Question: Code for Linked List: public interface Queue { public void enqueue(Object n); // add an object at the rear of the queue public Object dequeue();
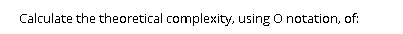
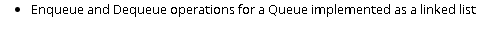

Code for Linked List:
public interface Queue {
public void enqueue(Object n); // add an object at the rear of the queue
public Object dequeue(); // remove an object from the front of the queue
public boolean isEmpty(); // true if queue is empty
public boolean isFull(); // true if queue is full (if it has limited storage)
public Object front(); // examine front object on queue without removing it
}
public class Node { // Instance variables: private Object element; private Node next;
/** Creates a node with null references to its element and next node. */ public Node() { this(null, null); }
/** Creates a node with the given element and next node. */ public Node(Object e, Node n) { element = e; next = n; } // Accessor methods: public Object getElement() { return element; } public Node getNext() { return next; }
// Modifier methods: public void setElement(Object newElem) { element = newElem; } public void setNext(Node newNext) { next = newNext; } }
public class SLinkedList
{
protected Node head; // head node of the list
protected Node tail; // last position in the list
protected Node curr; // node referencing current position in the list
protected long size; // number of nodes in the list
/** Default constructor that creates an empty list. */
public SLinkedList() {
curr = tail = head = null;
size = 0;
}
public long size() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (head == null);
}
public Object getCurr() {
if (curr == null) // Verify that there is a current node
return null;
return curr.getElement();
}
public boolean gotoHead() {
if (isEmpty())
return false;
curr = head;
return true;
}
public boolean gotoNext() {
if (curr == tail)
return false;
curr = curr.getNext();
return true;
}
public boolean gotoTail() {
if (isEmpty())
return false;
curr = tail;
return true;
}
public void insertNext(Object el) {
if (head == null) {
insertHead(el); // If haven't inserted a head, do so now (for convenience)
return;
}
Node newnode = new Node(el, curr.getNext()); // create new node with its next node equal to curr's next node
curr.setNext(newnode); // update the next node of the current node to point to the new one
size++;
// update the tail if at the end of the list
if (tail == curr)
tail = newnode;
// make this new node the current one
curr = newnode;
}
public void deleteNext() {
if (curr == null || curr.getNext() == null) return; // no next: list empty or already at end
// update the tail if the node we are deleting is the tail
if (tail == curr.getNext())
tail = curr;
curr.setNext(curr.getNext().getNext()); // set curr's next equal to the next node's next
// Note: Garbage collector will automatically clear up the node no longer referenced
size--;
}
public void insertHead(Object el) {
Node oldhead = head;
head = new Node(el, oldhead);
size++;
curr = head;
if (size == 1) // if this is the first node, it is both head and tail
tail = head;
}
public void deleteHead() {
if (head == null) return; // list already empty
head = head.getNext();
size--;
curr = head;
if (size == 0) // if this was the only node, get rid of ref to tail as well as head
tail = null;
}
}
public class LLQueue implements Queue{
protected SLinkedList linkedList;
public LLQueue(){
linkedList = new SLinkedList(); //Creation of empty linked list
}
@Override
public void enqueue(Object n) {
if (linkedList.gotoTail()){
linkedList.insertNext(n); //Objects are added at the end of the list
}
else linkedList.insertHead(n); //If the list is empty, the element that is enqueued will be the head
}
@Override
public Object dequeue() {
if(linkedList.gotoHead()){
Object x = linkedList.getCurr();
linkedList.deleteHead();
return x; //Object is deleted and returned
}
return null; //If the list is empty, an object cannot be dequeued
}
}
Calculate the theoretical complexity, using O notation, of
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


