Question: COMPLETE SLUTION IN WRITTEN FORM NO IMAGEAND ONLY ORIGINAL WORK fAssume that f(x) = 6x + 14 and g(x) = 5x - 1. Find the
COMPLETE SLUTION IN WRITTEN FORM NO IMAGEAND ONLY ORIGINAL WORK
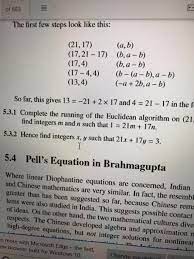





![by ph= - log[H*], where [H*] is the hydrogen ion concentration in](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2025/02/67a8c35de863c_30967a8c35dcff22.jpg)
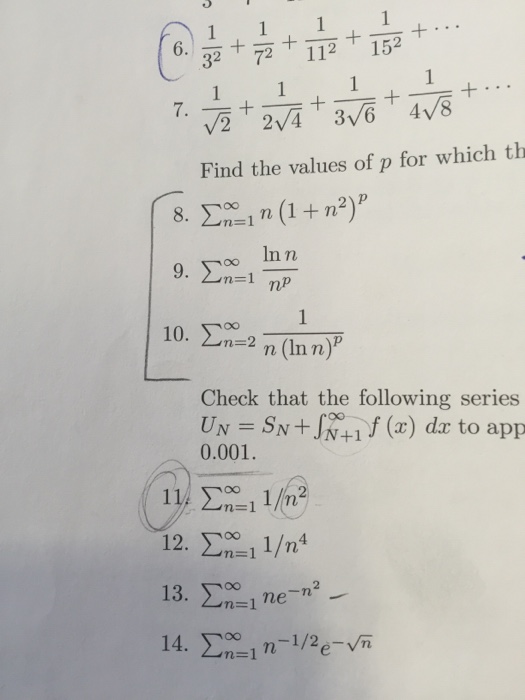
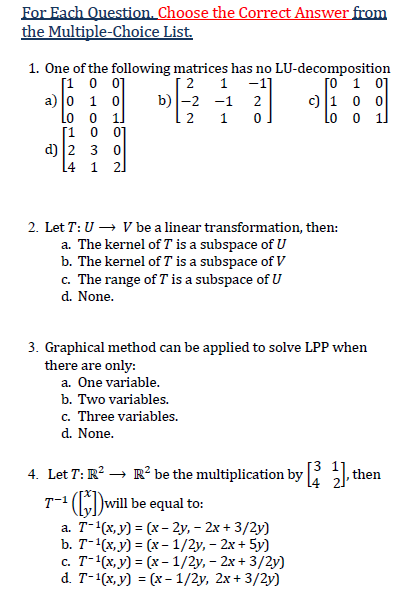
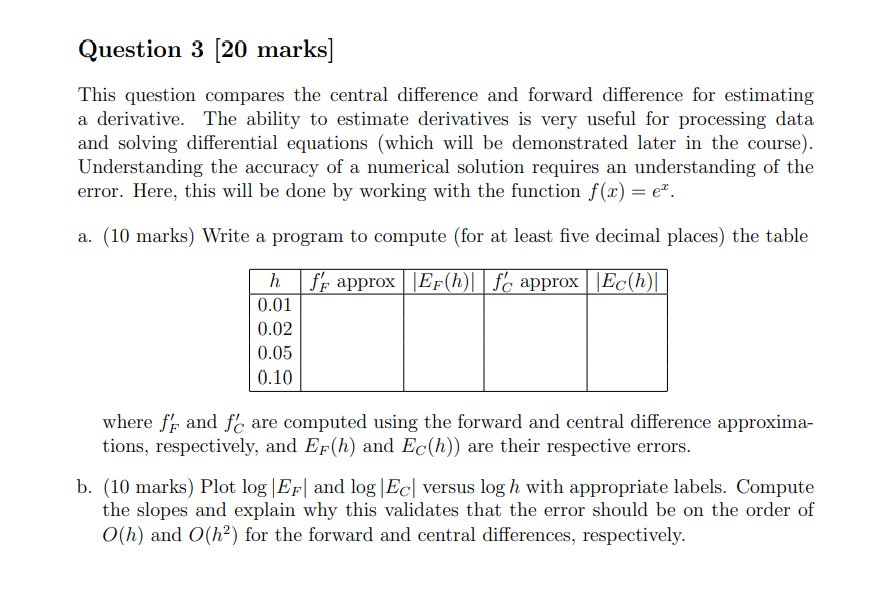
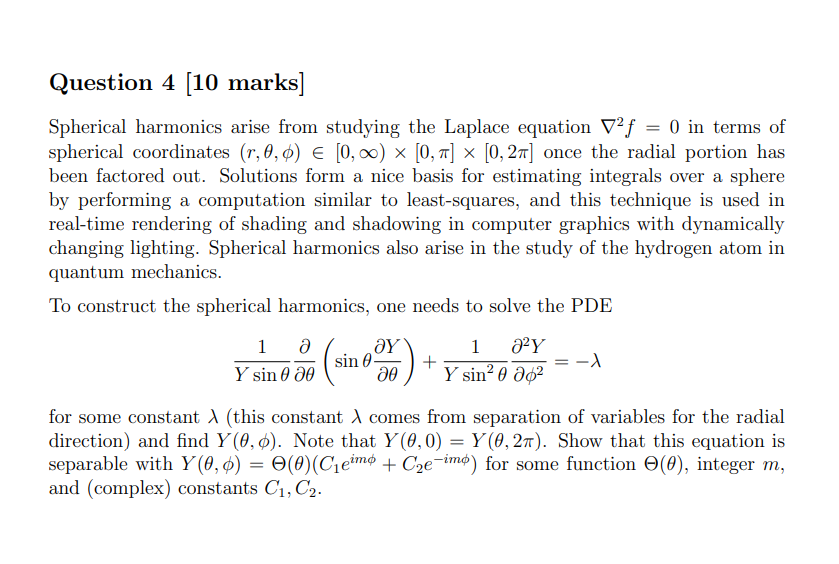
\fAssume that f(x) = 6x + 14 and g(x) = 5x - 1. Find the composition (fog)(x) (A) 30x + 20 (B) 30x + 13 (C) 30x + 69 (D) 30x + 8 The number of reports of a certain virus has increased exponentially since 1960. The current number of cases can be approximated using the function r(t)=290e.005t , where t is the number of years since 1960. Estimate the number of cases in the year 2000. (A) 708 cases (B) 266 cases (C) 354 cases (D) 337 cases In chemistry, the pH of a substance is defined by ph= - log[H*], where [H*] is the hydrogen ion concentration in moles per liter. Find the pH of a sample of lake water whose hydrogen ion concentration, [H*], is 3.05 x 10" moles per liter. (Round to the nearest tenth.) (A) 7.3 (B) 6.4 (C) 8.5 (D) 10.1 Solve the logarithmic equation In x - In (x - 9) = In 5 9 In5 (A) 45 (B) No solution (C) 4 (D) In5-1 How long will it take for $1500 deposited at 4.5% compounded continuously to grow to $1650? State your result to the nearest tenth of a year. A) 2.1 yrs (B) 1.2 yrs (C) 3.1 yrs (D) 1.8 yrs\fFor Each Question. Choose the Correct Answer from the Multiple-Choice List. 1. One of the following matrices has no LU-decomposition 1 0 0 2 1 -1 0 1 0 al 0 O b) -2 -1 2 c) 1 0 0 O O 2 1 O 0 d) 2 NO 4 2. Let 7: U - V be a linear transformation, then: a. The kernel of T is a subspace of U b. The kernel of T is a subspace of V c. The range of T is a subspace of U d. None. 3. Graphical method can be applied to solve LPP when there are only: a. One variable. b. Two variables. c. Three variables. d. None. 4. Let 7: R- - R- be the multiplication by 2/ then T- (ly]) will be equal to: a. T- 1(x, y) = (x - 2y, - 2x + 3/2y) b. T-1(x, y) = (x - 1/2y, - 2x + 5y] c. T-1(x, y) = (x - 1/2y, - 2x + 3/2y) d. T-1(x, y) = (x - 1/2y, 2x+ 3/2y)\fQuestion 3 [20 marks] This question compares the central difference and forward difference for estimating a derivative. The ability to estimate derivatives is very,r useful for processing data and solving differential equations [which will be demonstrated later in the course). Understanding the accuracy of a numerical solution requires an understanding of the error. Here, this will he done by working with the function x) = cm. a. (10 marks) Write a program to compute [for at least ve decimal places) the table where f}; and f3 are computed using the forward and central difference approxima- tions, respectively1 and EF[h) and E(h)) are their respective errors. h. (10 marks) Plot log |EF| and log |Ec| versus log I: with appropriate lahels. Compute the slopes and explain why this validates that the error should be on the order of 0(h} and 0&2) for the forward and central differences, respectively. Question 4 [10 marks] Spherical harmonics arise from studying the Laplace equation V2)\" = 0 in terms of spherical coordinates [r,3,) E [(1,010) X [0,:rr] x [0,211'] once the radial portion has been factored out. Solutions form a nice basis for estimating integrals over a sphere by performing a computation similar to least-squares, and this technique is used in real-time rendering of shading and shadowing in computer graphics with dynamically changing lighting. Spherical harmonics also arise in the study of the hydrogen atom in quantum mechanics. To construct the spherical harmonics, one needs to solve the PDE 1 a ( BY) 1 821/ . 3_ _ 3m + ran? a as? as = 4' it\"sinif'l 36' for some constant A (this constant A comes from separation of variables for the radial direction) and nd Y{S, c5). Note that Yi, 0) = 1'09, 271'). Show that this equation is separable with Y{,) = B(E](Clcim' + Cgeim) for some function 8(9), integer m, and (complex) constants Cl} 02. 4) Prove or disprove using a truth table: p -> (q=> r) = (pq)=>r 5) Prove using Boolean Algebra: ~ (pv ~q) v (~ PA ~ q) =~ P H 6) Prove using Boolean Algebra: (PA(~(~pvq)))(pq) = p 7) Create a truth table for the following logical statement: ~(p=>r) (p =>q) 8) Write the converse, inverse, and contrapositive for each of the following statements in a sentence form (do not use symbols): a. "If the Orioles get better pitching, then they will not come in last place. b. "If n is divisible by 6, then n is divisible by 2 and n is divisible by 3." 9) Use a truth table to determine if each argument form is valid: paq->r par pv ~ q b. q->r . ~ q->P :: ( pvq) -rQuestion 1 [15 marks] This question investigates a nonstande inner product on 1&2 that arises in quantum mechanics [and other areas of mathematics). which comes from looking at reections of a triangle. The goal of this problem is to show that mm} = {(vijvgla(w1.w2)}= [t1 \"2] [f1 31] [m] we is an inner product on R2 and to compute an orthogonal basis. a. (5 marks) Show that (mm) = (is, 11.1). b. {7' marks) Show that (my) 1: U and that {1.1.2.1} = U if and onlyr if v = 0. c. {3 marks) Find a vector orthogonal to c1 = [1. [1) with respect to this inner product. 3. Proof using propositional logic properties Using propositional logic properties and other logical equivalences (not truth tables), prove the following statements: 1. (pV q) V (p V -q) is a tautology 2. ((p- r) A (q - r)A(pvq)) -r is a tautology 3. (pvq) A (-pA -q) is a contradiction 4. -(q - p) A(pAqAs - r) Ap is a contradiction 5. ( p - q) A (p -r) =p - (qAr) Solution: 1. (pvq) V (p V -q) = p V q V -q= P VT = T 2. ((p - r) A(q - r)A(pvq)) -r= (p/q- r) V(pvq) =-pV-qVrVpVq =TVTVr=T 3. (pvq) A (-PA -q) = (pv q) A -(PV q) = F 4. -(q - p) A(pqAs - r) Ap= (paqAs - r) A-(-qVp)Ap=(pqAs - r) AqA-php= (pAqAs- r) AqAFF 5. (p- q) A (p-r) = (-pvq) A ( -pvr) = -pv (qAr) = p -> (qAr). 6. + 72 + + 32 112 152 1 . . 7. + + + 2V/4 3 v 6 4 8 Find the values of p for which th 8 . Inn ( 1 + n 2 ) p In n 9. En=1 np 1 10. En=2 n ( Inn) P Check that the following series UN = SN+SN+If (x) dx to app 0.001. 114 En=1 12 12. En= 1 100 ne-n? 13. En= 14. En-in-1/2e- Vn
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


