Question: Code required in python. Class extended from: class CircularQueue: def __init__(self, size): self.size = size self.queue = [] def enqueue(self, item): if(len(self.queue))== self.size: raise IndexError(The
Code required in python.
Class extended from:
class CircularQueue: def __init__(self, size): self.size = size self.queue = [] def enqueue(self, item): if(len(self.queue))== self.size: raise IndexError("The queue is full.") else: self.queue.append(item) def dequeue(self): if len(self.queue) ==0: raise IndexError("The queue is empty.") else: item = self.queue[0] del self.queue[0] return item def peek(self): if len(self.queue) ==0: raise IndexError("The queue is empty.") else: return self.queue[0]
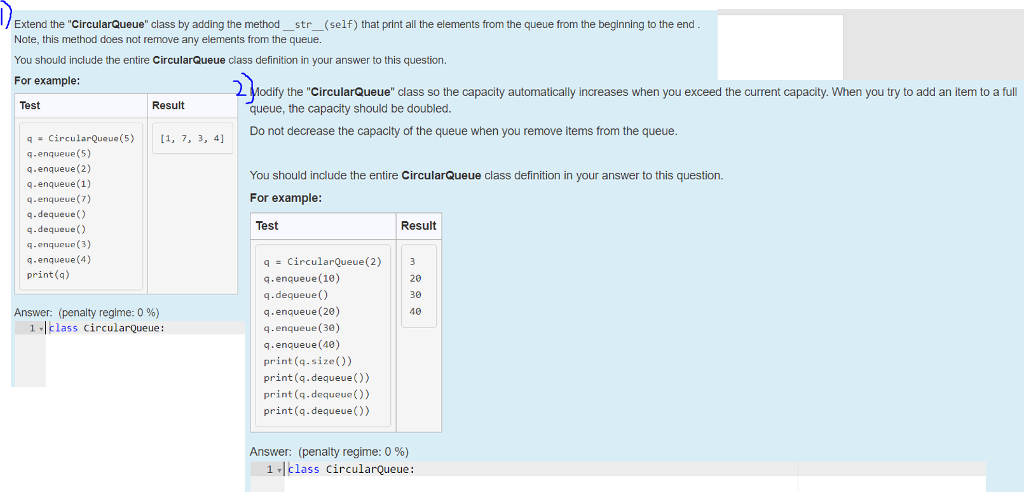
Extend the "CircularQueue" class by adding the method-str-(self) that print all the elements from the queue from the beginning to the end Note, this method does not remove any elements from the queue. You should include the entire CircularQueue class definition in your answer to this question. For example Modity the "CircularQueue" class so the capacity automatically increases when you exceed the current capacity,. When you try to add an item to a ful queue, the capacity should be doubled. Do not decrease the capacity of the queue when you remove items from the queue Test Result q# CircularQueue(5) q.enqueue(5) q.enqueue(2) q.enqueue(1) q.enqueue(7) q.dequeue) q.dequeue) q.enquou(3) q.enqueue(4) print(q) | [1, 7, 3, 4] You should include the entire CircularQueue class definition in your answer to this question. For example Test Result qCircularQueue(2)3 q.enqueue (10) q.dequeue) q.enqueue (20) q.enqueue (30) q.enqueue (40) print (q.size)) print (q.dequeue()) print (q.dequeue )) print (q.deque)) 20 30 40 Answer: (penalty regime: 0 %) 1-1 class circularQueue : Answer: (penalty regime: 0 %) 1 -lclass circularqueue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


