Question: Compute the distance vector at Node C and D during the round T=1 in the example of the Distance-Vector routing algorithm in the lecture note.
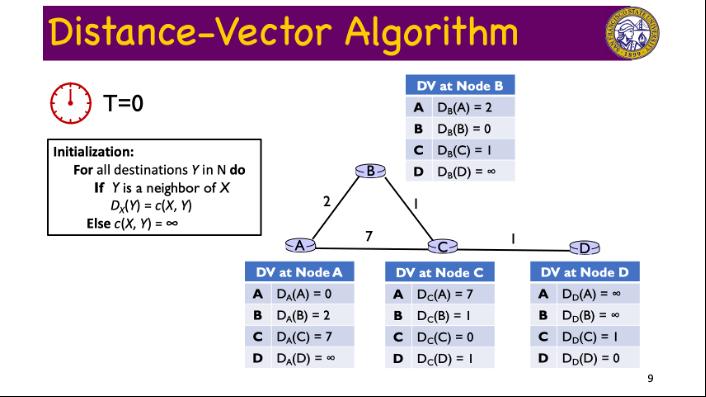
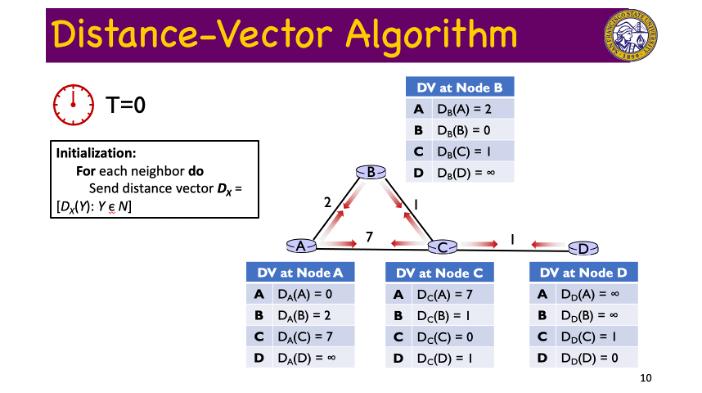
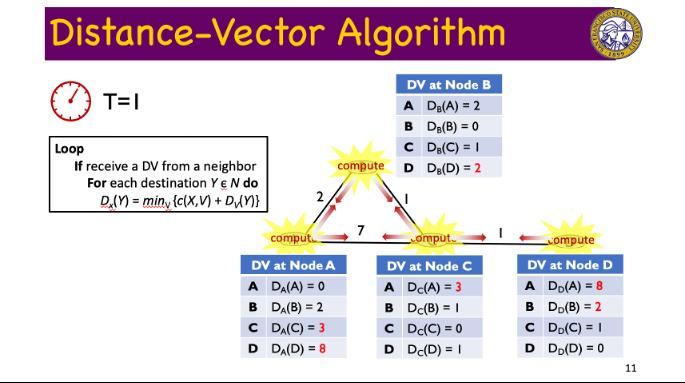
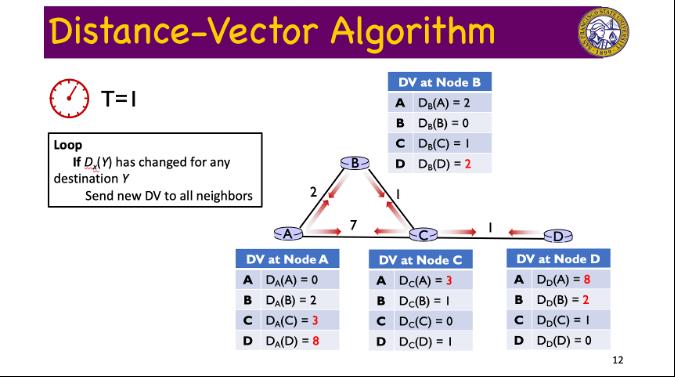
Distance-Vector Algorithm T=0 Initialization: For all destinations Y in N do If Y is a neighbor of X DX(Y) = c(X, Y) Else c(X, Y) = 2 DV at Node A A DA(A) = 0 BD(B) = 2 C DA(C) = 7 D DA(D) = 00 B 7 DV at Node B A DB(A) = 2 B DB(B) = 0 C D DB(C) = 1 DB(D) = 00 DV at Node C A Dc(A) = 7 B Dc(B) = 1 C Dc(C) = 0 D Dc(D) = 1 wp DV at Node D A DD(A) = 00 B DD(B) = C DD(C) = 1 D DD (D) = 0 9
Step by Step Solution
3.60 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Answer In Round T 1 hode C have its neighbors node AB and D Distance vector table informati... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


