Question: Complete the C# Merge-Sort Program by completing the methods in this program. This program consists of two parts: 1. Main - which runs the entire
Complete the C# Merge-Sort Program by completing the methods in this program. This program consists of two parts:
1. Main - which runs the entire program.
2. LinkedNode - LinkedNode is a class containing methods to preform Merge-Sort. The goal is to complete these methods These Methods are:
- Sort
-SortFromList
-AddLast
-AddFirst
-InsertAfter
-InsertBefore
- Find
-SetNext
-PrintList
These functions are used in larger functions called:
- DoMergeSort
- SplitList
- MergeLists
- SwapNodes
Algorithms written in C are provided for the Merge, doMerge, and SwapNodes methods
Below is the code for main()
public static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello Merge Sort World!"); LinkNode
Next, this is the code for the LinkedNode Class This is the where the methods are that need to be completed:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; namespace MergeSort { public class LinkNode
public LinkNode
Merge code algorithm in C:
void doMergeSort(contact **head, int sortBy, int sortOrder); void splitList (contact *head, contact **h1, contact **h2); contact *mergeLists(contact *l1, contact *l2); void swapNodes(contact **node1, contact **node2);
doMergeSort algorithm in C:
void doMergeSort(contact **head, int sortBy, int sortOrder) { // do not process empty or single-node list if (head==NULL || *head == NULL || (*head)->next==NULL) return; contact *first, *second; // split the list in half splitList(*head, &first, &second); // perform recursive merge sort on both halves doMergeSort(&first, sortBy, sortOrder); doMergeSort(&second, sortBy, sortOrder); // Merge both halves back together, // sorting as indicated by sortBy and sortOrder. if (sortBy==0) *head = mergeListsByLastName(first, second, sortOrder); else *head = mergeListsByFirstName(first, second, sortOrder);
swapNodes algorithm in C:
void splitList (contact *head, contact **h1, contact **h2) { *h1 = head; *h2 = NULL; contact *low = head; contact *high = head->next; // find where split will happen... while (high) { high = high->next; if (high==NULL) break; high = high->next; low = low->next; } //assign second half to h2 *h2 = low->next; // chop first half by setting next member to NULL low->next=NULL; } contact *mergeLists (contact *l1, contact*l2) { // setup our "control" variables contact *head = NULL; contact **lastRef = &head; while (1) // while TRUE... { if (l1==NULL || l2==NULL) { *lastRef = l1?l1:l2; break; } // do comparison here. if (strcmp(l1->lastName,l2->lastName)next); } return head; } void swapNodes(contact **node1, contact **node2) { contact *src = *node1; *node1 = (*node1)->next; src->next = *node2; *node2 = src; }
Here is a diagram showing the Merge-Sort Algorithm:
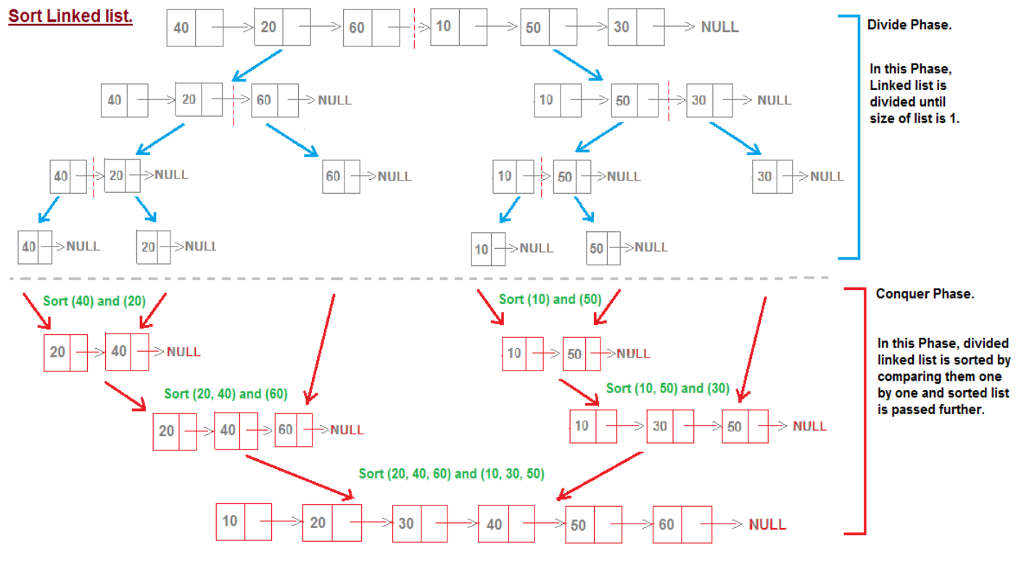
Sort Linked list. > NULL Divide Phase. 40-20-60 - 1060|| 30 NULL O NULL In this Phase, Linked list is divided until size of list is 1. NULL > NULL NULL | 40 --> NULL 20 ->NULI 10->NULL 50 NULL Sort (40) and (20) Sort (10) and (50) Conquer Phase. + 40 + NULL In this Phase, divided linked list is sorted by comparing them one by one and sorted list is passed further. 10 500 -NULL 1030 E 60 E > NULL Sort (20, 40) and (60) Sort (10, 50) and (30) 201 - 40-60 +-nu Sort (20, 40, 60) and (10, 30, 50) 10-200 - 406000 + NULL
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


