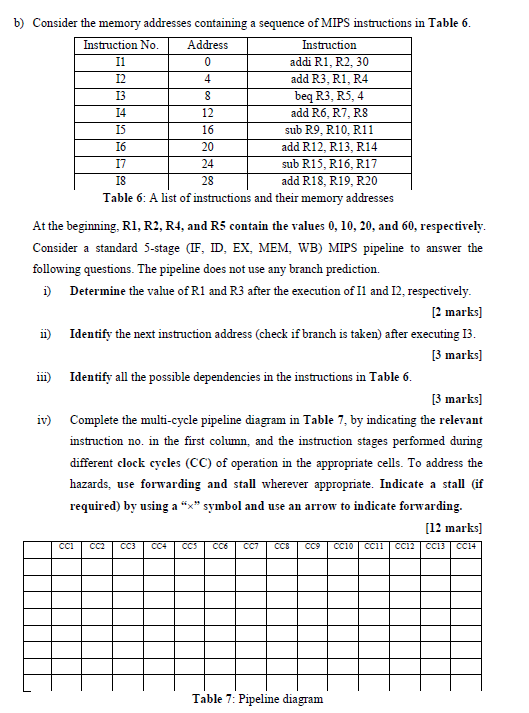
Question: computer architecture b) Consider the memory addresses containing a sequence of MIPS instructions in Table 6. Instruction No. Address Instruction I1 0 addi R1, R2,
 computer architecture
computer architecture
b) Consider the memory addresses containing a sequence of MIPS instructions in Table 6. Instruction No. Address Instruction I1 0 addi R1, R2, 30 12 4 add R3, R1, R4 13 8 beq R3, R5,4 14 12 add R6, R7, RS IS 16 sub R9, R10 R11 16 20 add R12, R13, R14 17 24 sub R15, R16, R17 18 28 add R18, R19, R20 Table 6: A list of instructions and their memory addresses At the beginning, R1, R2, R4, and R5 contain the values 0, 10, 20, and 60, respectively. Consider a standard 5-stage (IF, ID, EX, MEM, WB) MIPS pipeline to answer the following questions. The pipeline does not use any branch prediction. i) Determine the value of R1 and R3 after the execution of I1 and 12, respectively. [2 marks] ii) Identify the next instruction address (check if branch is taken) after executing 13. [3 marks) Identify all the possible dependencies in the instructions in Table 6. [3 marks] iv) Complete the multi-cycle pipeline diagram in Table 7, by indicating the relevant instruction no. in the first column, and the instruction stages performed during different clock cycles (CC) of operation in the appropriate cells. To address the hazards, use forwarding and stall wherever appropriate. Indicate a stall (if required) by using a "x" symbol and use an arrow to indicate forwarding. [12 marks] ccllcC12CC13 CC14 111) CCI CC3 CCS CC6 CC7 CCS CC9 CCIO Table 7: Pipeline diagram b) Consider the memory addresses containing a sequence of MIPS instructions in Table 6. Instruction No. Address Instruction I1 0 addi R1, R2, 30 12 4 add R3, R1, R4 13 8 beq R3, R5,4 14 12 add R6, R7, RS IS 16 sub R9, R10 R11 16 20 add R12, R13, R14 17 24 sub R15, R16, R17 18 28 add R18, R19, R20 Table 6: A list of instructions and their memory addresses At the beginning, R1, R2, R4, and R5 contain the values 0, 10, 20, and 60, respectively. Consider a standard 5-stage (IF, ID, EX, MEM, WB) MIPS pipeline to answer the following questions. The pipeline does not use any branch prediction. i) Determine the value of R1 and R3 after the execution of I1 and 12, respectively. [2 marks] ii) Identify the next instruction address (check if branch is taken) after executing 13. [3 marks) Identify all the possible dependencies in the instructions in Table 6. [3 marks] iv) Complete the multi-cycle pipeline diagram in Table 7, by indicating the relevant instruction no. in the first column, and the instruction stages performed during different clock cycles (CC) of operation in the appropriate cells. To address the hazards, use forwarding and stall wherever appropriate. Indicate a stall (if required) by using a "x" symbol and use an arrow to indicate forwarding. [12 marks] ccllcC12CC13 CC14 111) CCI CC3 CCS CC6 CC7 CCS CC9 CCIO Table 7: Pipeline diagram
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


