Question: Code with comments for each line of code please. bstree.h is provided in the pictures. main.cpp is provided in the question. Binary Search Tree Constructor
Code with comments for each line of code please. bstree.h is provided in the pictures. main.cpp is provided in the question.
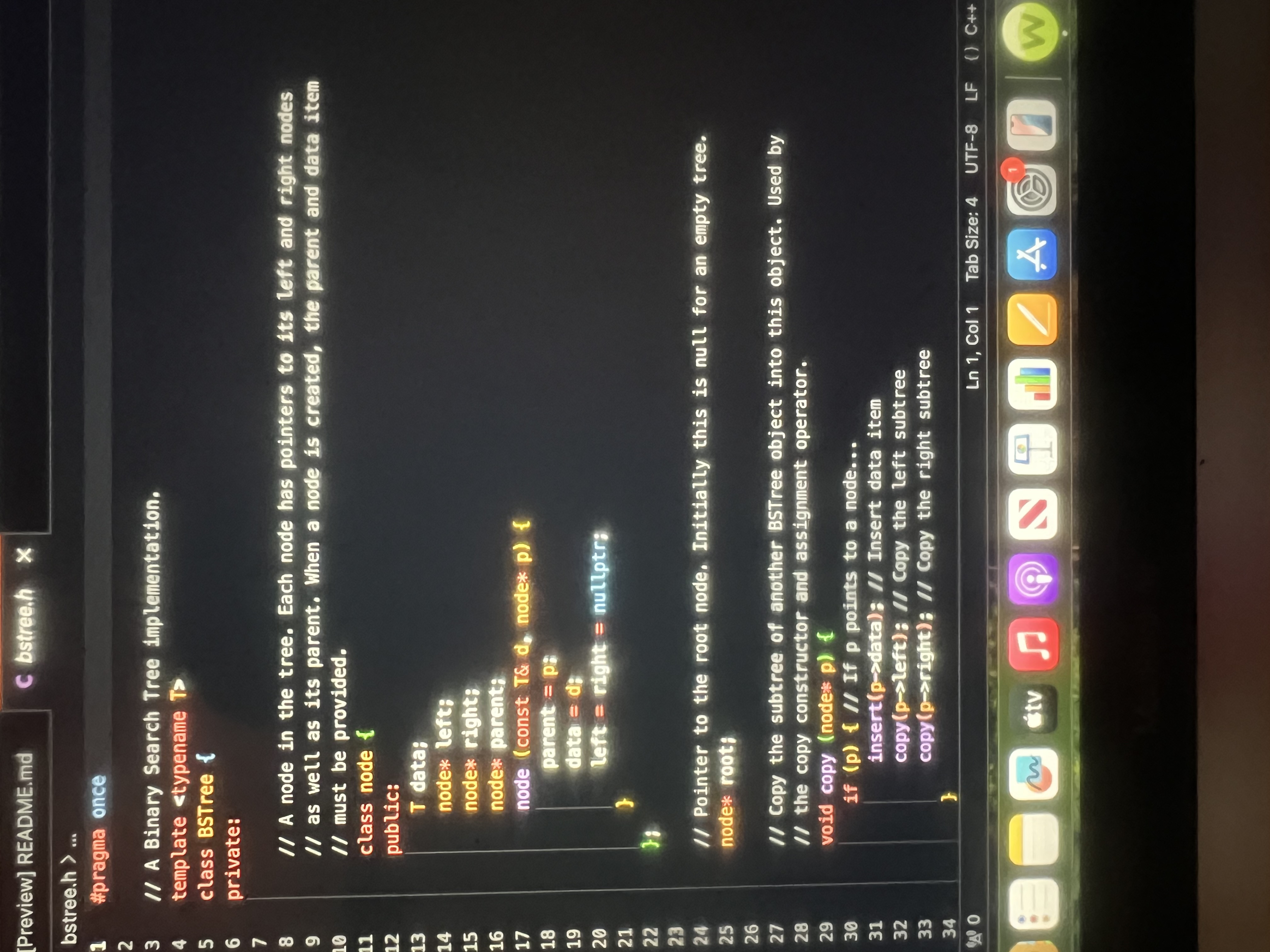
Binary Search Tree Constructor and related operations
Devise an algorithm for loading a binary search tree from a vector such that
the resulting tree is wellbalanced. In other words, your algorithm should
insert values from the vector into the tree, using BSTrees insert
function, in an order that makes searching the tree most efficient. You
should make no assumptions about the ordering of values in the given vector.
Modify the BSTree class in the supplied code as outlined below.
Constructor from a vector
Build a constructor
that takes a vector as a parameter and uses your algorithm to load the
values from that vector into the binary search tree.
The constructor prototype should be as follows:
BSTreevector v;
Note that this prototype uses a value parameter. This gives you a copy of
the supplied vector that you can manipulate as necessary.
Remember to include the vector library in bstreehit is currently not
included as it is not used in the current implementation Also, note that the
vector class has a builtin sort function should your algorithm require
that the vector be sorted.
Modify the Copy Constructor
The purpose of a copy constructor is to construct an object from another
object of the same type. The copy is one that is logically equivalent to
the given object, but may have a different internal structure. The copy
constructor implementation in the given code creates an internal structure
that is identical to the given source BSTree object.
Modify the copy constructor such that the internal structure of the new
object is wellbalanced but remains logically equivalent to the given
source object. You might do this by creating a vector of the values in
the source object and use your algorithm to load values into the new object.
Assignment Operator Overload
The purpose of the assignment operator overload is to make the destination
object logically equivalent to the source object. Again, the internal
structure may be different. The overload implemented in the given code
creates an internal stucture that is identical to that of the source
object.
Modify the assignment operator overload such that the internal structure
of the destination object is wellbalanced but remains logically
equivalent to the source object.
Test Program
Modify the supplied maincpp to set up tests that show your
implementations work as expected.
Produce output that shows the internal structure of the tree using the
preorder function
Be sure to include code in maincpp that shows all three functions
mentioned above are working as expected.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include "bstree.h
Prints a single string, used by FSTree::inorder to print all
values in the tree in correct order.
void printstring string s cout s endl;
Prints a single string preceeded by a number of hyphens, used by
BSTree::preorder to print a visual representation of the tree.
void printstringdepth string s int n
for int i ; i n; i
cout ;
cout s endl;
int main
Create a binary search tree.
BSTree t;
Insert some strings for testing.
tinsertdog;
tinsertbird;
tinsertcat;
tinsertturtle;
tinsertgiraffe;
tinsertsnake;
tinsertdeer;
tinsertgroundhog;
tinserthorse;
Output the values stored in the tree.
cout "Values stored in the tree are:
;
tinorderprintstring;
cout
;
cout "The structure of the tree is as follows:
;
tpreorderprintstringdepth;
cout
;
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


