Question: Clipboard Font Alignment Number BE Sty D11 X + fx 27 E . B D 1 Payer Full Rate Contracted Rate Contractual Allowance 2 FHP
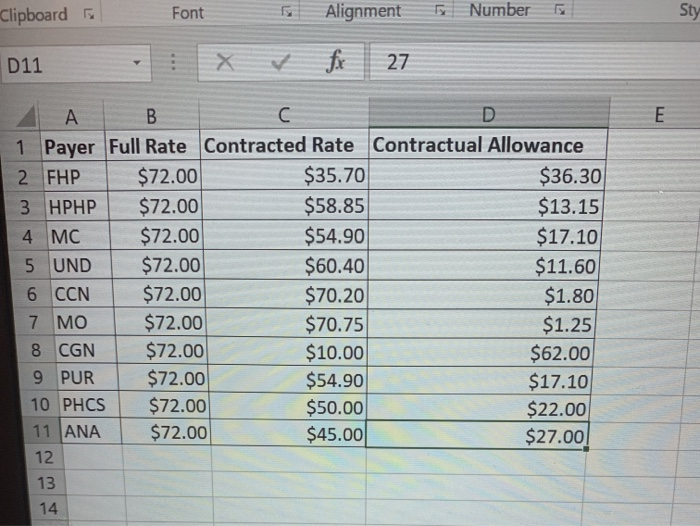

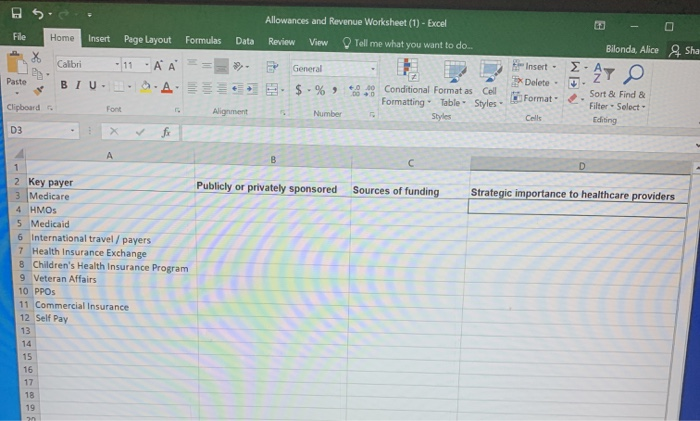
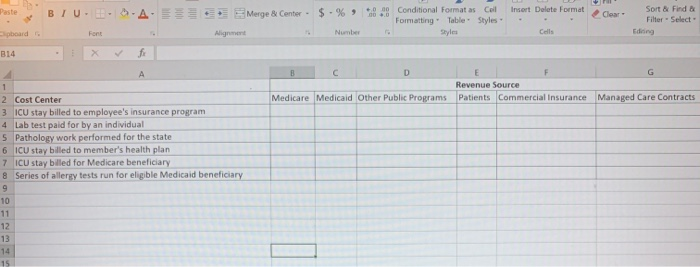

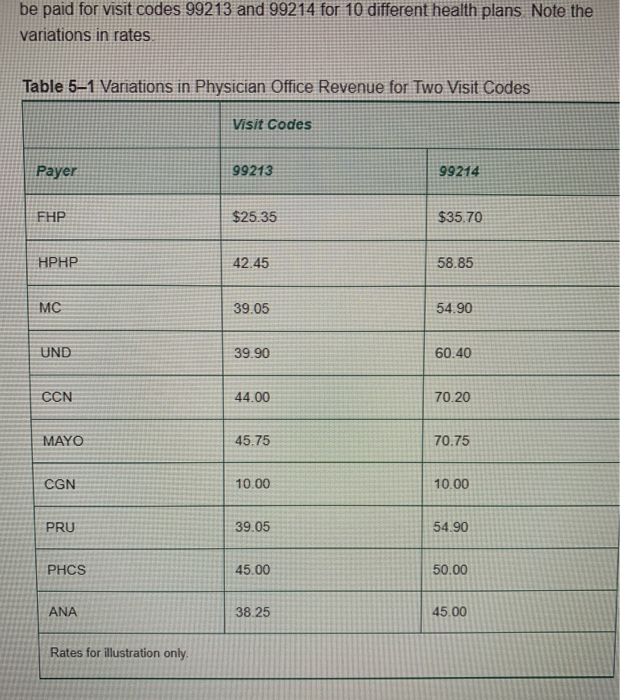
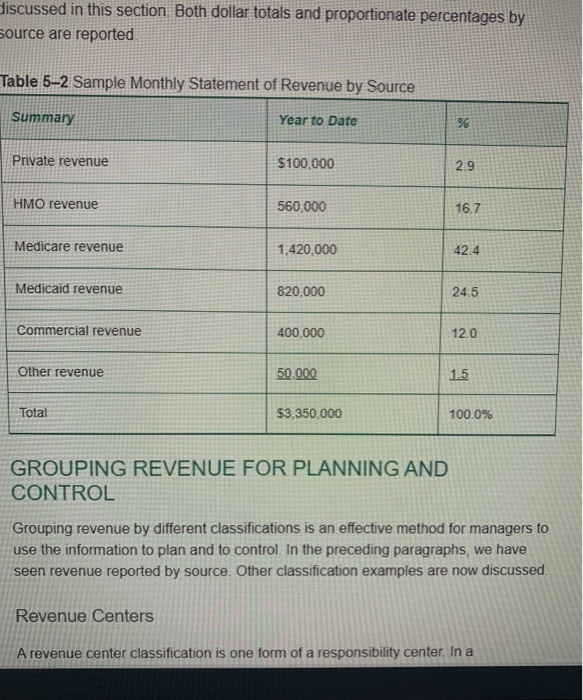
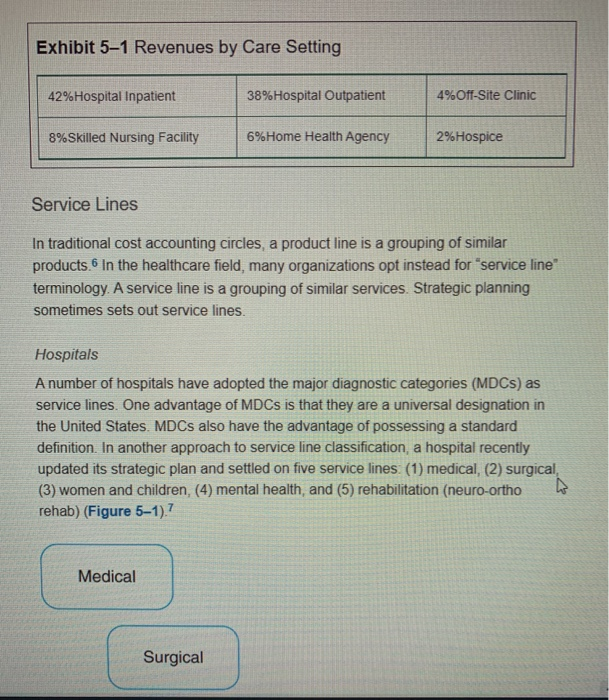
Clipboard Font Alignment Number BE Sty D11 X + fx 27 E . B D 1 Payer Full Rate Contracted Rate Contractual Allowance 2 FHP $72.00 $35.70 $36.30 3 HPHP $72.00 $58.85 $13.15 4 MC $72.00 $54.90 $17.10 5 UND $72.00 $60.40 $11.60 6 CCN $72.00 $70.20 $1.80 7 MO $72.00 $70.75 $1.25 8 CGN $72.00 $10.00 $62.00 9 PUR $72.00 $54.90 $17.10 10 PHCS $72.00 $50.00 $22.00 11 ANA $72.00 $45.00 $27.00 12 13 14 Section 2: Complete section two (tab two on the excel spreadsheet) for the second part of the assignment. On the spreadsheet, complete columns B, C and D. In column B, indicated if the payer is publicly sponsored (taxes dollars) or privately sponsored (employer or individual purchased). In column C, list where the funds come to purchase the insurance (federal government, state government, employer expense, etc). In column D, provide a short summary of why the payer is important to healthcare providers. Section 3: Review the six situations located on the third tab of the downloaded spread sheet. Each situation is an unique service provided by a healthcare provider that will be reimbursed by a healthcare payer. In columns B through G for each situation, indicate with an X if the payer listed in each column will reimburse the provider for the healthcare service being provided. For example, for an "ICU stay billed to employee's insurance program," would Medicare, Medicaid, other public programs, patients, commercial insurance or managed care pay for this service? Indicate with an X if the payer would pay for this service. Remember, rows can have multiple Xs since multiple payers can reimburse for the same service. Allowances and Revenue Worksheet (1) - Excel File Home Insert Page Layout Formulas Data Review View Tell me what you want to do... Bilonda, Alice & Sha General - Paste Calibri AA = BIU.9. A. Font Alignment Insert - Delete- Format 270 Clipboard $ -% 6.8 Conditional Format as Cell Formatting Table - Styles Number Styles Sort & Find & Filter - Select- Editing Cells D3 X B C D Publicly or privately sponsored Sources of funding Strategic importance to healthcare providers 2 Key payer 3 Medicare 4 HMOs 5 Medicaid 6 International travel/payers 7 Health Insurance Exchange 8 Children's Health Insurance Program 9 Veteran Affairs 10 PPOS 11 Commercial Insurance 12 Self Pay 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2. Paste BIUDAMerge & Center - $ -%% Insert Delete Format +0.00 Conditional Format as Coil Formatting Table Styles Clear Sort & Find Filter - Select - Edining Sipboard Font Alignment Number Cells B14 f B D G Medicare Medicaid Other Public Programs Revenue Source Patients Commercial Insurance Managed Care Contracts A 1 2 Cost Center 3 ICU stay billed to employee's insurance program 4 Lab test paid for by an individual 5 Pathology work performed for the state 6 ICU stay billed to member's health plan 7 ICU stay billed for Medicare beneficiary 8 Series of allergy tests run for eligible Medicaid beneficiary 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 FIFTH EDITION HEALTH CARE FINANCE Basic Tools For Nonfinancial Managers CHAPTER 5: Revenues (Inflow) OLFor/Shutterstock Progress Note After completing this chapter, you should be able to 1. Understand how receiving revenue for services is a revenue stream 2. Recognize contractual allowances and discounts and their impact on revenue. 3. Understand the differences in sources of healthcare revenue. 4. See how to group revenue for planning and control. be paid for visit codes 99213 and 99214 for 10 different health plans Note the variations in rates Table 51 Variations in Physician Office Revenue for Two Visit Codes Visit Codes Payer 99213 99214 FHP $25.35 $35.70 HPHP 42.45 58.85 MC 39.05 54.90 UND 39.90 60.40 CCN 44.00 70.20 MAYO 45.75 70.75 CGN 10.00 10.00 PRU 39.05 54.90 PHCS 45.00 50.00 ANA 38.25 45.00 Rates for illustration only discussed in this section Both dollar totals and proportionate percentages by source are reported. Table 5-2 Sample Monthly Statement of Revenue by Source Summary Year to Date % Private revenue $100,000 2.9 HMO revenue 560,000 16.7 Medicare revenue 1,420,000 42.4 Medicaid revenue 820,000 24.5 Commercial revenue 400,000 120 Other revenue 50.000 1.5 Total $3,350,000 100.0% GROUPING REVENUE FOR PLANNING AND CONTROL Grouping revenue by different classifications is an effective method for managers to use the information to plan and to control. In the preceding paragraphs, we have seen revenue reported by source. Other classification examples are now discussed. Revenue Centers A revenue center classification is one form of a responsibility center. In a Exhibit 5-1 Revenues by Care Setting 42% Hospital Inpatient 38%Hospital Outpatient 4% Off-Site Clinic 8% Skilled Nursing Facility 6%Home Health Agency 2%Hospice Service Lines In traditional cost accounting circles, a product line is a grouping of similar products. In the healthcare field, many organizations opt instead for service line terminology. A service line is a grouping of similar services. Strategic planning sometimes sets out service lines. Hospitals A number of hospitals have adopted the major diagnostic categories (MDCs) as service lines. One advantage of MDCs is that they are a universal designation in the United States. MDCs also have the advantage of possessing a standard definition. In another approach to service line classification, a hospital recently updated its strategic plan and settled on five service lines: (1) medical, (2) surgical, (3) women and children, (4) mental health, and (5) rehabilitation (neuro-ortho rehab) (Figure 5-1).7 Medical Surgical Clipboard Font Alignment Number BE Sty D11 X + fx 27 E . B D 1 Payer Full Rate Contracted Rate Contractual Allowance 2 FHP $72.00 $35.70 $36.30 3 HPHP $72.00 $58.85 $13.15 4 MC $72.00 $54.90 $17.10 5 UND $72.00 $60.40 $11.60 6 CCN $72.00 $70.20 $1.80 7 MO $72.00 $70.75 $1.25 8 CGN $72.00 $10.00 $62.00 9 PUR $72.00 $54.90 $17.10 10 PHCS $72.00 $50.00 $22.00 11 ANA $72.00 $45.00 $27.00 12 13 14 Section 2: Complete section two (tab two on the excel spreadsheet) for the second part of the assignment. On the spreadsheet, complete columns B, C and D. In column B, indicated if the payer is publicly sponsored (taxes dollars) or privately sponsored (employer or individual purchased). In column C, list where the funds come to purchase the insurance (federal government, state government, employer expense, etc). In column D, provide a short summary of why the payer is important to healthcare providers. Section 3: Review the six situations located on the third tab of the downloaded spread sheet. Each situation is an unique service provided by a healthcare provider that will be reimbursed by a healthcare payer. In columns B through G for each situation, indicate with an X if the payer listed in each column will reimburse the provider for the healthcare service being provided. For example, for an "ICU stay billed to employee's insurance program," would Medicare, Medicaid, other public programs, patients, commercial insurance or managed care pay for this service? Indicate with an X if the payer would pay for this service. Remember, rows can have multiple Xs since multiple payers can reimburse for the same service. Allowances and Revenue Worksheet (1) - Excel File Home Insert Page Layout Formulas Data Review View Tell me what you want to do... Bilonda, Alice & Sha General - Paste Calibri AA = BIU.9. A. Font Alignment Insert - Delete- Format 270 Clipboard $ -% 6.8 Conditional Format as Cell Formatting Table - Styles Number Styles Sort & Find & Filter - Select- Editing Cells D3 X B C D Publicly or privately sponsored Sources of funding Strategic importance to healthcare providers 2 Key payer 3 Medicare 4 HMOs 5 Medicaid 6 International travel/payers 7 Health Insurance Exchange 8 Children's Health Insurance Program 9 Veteran Affairs 10 PPOS 11 Commercial Insurance 12 Self Pay 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2. Paste BIUDAMerge & Center - $ -%% Insert Delete Format +0.00 Conditional Format as Coil Formatting Table Styles Clear Sort & Find Filter - Select - Edining Sipboard Font Alignment Number Cells B14 f B D G Medicare Medicaid Other Public Programs Revenue Source Patients Commercial Insurance Managed Care Contracts A 1 2 Cost Center 3 ICU stay billed to employee's insurance program 4 Lab test paid for by an individual 5 Pathology work performed for the state 6 ICU stay billed to member's health plan 7 ICU stay billed for Medicare beneficiary 8 Series of allergy tests run for eligible Medicaid beneficiary 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 FIFTH EDITION HEALTH CARE FINANCE Basic Tools For Nonfinancial Managers CHAPTER 5: Revenues (Inflow) OLFor/Shutterstock Progress Note After completing this chapter, you should be able to 1. Understand how receiving revenue for services is a revenue stream 2. Recognize contractual allowances and discounts and their impact on revenue. 3. Understand the differences in sources of healthcare revenue. 4. See how to group revenue for planning and control. be paid for visit codes 99213 and 99214 for 10 different health plans Note the variations in rates Table 51 Variations in Physician Office Revenue for Two Visit Codes Visit Codes Payer 99213 99214 FHP $25.35 $35.70 HPHP 42.45 58.85 MC 39.05 54.90 UND 39.90 60.40 CCN 44.00 70.20 MAYO 45.75 70.75 CGN 10.00 10.00 PRU 39.05 54.90 PHCS 45.00 50.00 ANA 38.25 45.00 Rates for illustration only discussed in this section Both dollar totals and proportionate percentages by source are reported. Table 5-2 Sample Monthly Statement of Revenue by Source Summary Year to Date % Private revenue $100,000 2.9 HMO revenue 560,000 16.7 Medicare revenue 1,420,000 42.4 Medicaid revenue 820,000 24.5 Commercial revenue 400,000 120 Other revenue 50.000 1.5 Total $3,350,000 100.0% GROUPING REVENUE FOR PLANNING AND CONTROL Grouping revenue by different classifications is an effective method for managers to use the information to plan and to control. In the preceding paragraphs, we have seen revenue reported by source. Other classification examples are now discussed. Revenue Centers A revenue center classification is one form of a responsibility center. In a Exhibit 5-1 Revenues by Care Setting 42% Hospital Inpatient 38%Hospital Outpatient 4% Off-Site Clinic 8% Skilled Nursing Facility 6%Home Health Agency 2%Hospice Service Lines In traditional cost accounting circles, a product line is a grouping of similar products. In the healthcare field, many organizations opt instead for service line terminology. A service line is a grouping of similar services. Strategic planning sometimes sets out service lines. Hospitals A number of hospitals have adopted the major diagnostic categories (MDCs) as service lines. One advantage of MDCs is that they are a universal designation in the United States. MDCs also have the advantage of possessing a standard definition. In another approach to service line classification, a hospital recently updated its strategic plan and settled on five service lines: (1) medical, (2) surgical, (3) women and children, (4) mental health, and (5) rehabilitation (neuro-ortho rehab) (Figure 5-1).7 Medical Surgical
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


