Question: class rational { friend istream& operator>>(istream &in, rational &r); // The user is prompted to enter two integer values for the numerator and denominator of
class rational
{
friend istream& operator>>(istream &in, rational &r);
// The user is prompted to enter two integer values for the numerator and denominator of a rational number
// Postcondition: the calling rational object is assigned with values entered by the user
friend ostream& operator
// Postcondition: The rational object referenced by r is display as a / b, e.g., 1 / 2, -5 /9 (not 5 / -9), 1 / 4 (not 2 / 8, etc.).
public:
rational();
// Postcondition: declared rational number is initialized to 0 / 1.
rational(int aa, int bb);
// Postcondition: declared rational number is initialized to aa / bb.
void set(int aa, int bb);
// Postcondition: the calling rational object is set to aa / bb.
rational operator+(const rational &r2) const;
// Postcondition: returns the sum of the calling rational object and r2
rational operator-(const rational &r2) const;
// Postcondition: returns the difference of subtracting r2 from the calling rational object.
rational operator*(const rational &r2) const;
// Postcondition: returns the product of the calling rational object and r2.
rational operator/(const rational &r2) const;
// Postcondition: returns the quotient of dividing the calling rational object by r2.
int operator>(const rational&r2) const;
// Postcondition: returns 1 if the calling object is greater than r2; 0 if it is equal to r2; -1 is it is less than r2
private:
int GCD() const;
// A helper member function. You must use the Euclidean algorithm. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_algorithm
// Postcondition: returns the "greatest common divisor" between the numerator and denominator of the calling rational object
int a; // numerator part of a rational number a / b
int b; // denominator part of a rational number a / b
};
int fillArray(rational arr[], int size);
void displayArray(rational arr[], int n);
void sort(rational arr[], int n);
void swap(rational &x, rational &y);
You are asked to:
Implement all member and non-member functions defined above and stored the code in the second file and name it rational.cpp.
Write a main() function containing code to test the four non-member and all member function of the rational class. The main() function must be stored in the third file named rationalMain.cpp.
Use the separate-file approach to compile and link three file into a load module (i.e., the executable code) and run the program.
The output of your program should be similar to the following sample display. Note that you must enter at least six different rational numbers into the array in testing the sort function. You may sort the array in either ascending or descending order or both.
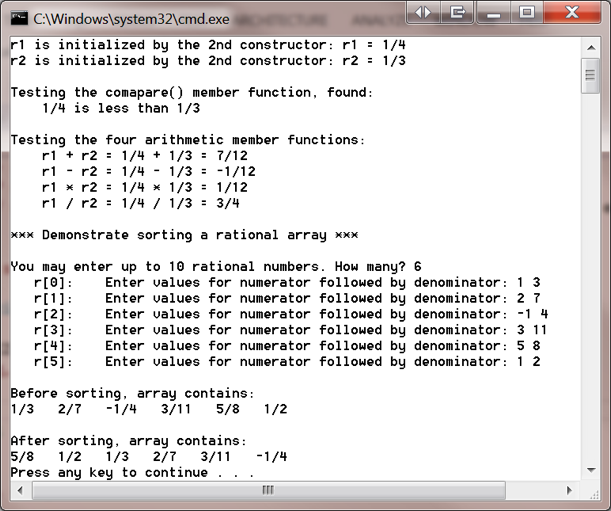
C.\Windows system32\cmd.exe rl is initialized by the 2nd constructor: rl 1/4 r2 is initialized by the 2nd constructor: r2 1/3 Testing the comapare) member function, found 1/ is less than 1/3 Testing the four arithmetic member functions r1 r21/4 1/3 7/12 r1 r2 1/4 1/31/12 rl r2 1/4 1/33/4 xx Demonstrate sorting a rational array xx You may enter up to 10 rational numbers. How many?6 r[0] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator: 1 3 r1 Enter values for numerator followed by denominator 27 r[2] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator: -1 r[3] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator: 3 11 r[4] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator: 5 8 r[5] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator 1 2 Before sorting, array contains: After sorting, array contains: Press any key to continue . . C.\Windows system32\cmd.exe rl is initialized by the 2nd constructor: rl 1/4 r2 is initialized by the 2nd constructor: r2 1/3 Testing the comapare) member function, found 1/ is less than 1/3 Testing the four arithmetic member functions r1 r21/4 1/3 7/12 r1 r2 1/4 1/31/12 rl r2 1/4 1/33/4 xx Demonstrate sorting a rational array xx You may enter up to 10 rational numbers. How many?6 r[0] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator: 1 3 r1 Enter values for numerator followed by denominator 27 r[2] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator: -1 r[3] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator: 3 11 r[4] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator: 5 8 r[5] Enter values for numerator followed by denominator 1 2 Before sorting, array contains: After sorting, array contains: Press any key to continue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


