Question: 1. Consider a so-called 'open system', i.e., a volume of 1L demineralized water is out into the open air at 25C. Na,C204 (sodium oxalate,
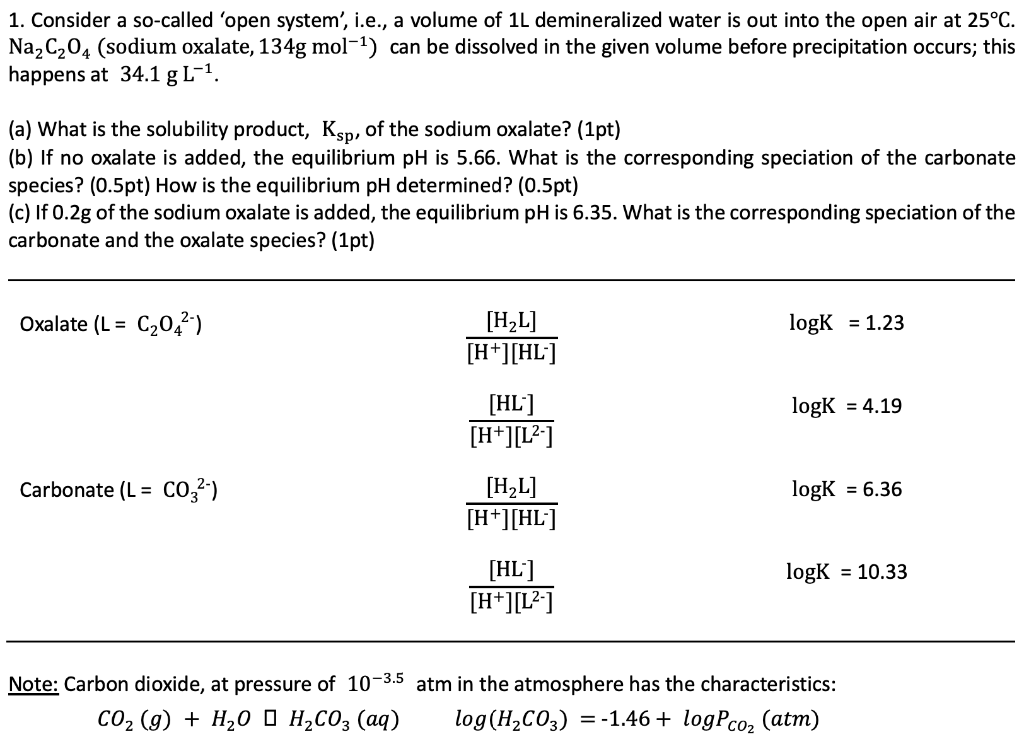

1. Consider a so-called 'open system', i.e., a volume of 1L demineralized water is out into the open air at 25C. Na,C204 (sodium oxalate, 134g mol-1) can be dissolved in the given volume before precipitation occurs; this happens at 34.1 g L-1. (a) What is the solubility product, Ksp, of the sodium oxalate? (1pt) (b) If no oxalate is added, the equilibrium pH is 5.66. What is the corresponding speciation of the carbonate species? (0.5pt) How is the equilibrium pH determined? (0.5pt) (c) If 0.2g of the sodium oxalate is added, the equilibrium pH is 6.35. What is the corresponding speciation of the carbonate and the oxalate species? (1pt) [H,L] [H*][HL*] Oxalate (L = C20,) logK = 1.23 [HL] [H*][L*] logK = 4.19 [H,L] [H*][HL*] Carbonate (L = co,?) logK = 6.36 [HL] [H*][L*] logk = 10.33 Note: Carbon dioxide, at pressure of 10-3.5 atm in the atmosphere has the characteristics: , (0) + H, ,, () log(H,CO3) = -1.46 + logPco, (atm) Surface water is sampled with a Winkler bottle of 297.6mL. In the analysis 4mL of MnSO4 solution and 4mL of KOH/KI are added. After adding the acid, using 2.5mL of H2S04, the solution is brought into an Erlenmeyer. The subsequent titration requires 10.4ml of a 0.035M Na,S203 solution. What is the value for DO?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 a Ksp 00659 or 65910 2 b At pH566 log K636 s... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (2 attachments)
636a1ece1227b_241561.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
636a1ece1227b_241561.docx
120 KBs Word File


