Question: class Feline { } public String type public Feline () { } } public class Cougar extends Feline { public Cougar () { System.out.print
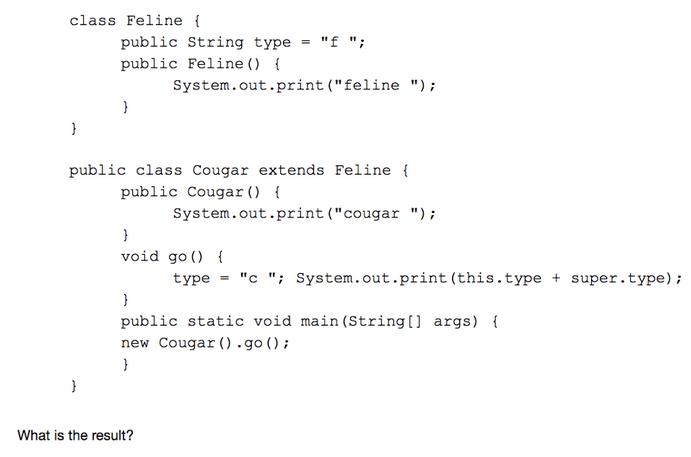
class Feline { } public String type public Feline () { } } public class Cougar extends Feline { public Cougar () { System.out.print ("cougar "); = "f "; System.out.print("feline "); } void go () { What is the result? type = "c"; System.out.print(this.type + super.type); } public static void main(String[] args) { new Cougar ().go(); }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
the resul... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


