Question: Class Management I Help Energy and Work Part 2 Begin Date: 4/1/2022 12:01:00 AM -- Due Date: 4/15/2022 11:59:00 PM End Date: 5/15/2022 11:59:00 PM
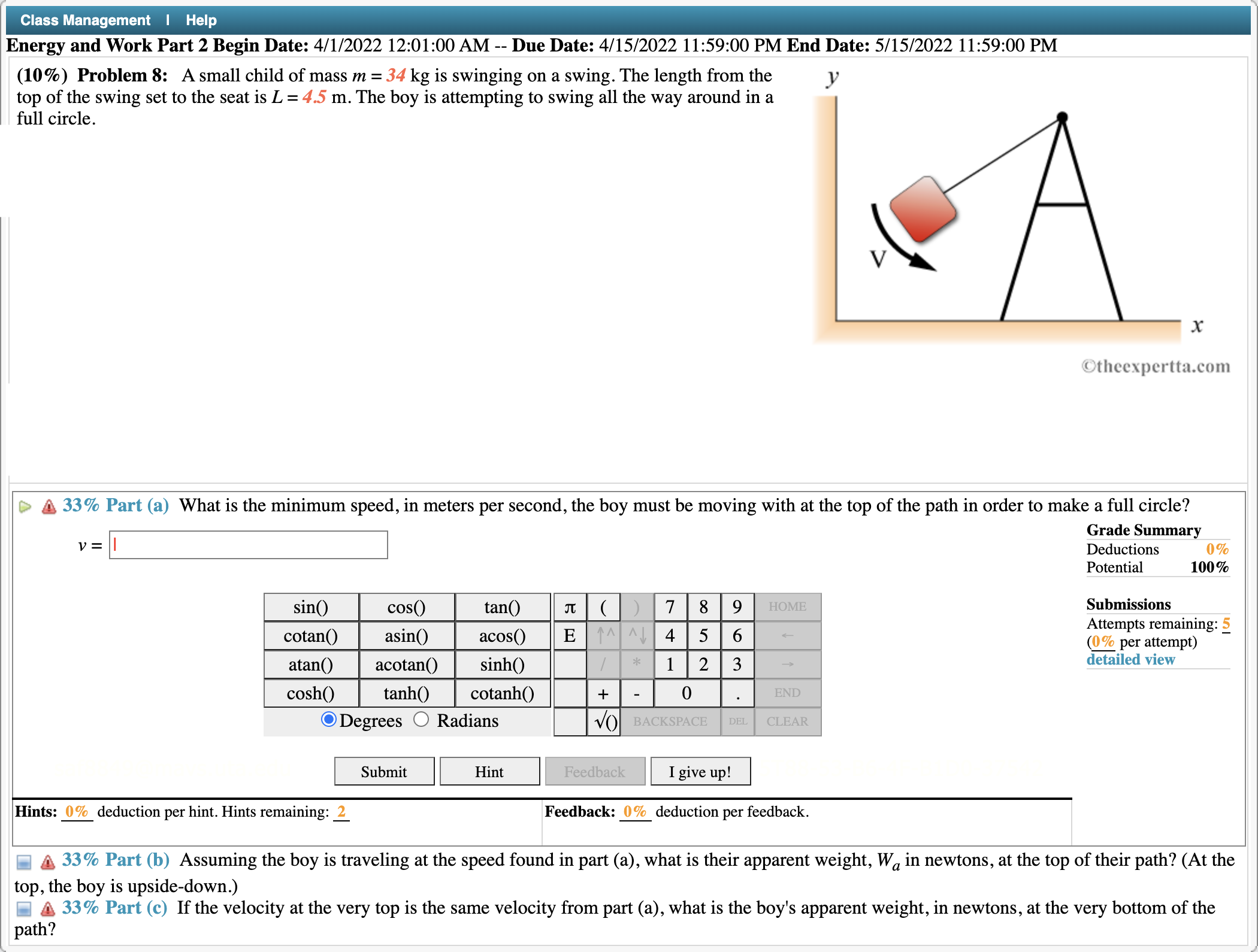
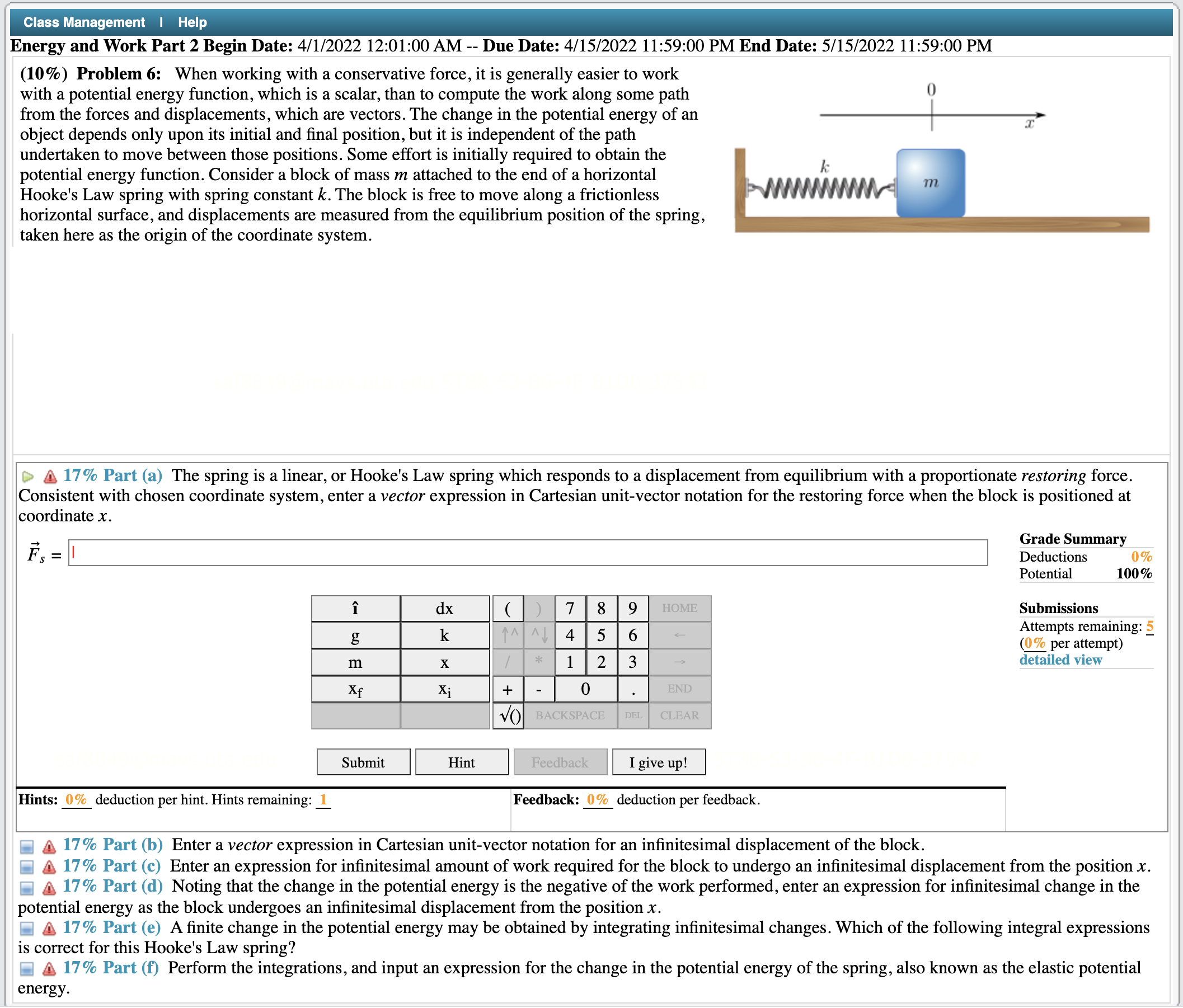
Class Management I Help Energy and Work Part 2 Begin Date: 4/1/2022 12:01:00 AM -- Due Date: 4/15/2022 11:59:00 PM End Date: 5/15/2022 11:59:00 PM (10%) Problem 8: A small child of mass m = 34 kg is swinging on a swing. The length from the y top of the swing set to the seat is L = 4.5 m. The boy is attempting to swing all the way around in a full circle. x iltllccxportmxmn [> a 33% Part (a) What is the minimum speed, in meters per second, the boy must be moving with at the top of the path in order to make a full circle? Grade Summary v = I Deductions 0% Potential 100% sin() Submissions Attempts remaining: 5 mum) \"mm\" cosh() memes 0 Mans I_I- Submit Hint Feedback I give up! Hints: 0% deduction per hint. Hints remaining: 1 Feedback: 0% deduction per feedback. a 33% Part (b) Assuming the boy is traveling at the speed found in part (a), what is their apparent weight, Wa in newtons, at the top of their path? (At the top, the boy is upside-down.) & 33% Part (c) If the velocity at the very top is the same velocity from part (a), what is the boy's apparent weight, in newtons, at the very bottom of the path? \\ Class Management | Help Energy and Work Part 2 Begin Date: 4/1/2022 12:01:00 AM -- Due Date: 4/15/2022 11:59:00 PM End Date: 5/15/2022 11:59:00 PM (10%) Problem 6: When working with a conservative force, it is generally easier to work with a potential energy function, which is a scalar, than to compute the work along some path 0 from the forces and displacements, which are vectors. The change in the potential energy of an i:r' object depends only upon its initial and nal position, but it is independent of the path ' undertaken to move between those positions. Some effort is initially required to obtain the potential energy function. Consider a block of mass m attached to the end of a horizontal Hooke's Law spring with spring constant k. The block is free to move along a frictionless horizontal surface, and displacements are measured from the equilibrium position of the spring, taken here as the origin of the coordinate system. D 3 17% Part (a) The spring is a linear, or Hooke's Law spring which responds to a displacement from equilibrium with a proportionate restoring force. Consistent with chosen coordinate system, enter a vector expression in Cartesian unit-vector notation for the restoring force when the block is positioned at coordinate x. _. Grade Summary F: = I Deductions 0% Potential 100% Submissions Attempts remaining: (% per attempt) detailed view Submit Hint Feedback I give up! Hints: 0% deduction per hint. Hints remaining: 1 Feedback: 0% deduction per feedback. 5 17 % Part (b) Enter a vector expression in Cartesian unit-vector notation for an innitesimal displacement of the block. 17 % Part (c) Enter an expression for innitesimal amount of work required for the block to undergo an innitesimal displacement from the position x. 3 l7 % Part (d) Noting that the change in the potential energy is the negative of the work performed, enter an expression for innitesimal change in the potential energy as the block undergoes an innitesimal displacement from the position x. A 17% Part (e) A nite change in the potential energy may be obtained by integrating innitesimal changes. Which of the following integral expressions is correct for this Hooke's Law spring? 17 % Part (f) Perform the integrations, and input an expression for the change in the potential energy of the spring, also known as the elastic potential energy
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


