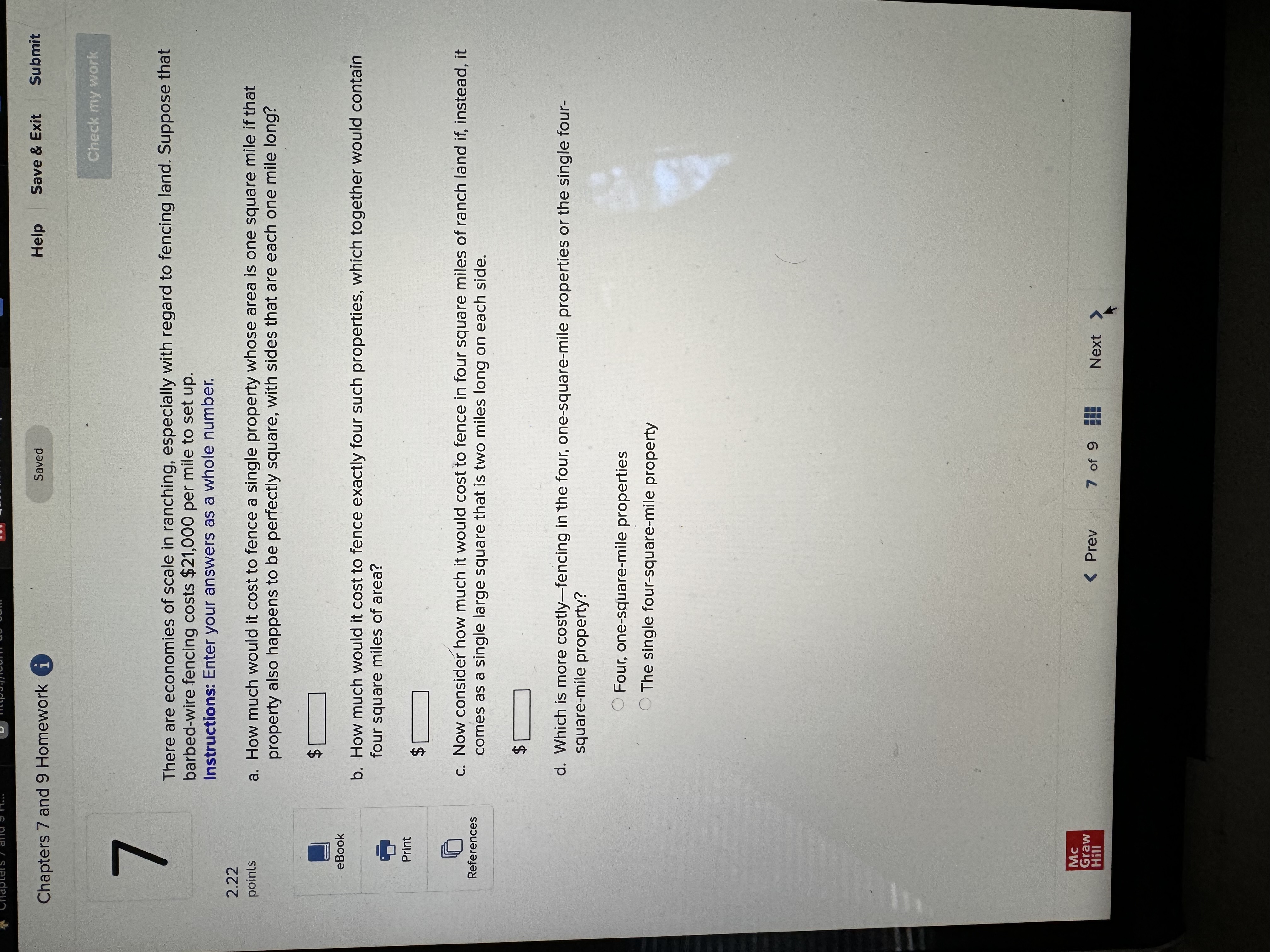
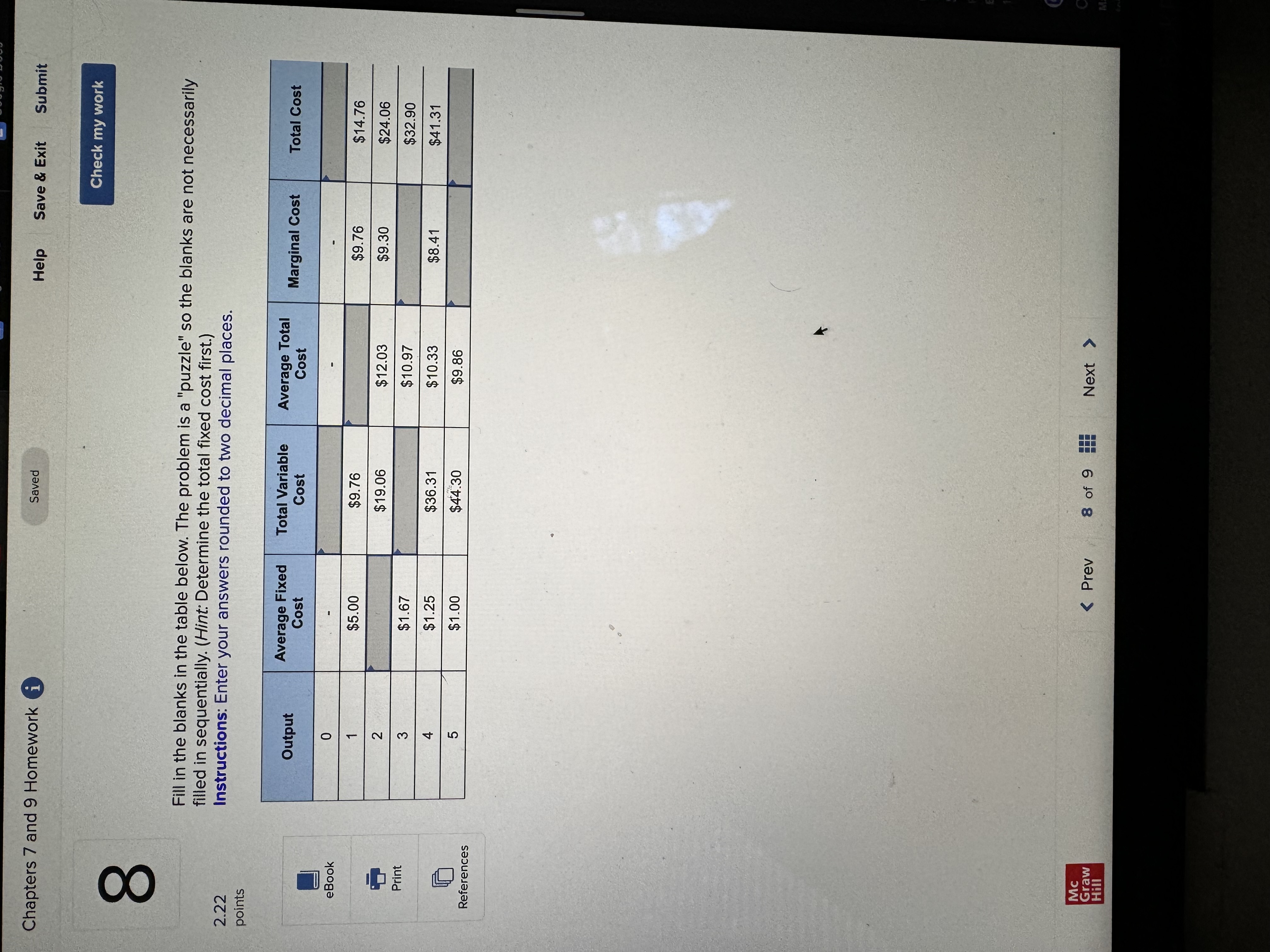
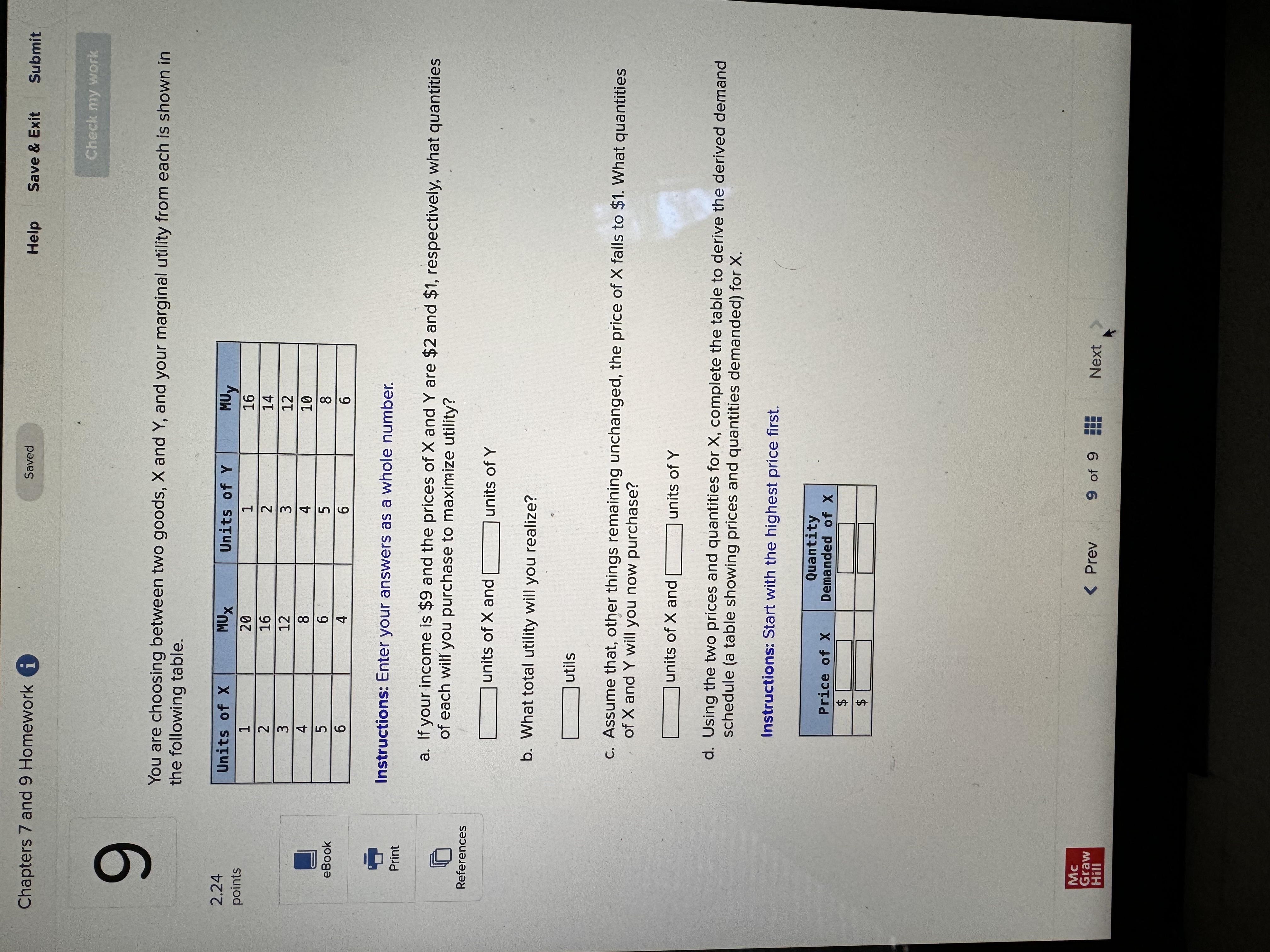
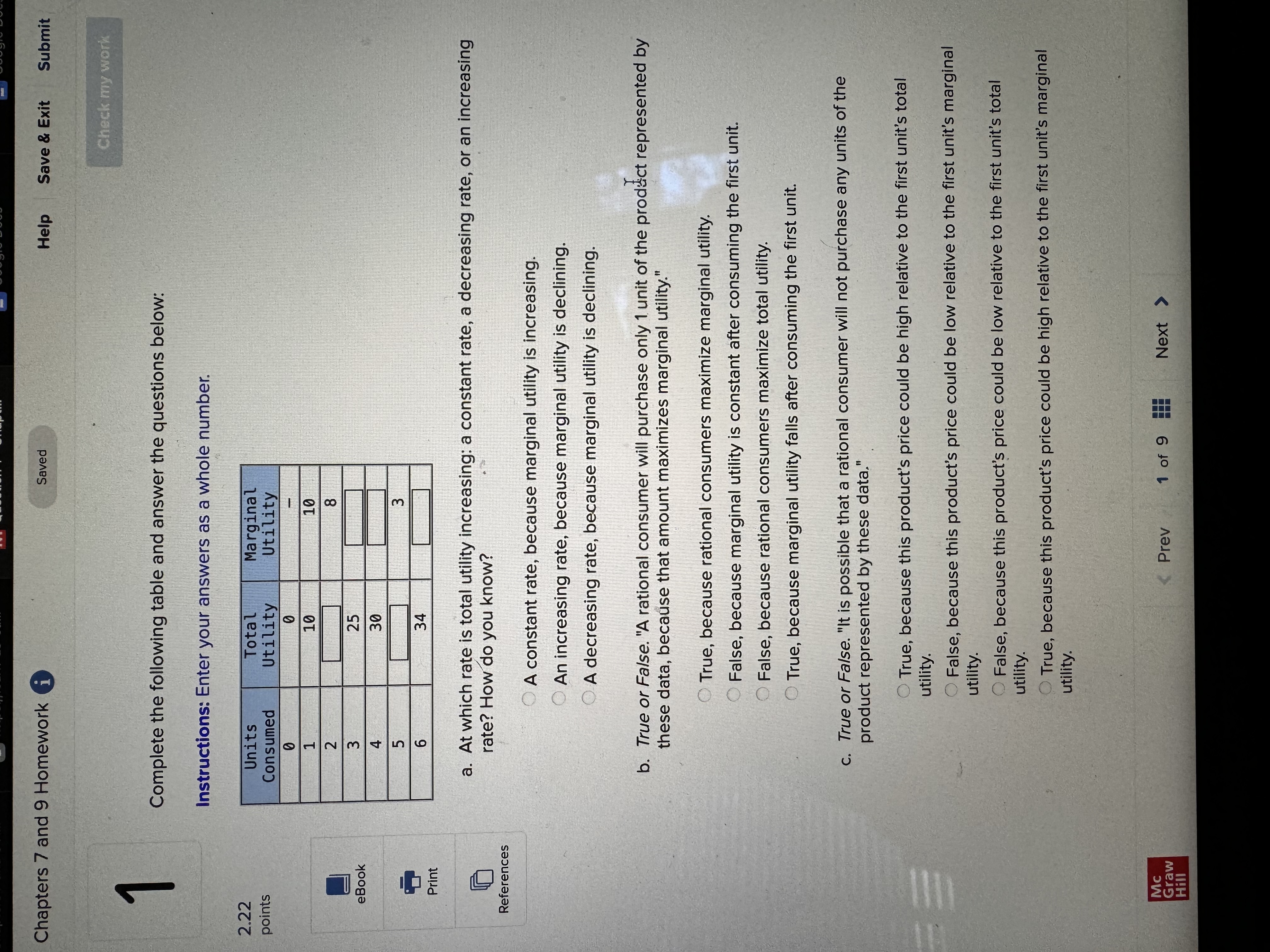
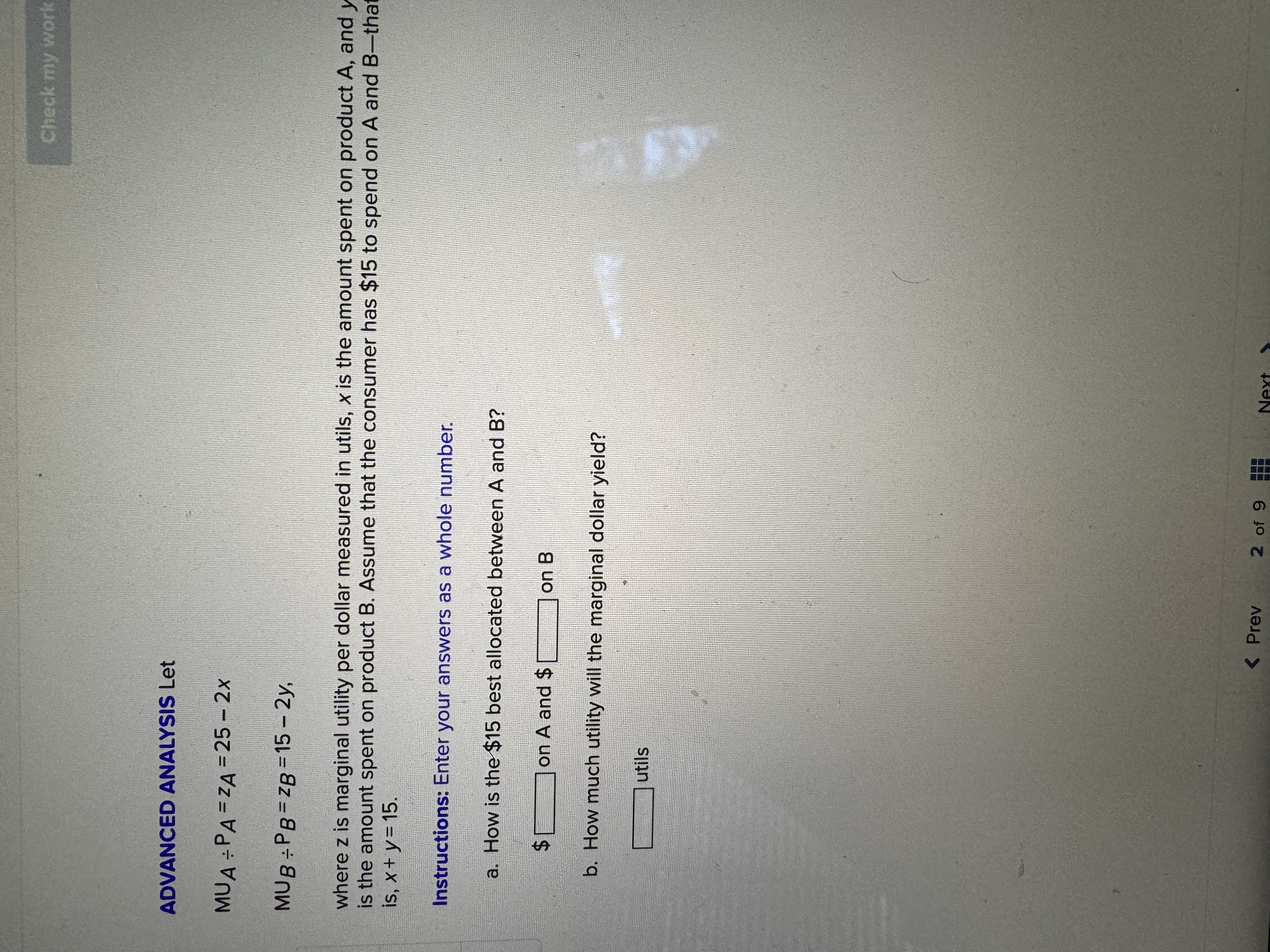
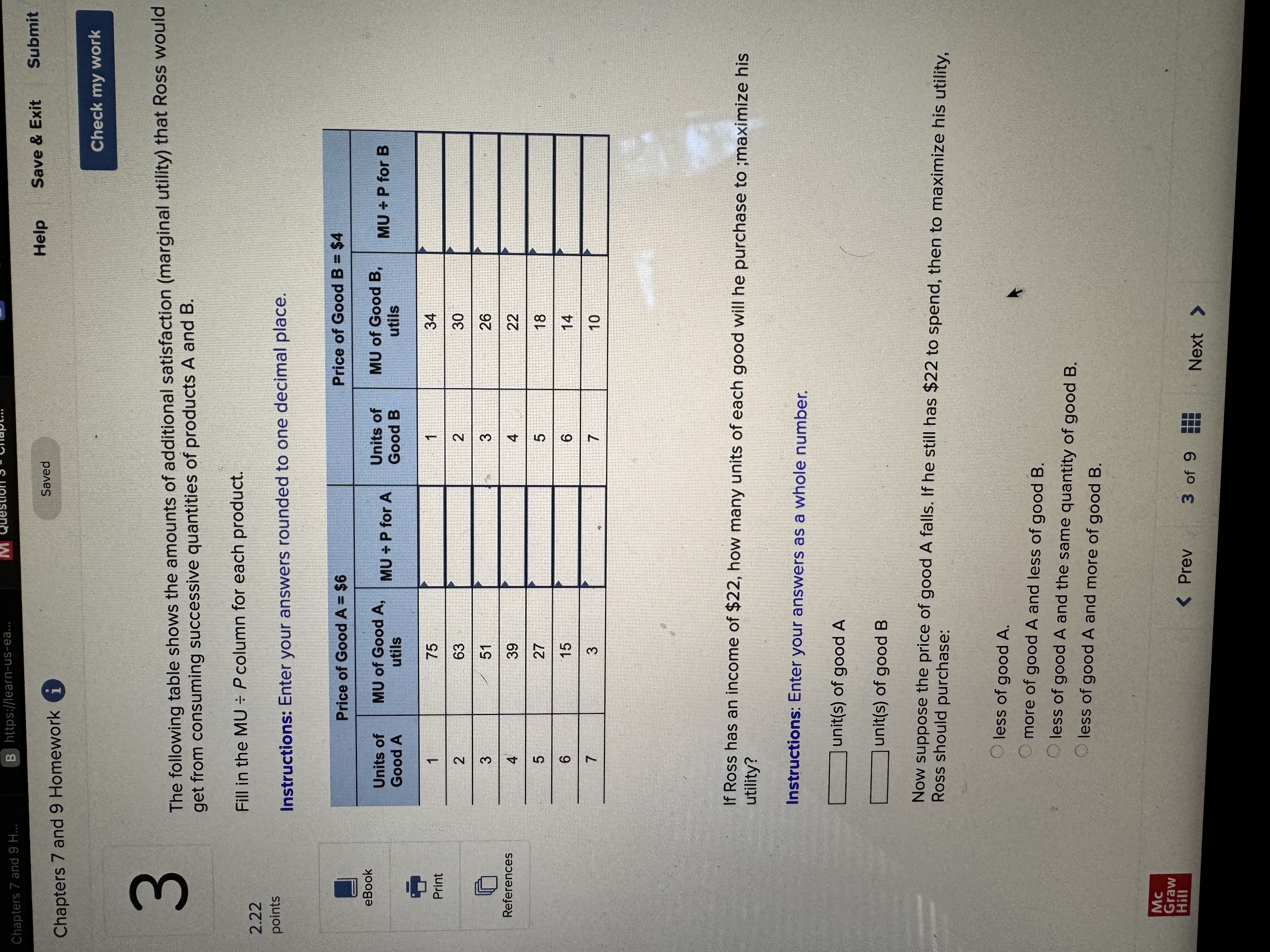
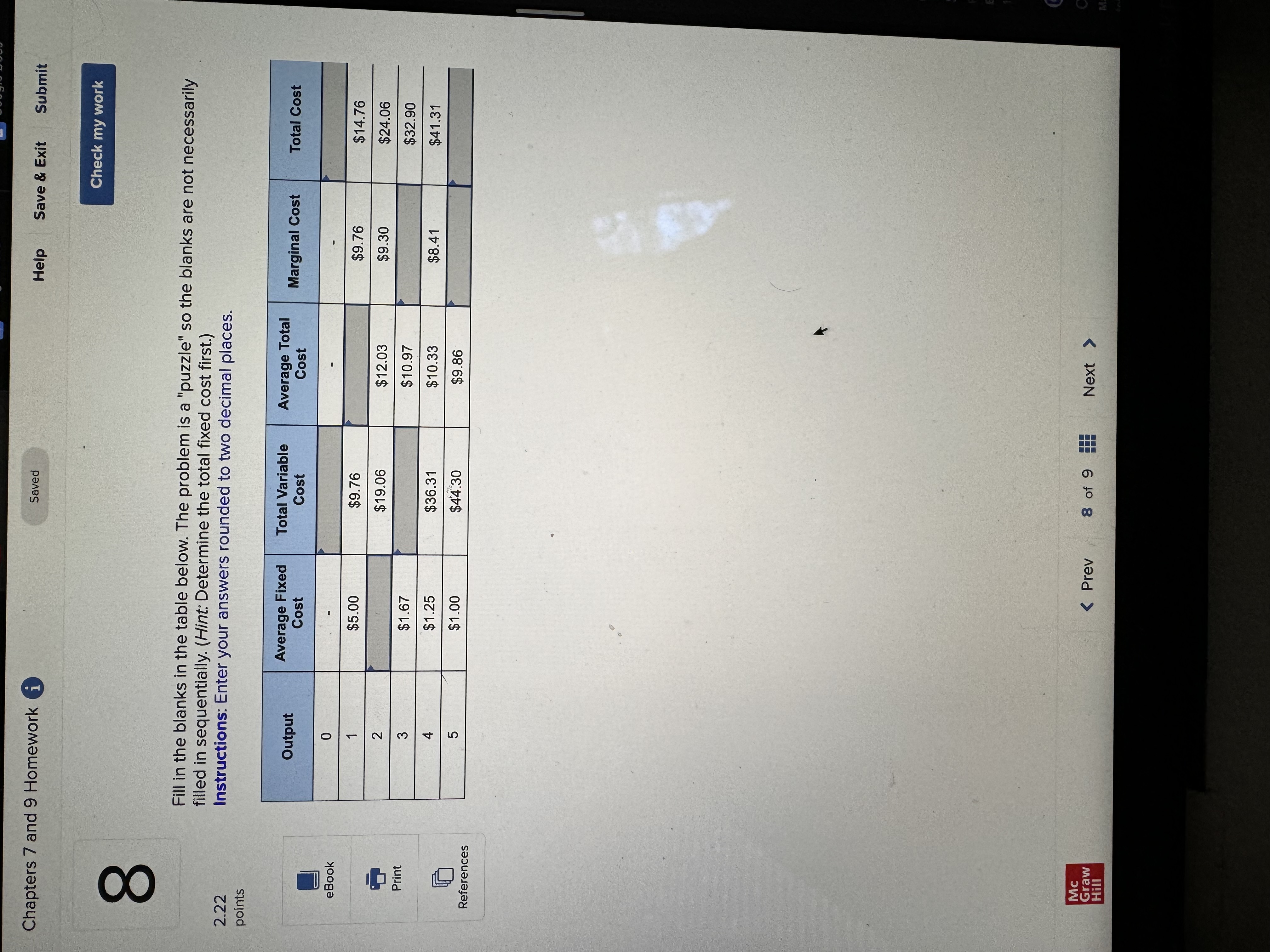
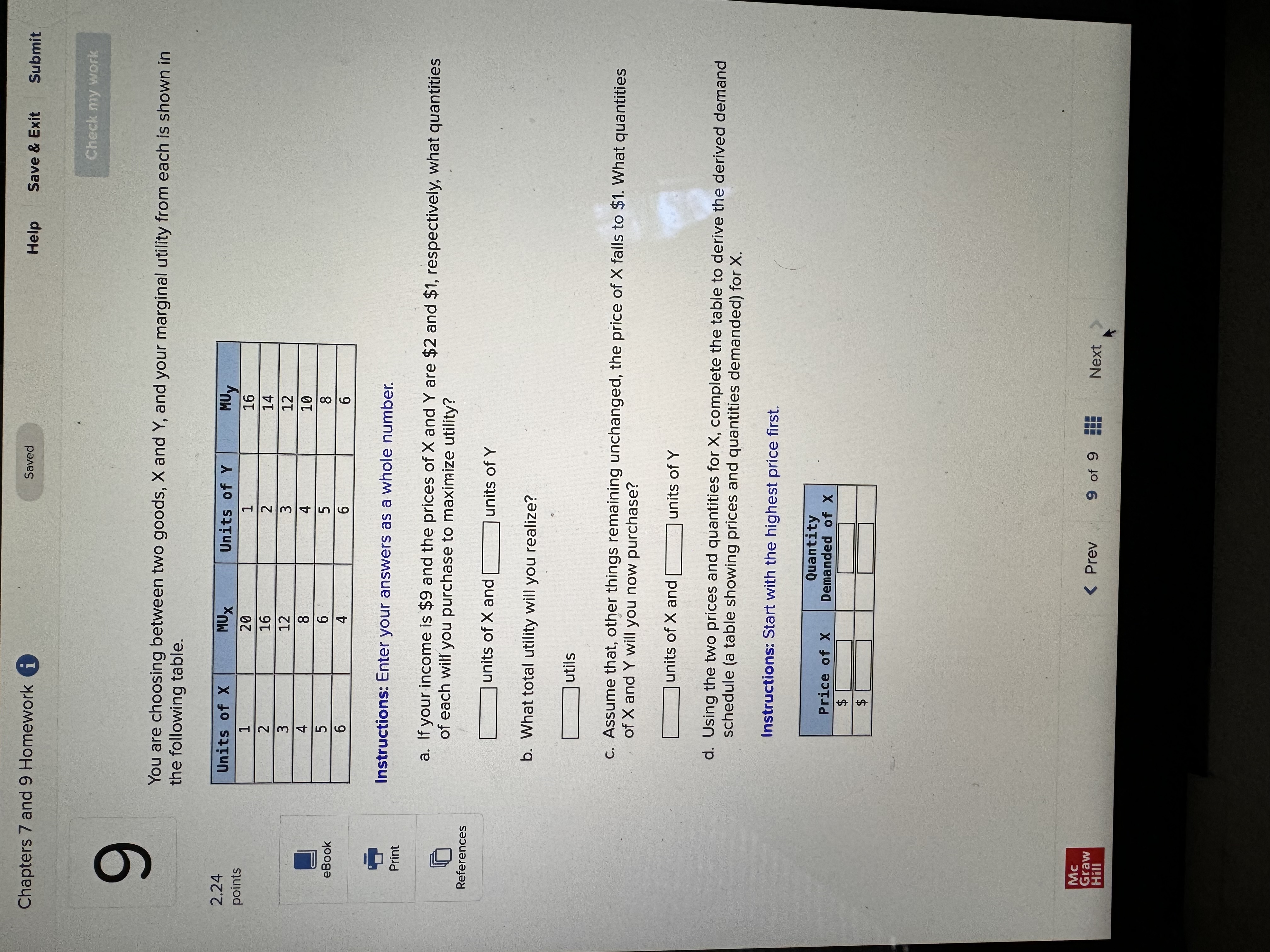
Chapters 7 and 9 Homework i Saved Help Save & Exit Submit Check my work Complete the following table and answer the questions below: Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. 2.22 Units Total Marginal points Consumed Utility Utility 0 0 1 10 10 2 8 3 eBook 25 4 30 UT 3 6 34 Print a. At which rate is total utility increasing: a constant rate, a decreasing rate, or an increasing rate? How do you know? References A constant rate, because marginal utility is increasing. An increasing rate, because marginal utility is declining. A decreasing rate, because marginal utility is declining. b. True or False. "A rational consumer will purchase only 1 unit of the product represented by these data, because that amount maximizes marginal utility." True, because rational consumers maximize marginal utility. False, because marginal utility is constant after consuming the first unit. False, because rational consumers maximize total utility. True, because marginal utility falls after consuming the first unit. c. True or False. "It is possible that a rational consumer will not purchase any units of the product represented by these data." True, because this product's price could be high relative to the first unit's total utility. False, because this product's price could be low relative to the first unit's marginal utility. False, because this product's price could be low relative to the first unit's total utility. True, because this product's price could be high relative to the first unit's marginal utility. Mc Graw Check my work ADVANCED ANALYSIS Let MUA + PA = ZA=25 - 2x MUB + PB= ZB =15 - 2y, where z is marginal utility per dollar measured in utils, x is the amount spent on product A, and is the amount spent on product B. Assume that the consumer has $15 to spend on A and B-tha is, x + y = 15. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. a. How is the $15 best allocated between A and B? $ on A and $ on B b. How much utility will the marginal dollar yield? utils Submit Chapters 7 and 9 Homework i Saved Help Save & Exit Check my work 4 Explicit costs are payments the firm makes for 2.22 points outputs such as desks for its employees, whereas implicit costs are nonexpenditure costs that occur through the use of self-owned resources such as forgone income O inputs such as wages and salaries to employees, whereas implicit costs are expenditure costs that occur for services such as employee travel expenses. eBook outputs such as desks for its employees, whereas implicit costs are expenditure costs that occur for services such as employee travel expenses. Print inputs such as wages and salaries to employees, whereas implicit costs are nonexpenditure costs that occur through the use of self-owned resources such as forgone income. References The explicit costs of going to college include the cost of tuition and books, while implicit costs include forgone income. the fees paid to the college, while implicit costs include the cost of tuition. the cost of tuition, while implicit costs include the fees paid to the college. forgone income, while implicit costs include the cost of tuition and books. Mc Graw Chapters 7 and 9 Homework i Saved Help Save & Exit Submit Check my work 7 There are economies of scale in ranching, especially with regard to fencing land. Suppose that barbed-wire fencing costs $21,000 per mile to set up. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. 2.22 points a. How much would it cost to fence a single property whose area is one square mile if that property also happens to be perfectly square, with sides that are each one mile long? Book b. How much would it cost to fence exactly four such properties, which together would contain four square miles of area? Print c. Now consider how much it would cost to fence in four square miles of ranch land if, instead, it References comes as a single large square that is two miles long on each side. $ d. Which is more costly-fencing in the four, one-square-mile properties or the single four- square-mile property? OFour, one-square-mile properties The single four-square-mile property Mc raw Hill HillChapters 7 and 9 Homework i Saved Help Save & Exit Submit Check my work 9 You are choosing between two goods, X and Y, and your marginal utility from each is shown in the following table. 2.24 Units of X MUX Units of Y MUV points 1 20 16 16 14 12 12 8 OUT A W N 10 Book 8 4 6 Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. Print a. If your income is $9 and the prices of X and Y are $2 and $1, respectively, what quantities of each will you purchase to maximize utility? References units of X and units of Y b. What total utility will you realize? utils c. Assume that, other things remaining unchanged, the price of X falls to $1. What quantities of X and Y will you now purchase? units of X and units of Y d. Using the two prices and quantities for X, complete the table to derive the derived demand schedule (a table showing prices and quantities demanded) for X. Instructions: Start with the highest price first. Quantity Price of X Demanded of x $ $ Mc Graw Hill
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


