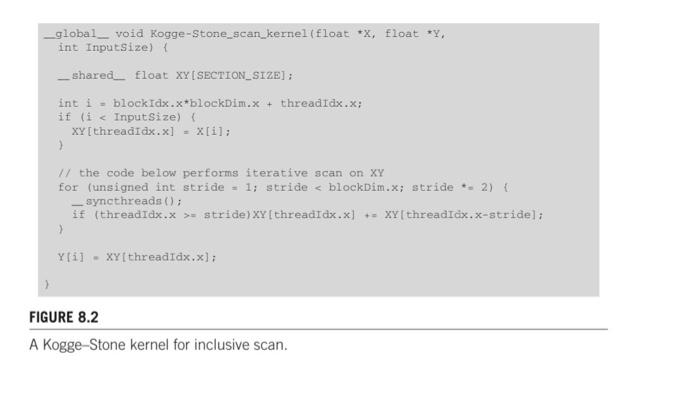
Question: Compute the inclusive scan using addition for the following array by using the Kogge-Stone kernel given in Figure 8.2 and Brent-Kung kernel given in Figure

![in Figure 8.6: [3 2 0 1 6 5 4 2] Show](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f4615a42159_73766f46159d2b78.jpg)
Compute the inclusive scan using addition for the following array by using the Kogge-Stone kernel given in Figure 8.2 and Brent-Kung kernel given in Figure 8.6: [3 2 0 1 6 5 4 2] Show each of the passes for both the algorithms using the above array as input. Compare the thread divergence, total number of memory accesses and additions required for both the algorithms. _global__ void Kogge-Stone_scan_kernel(float x,float *y, int InputSize) _ shared float XY (SECTION_SIZE]: int i - blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; if (i - stride)XY [ threadIdx.x] ++ XY[ threadIdx.x-stridel: > Y[i] - XY[ threadIdx,x); FIGURE 8.2 A Kogge-Stone kernel for inclusive scan. _global_ void Brent_Kung_scan_kernel (float x,float wY. int InputSize) { shared_float XY (SECTION_SIZE]: int i = 2*blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; if (i 0; stride /= 2) ( synethreads(); int index = (threadIdx.x+1)*stride 2 - 1; if(index + stride
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


