Question: Computer Architecture and Organization. Two part question..please help with both! PARALLEL SOTA LDUR X4, ADDI x6, [X6, #0] x6, #8 ; load a[0] : increment

![SOTA LDUR X4, ADDI x6, [X6, #0] x6, #8 ; load a[0]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/09/66dca4678abdf_03866dca466de83b.jpg)
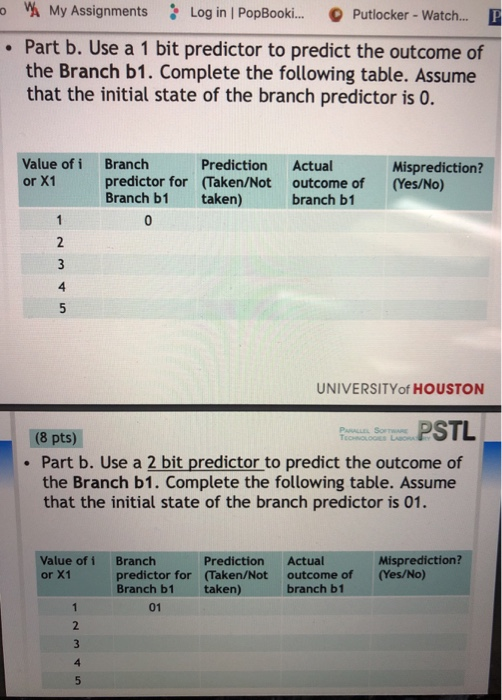
PARALLEL SOTA LDUR X4, ADDI x6, [X6, #0] x6, #8 ; load a[0] : increment memory address 2 3. LOOP: MOV X8, x4 BEQ X1, X2, JMARK Branch bl :if x1X2 goto JMARK ADD! STUR X8, ADDI X1, X1, #1 ADDI x6, x6, #8 MOV X4, x8 BNEQ x1, x10, Loop X8, X8, (X6, #1 a[i-a[i]+ 1 ; store a[i] : increment loop counter : increment memory address 6.1 JMARK : #0] 10. Branch b2 ; if x1 !.. X10 goto Loop UNIVERSITYof HOUSTON PARALLEL SOFTWARE (6 pts) . Part a. Find all data dependencies, output dependencies, anti-dependencies in the code segment. Note: please execute the loop only once (i.e. you do not have to track loop dependencies across the different iterations). wh My Assignments Log in l PopBooki o Putlocker-Watch G Part b. Use a 1 bit predictor to predict the outcome of the Branch b1. Complete the following table. Assume that the initial state of the branch predictor is 0. Value of i Branch Prediction Actual or X1 Misprediction? predictor for (Taken/Not outcome of (Yes/No) Branch b1 taken) branch b1 4 UNIVERSITYof HOUSTON (8 pts) PSTL . Part b. Use a 2 bit predictor to predict the outcome of the Branch b1. Complete the following table. Assume that the initial state of the branch predictor is 01 Misprediction? Value of i or X1 Branch predictor for (Taken/Not outcome of (Yes/No) Branch b1 taken) Prediction Actual branch b 01
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


