Question: Coding in C++, create a Chunklist Program: The main menu should be: 1. Append 2. GetLength 3. GetIndex 4. Contains 5. Print 6. Remove 7.
Coding in C++, create a Chunklist Program:
The main menu should be:
1. Append
2. GetLength
3. GetIndex
4. Contains
5. Print
6. Remove
7. IsEmpty
----------------------------------//--------------------------------
Example output for (Print option):
GetLength PutItem 5 PutItem 7 PutItem 6 PutItem 9 PrintList PutItem 1 PrintList GetItem 4 GetItem 5 GetItem 9 GetItem 10 IsFull DeleteItem 5 IsFull DeleteItem 1 DeleteItem 6 DeleteItem 9 PrintList MakeEmpty PrintList Error Quit
--------------------------------------------//--------------------------------------------------
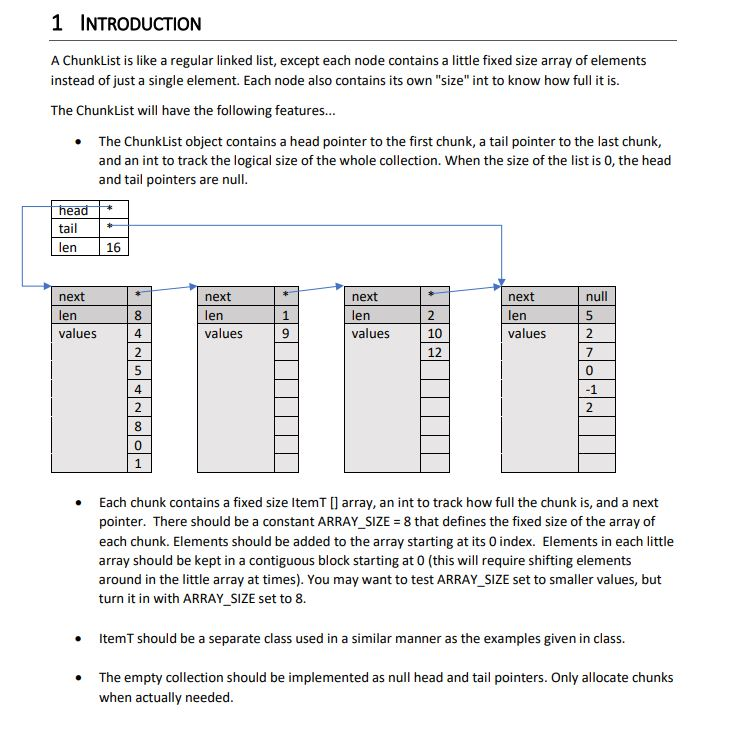

1 INTRODUCTION A Chunklist is like a regular linked list, except each node contains a little fixed size array of elements instead of just a single element. Each node also contains its own "size" int to know how full it is. The Chunklist will have the following features... The Chunklist object contains a head pointer to the first chunk, a tail pointer to the last chunk, and an int to track the logical size of the whole collection. When the size of the list is O, the head and tail pointers are null. head * len 16 next next null next len values next len values 2 len values len values Each chunk contains a fixed size Itemt [] array, an int to track how full the chunk is, and a next pointer. There should be a constant ARRAY_SIZE = 8 that defines the fixed size of the array of each chunk. Elements should be added to the array starting at its O index. Elements in each little array should be kept in a contiguous block starting at 0 (this will require shifting elements around in the little array at times). You may want to test ARRAY_SIZE set to smaller values, but turn it in with ARRAY_SIZE set to 8. Item T should be a separate class used in a similar manner as the examples given in class. The empty collection should be implemented as null head and tail pointers. Only allocate chunks when actually needed. Chunklist should implement the following methods: o Append(ItemT elem) o GetLength() (refers to the total number of elements, not the number of chunk nodes) o GetIndex(int i) (gets the item at index i) o Contains(ItemT elem) o Print 0 Remove(itemT elem) (removes first instance of elem) o IsEmpty The Append operation should add new elements at the end of the overall collection - i.e. new elements should go into the tail chunk. If the tail chunk is full, a new chunk should be added and become the new tail. We are not going to trouble ourselves shifting things around to use empty space in chunks in the middle of the list. The Remove operation should look through each chunk array until the target element is found. Since the Chunklist can potentially have duplicates of the same elements, Remove should just delete the first found instance of the element. If the chunk node is empty after removing the element, then the entire chunk should be removed from the link list. Keep a single "len" variable for the whole list that stores the total number of client data elements stored in the list. Similarly, keep a separate "len" variable in each chunk to know how full it is. Search should return true if the element if found. Otherwise it should return false. 1 INTRODUCTION A Chunklist is like a regular linked list, except each node contains a little fixed size array of elements instead of just a single element. Each node also contains its own "size" int to know how full it is. The Chunklist will have the following features... The Chunklist object contains a head pointer to the first chunk, a tail pointer to the last chunk, and an int to track the logical size of the whole collection. When the size of the list is O, the head and tail pointers are null. head * len 16 next next null next len values next len values 2 len values len values Each chunk contains a fixed size Itemt [] array, an int to track how full the chunk is, and a next pointer. There should be a constant ARRAY_SIZE = 8 that defines the fixed size of the array of each chunk. Elements should be added to the array starting at its O index. Elements in each little array should be kept in a contiguous block starting at 0 (this will require shifting elements around in the little array at times). You may want to test ARRAY_SIZE set to smaller values, but turn it in with ARRAY_SIZE set to 8. Item T should be a separate class used in a similar manner as the examples given in class. The empty collection should be implemented as null head and tail pointers. Only allocate chunks when actually needed. Chunklist should implement the following methods: o Append(ItemT elem) o GetLength() (refers to the total number of elements, not the number of chunk nodes) o GetIndex(int i) (gets the item at index i) o Contains(ItemT elem) o Print 0 Remove(itemT elem) (removes first instance of elem) o IsEmpty The Append operation should add new elements at the end of the overall collection - i.e. new elements should go into the tail chunk. If the tail chunk is full, a new chunk should be added and become the new tail. We are not going to trouble ourselves shifting things around to use empty space in chunks in the middle of the list. The Remove operation should look through each chunk array until the target element is found. Since the Chunklist can potentially have duplicates of the same elements, Remove should just delete the first found instance of the element. If the chunk node is empty after removing the element, then the entire chunk should be removed from the link list. Keep a single "len" variable for the whole list that stores the total number of client data elements stored in the list. Similarly, keep a separate "len" variable in each chunk to know how full it is. Search should return true if the element if found. Otherwise it should return false
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


