Question: Choose a real life problem (problems you could have at work, home, school, etc. ) and apply 1 quantitative method from the following 3: Linear
Choose a real life problem (problems you could have at work, home, school, etc. ) and apply 1 quantitative method from the following 3: Linear programming, Integer Programming, Queing Analysis
PLEASE USE THE FOLLOWING FORMAT TO ANSWER THE QUESTION:
Problem: ____
Scenario: ____
Objective: ____
Quantitative Method: ____
Tasks: ____
Possible results, conclusions, and recommendations: ____
Here are 2 examples: 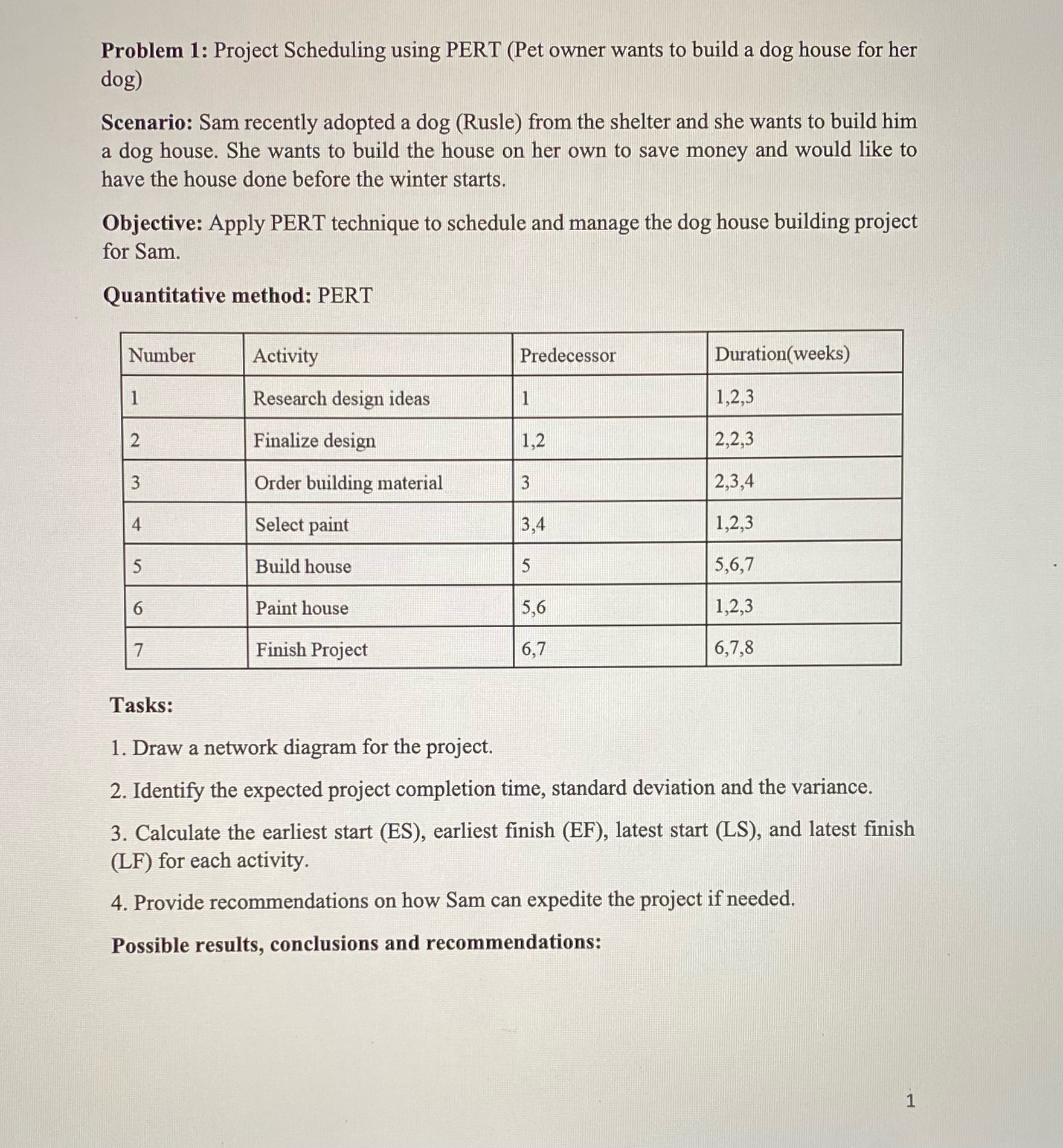

Problem 1: Project Scheduling using PERT (Pet owner wants to build a dog house for her dog) Scenario: Sam recently adopted a dog (Rusle) from the shelter and she wants to build him a dog house. She wants to build the house on her own to save money and would like to have the house done before the winter starts. Objective: Apply PERT technique to schedule and manage the dog house building project for Sam. Quantitative method: PERT Tasks: 1. Draw a network diagram for the project. 2. Identify the expected project completion time, standard deviation and the variance. 3. Calculate the earliest start (ES), earliest finish (EF), latest start (LS), and latest finish (LF) for each activity. 4. Provide recommendations on how Sam can expedite the project if needed. Possible results, conclusions and recommendations: Problem 2: Maximizing Profits from Online Jewelry Sales Scenario: Steve Smith wants to start selling jewelry online. Steve can only work a maximum of 50 hours a week. It takes 4 hours to make a silver ring, 5 hours to make a copper ring, and 3.5 hours to make a brass ring. He can buy up to 70 grams of silver a week for $0.70 per gram and must buy more than 5 grams of brass a week for $0.55. He can buy as much copper as he can produce rings. Each silver ring takes up to 10 grams of silver to make, and the brass rings take 14 grams. Steve can sell up to 12 rings each week and does not want to make more rings than he can sell. Steve also must pay an online fee for every ring he sells, and he puts aside $35 to cover this. He pays $2 per silver ring, $1 per copper ring, and $0.50 per brass ring. Steve makes a profit of $30 per silver ring, $15 per copper ring, and $13.50 per brass ring. Steve wants to figure out how many copper, silver, and brass rings to produce each week to maximize his profits. Objective: Steve Smith aims to maximize his weekly profits from selling silver, copper, and brass rings online, considering constraints on production time, material availability, sales limits, and associated costs. Quantitative method: Linear Programming Tasks: 1. Define decision variables. 2. Formulate the objective function. 3. Set up constraints. 4. Solve the Linear programming problem. 5. Interpret the solution. Possible results, conclusions and recommendations
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


