Question: code : /***************************************************************** * Program: multiply.C * * Purpose: implements/illustrates a recursive version of the russian * peasant's algorithm for multiplication * * Authors: *
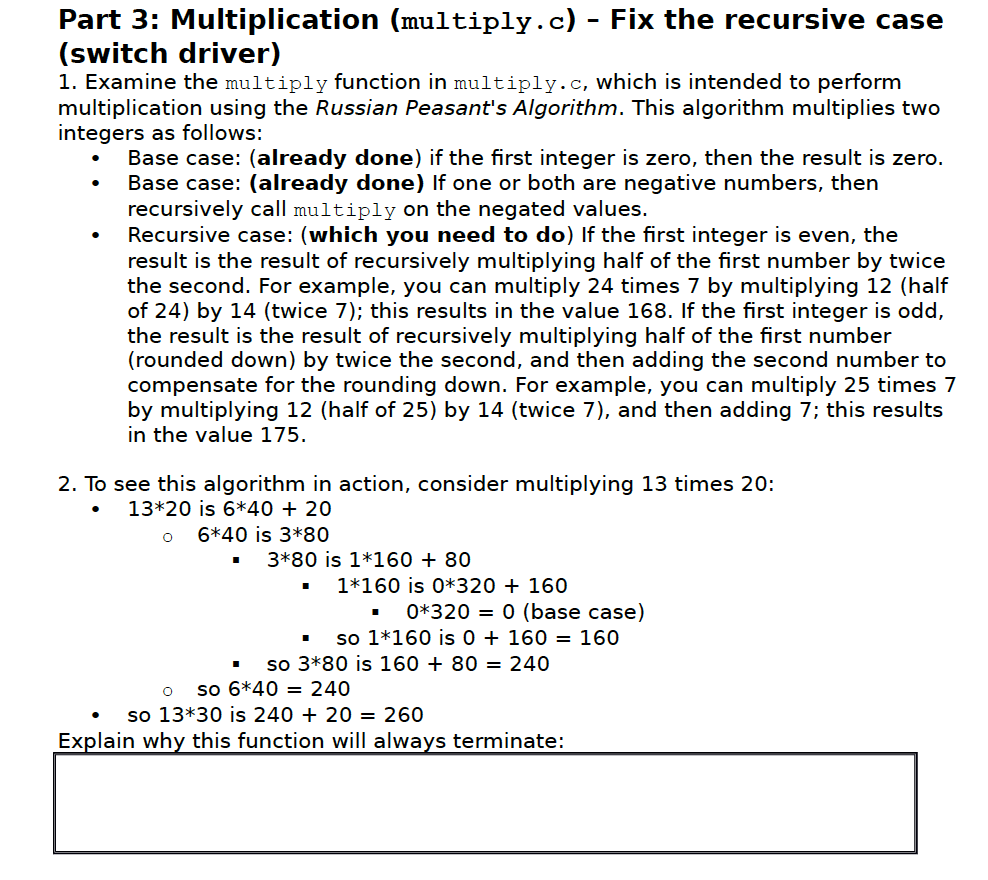
 code :
code :
/***************************************************************** * Program: multiply.C * * Purpose: implements/illustrates a recursive version of the russian * peasant's algorithm for multiplication * * Authors: * *****************************************************************/ #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


