Question: class: production and operations management subject: problem chase and level loaad needs answer only for question 1 & 4 hram/Desktop/Chase%20and%20Level%20load%20problems%20text%20and%20problem%20%231%20.pdf ile using Box Scanne Planned
 class: production and operations management
class: production and operations management
subject: problem chase and level loaad
needs answer only for question 1 & 4
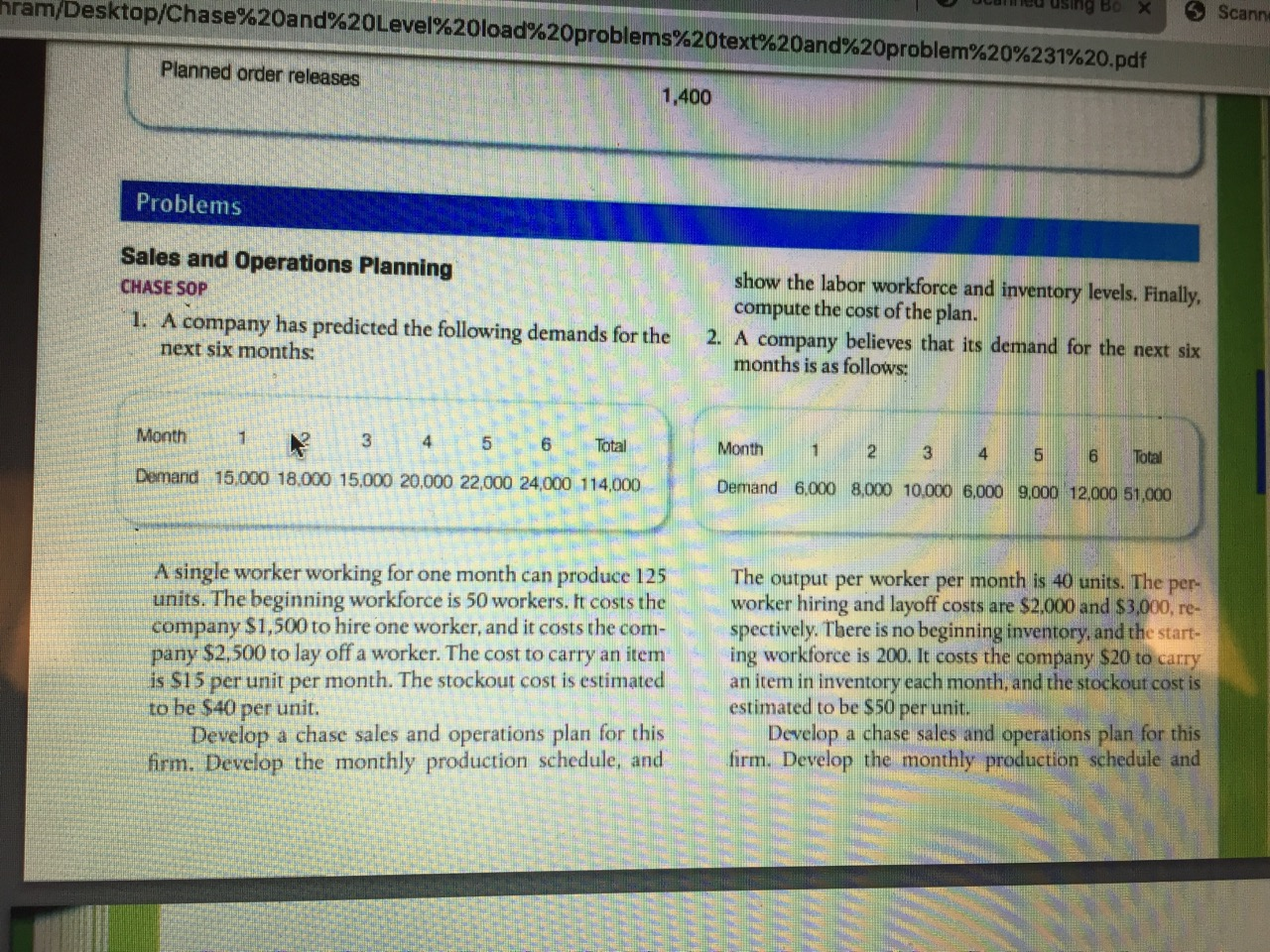
hram/Desktop/Chase%20and%20Level%20load%20problems%20text%20and%20problem%20%231%20.pdf ile using Box Scanne Planned order releases 1.400 Problems Sales and Operations Planning CHASE SOP 1. A company has predicted the following demands for the next six months show the labor workforce and inventory levels. Finally, compute the cost of the plan. A company believes that its demand for the next six months is as follows: Month 1 X 3 4 5 6 Total Demand 15,000 18.000 15,000 20,000 22,000 24,000 114.000 Month 6 Total Demand 6,000 8.000 10.000 6.000 9.000 12.000 51,000 NETURI A single worker working for one month can produce 125 units. The beginning workforce is 50 workers. It costs the company $1,500 to hire one worker, and it costs the com- pany $2,500 to lay off a worker. The cost to carry an item is $15 per unit per month. The stockout cost is estimated to be $40 per unit. Develop a chase sales and operations plan for this firm. Develop the monthly production schedule, and The output per worker per month is 40 units. The per- worker hiring and layoff costs are $2.000 and $3,000, re- spectively. There is no beginning inventory, and the start- ing workforce is 200. It costs the company $20 to carry an item in inventory each month, and the stockout cost is estimated to be $50 per unit. Develop a chase sales and operations plan for this firm. Develop the monthly production schedule and B TIFTELSEN CIVILE GE EBE NE 0,00 000 000 12. The beginning workforce is 125 employees. The monthly output per employee is 150 units. The costs to hire and lay off a worker are $2,500 and $4,000, respectively. The cost to carry an item in inventory for one month is esti- mated at $10, and the stockout cost is $25 per unit. Show the production schedule, the inventory levels, and the changes in workforce from period to period. Compute the plan's cost. The output per worker per month is 100 worker hiring and layoff costs are $2,00 respectively. There is no beginning inver starting workforce is 200. It costs the con carry an item in inventory each month, and cost is estimated to be $50 per unit. Develop a level sales and operations firm. Develop the monthly production show the labor workforce and inventory ! compute the cost of the plan. LEVEL SOP 4. A company has predicted the following demands for the next six months Month 6 Total Demand 15,000 18.000 15.000 20,000 22.000 24,000 114,000 A single worker working for one month can produce 125 units. The beginning workforce is 50 workers. It costs the company $1,500 to hire one worker, and it costs the com- pany $2,500 to lay off a worker. The cost to carry an item is $15 per unit per month. The stockout cost is estimated to be $40 per unit. Develop a level sales and operations plan for this firm. Develop the monthly production schedule and show the labor workforce and inventory levels. Finally, compute the cost of the plan. 5. Formulate a level sales and operations plan for a com pany with the following predicted demand: Capacity Planning MODELING CAPACITY 7. A process is designed to produce 500 un with a scrap rate of 1 percent and inherent in of 10 percent. With actual output at 425 un compute design capacity, available capa capacity, capacity utilization, efficiency, and measures A process is designed to produce 2,000 uni The process has a scrap rate 2 percent an cent inherent inefficiency. Assuming that output of the process is 1.750 units per hou the process design capacity, available capa capacity, capacity utilization, efficiency, and for this process? Calculate the process design capacity, availa ity, actual capacity, capacity utilization, effic output gap for a process that has been design duce 200 units per hour with a scrap rate of 0. inherent inefficiencies of 4 percent, and actu of 180 units per hour ROUGH-CUT CAPACITY PLANNING 10. The demand for three products selected from pany's sales and operations plan are shown no with each product's standard hours. Assuming Month 2 3 4 5 6 Total Demand 6,300 9.000 6.000 9.000 15.000 6.000 51,300Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


