Question: Computer Organization and Assembly Language Programming 1. For this lab, you ill be asked to perform arithmetic operations on numbers that are larger than 8
Computer Organization and Assembly Language Programming
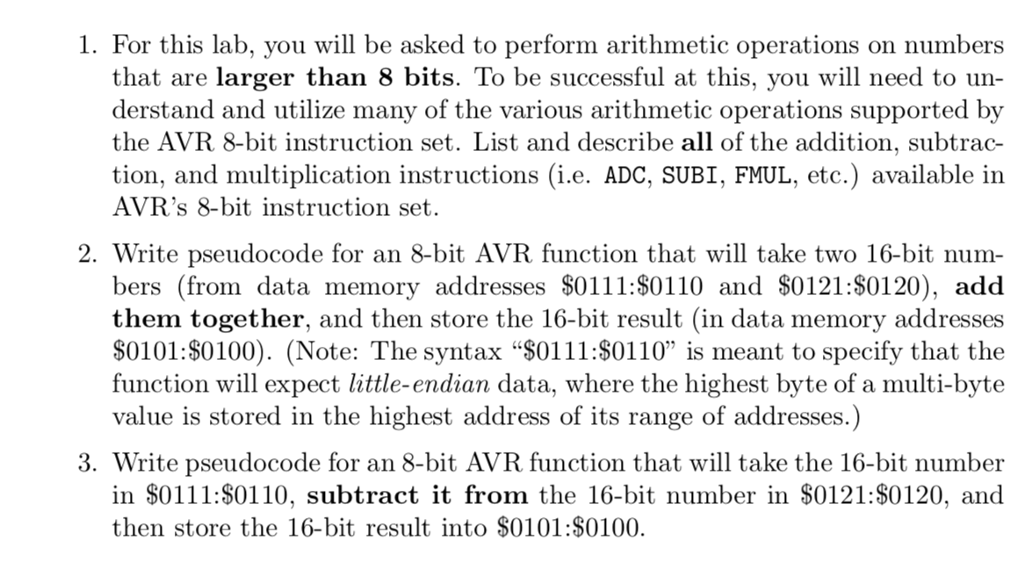
1. For this lab, you ill be asked to perform arithmetic operations on numbers that are larger than 8 bits. To be successful at this, you will need to un- derstand and utilize many of the various arithmetic operations supported by the AVR 8-bit instruction set. List and describe all of the addition, subtrac- tion, and multiplication instructions (i.e. ADC, SUBI, FMUL, etc.) available in AVR's 8-bit instruction set. 2. Write pseudocode for an 8-bit AVR function that will take two 16-bit num- bers (from data memory addresses $0111:S0110 and $0121:80120), add them together, and then store the 16-bit result (in data memory addresses S0101:S0100). (Note: The syntax "$0111:80110" is meant to specify that the function will expect little-endian data, where the highest byte of a multi-byte value is stored in the highest address of its range of addresses.) 3. Write pseudocode for an 8-bit AVR function that will take the 16-bit number in $0111:S0110, subtract it from the 16-bit number in $0121:$0120, and then store the 16-bit result into $0101:S0100. 1. For this lab, you ill be asked to perform arithmetic operations on numbers that are larger than 8 bits. To be successful at this, you will need to un- derstand and utilize many of the various arithmetic operations supported by the AVR 8-bit instruction set. List and describe all of the addition, subtrac- tion, and multiplication instructions (i.e. ADC, SUBI, FMUL, etc.) available in AVR's 8-bit instruction set. 2. Write pseudocode for an 8-bit AVR function that will take two 16-bit num- bers (from data memory addresses $0111:S0110 and $0121:80120), add them together, and then store the 16-bit result (in data memory addresses S0101:S0100). (Note: The syntax "$0111:80110" is meant to specify that the function will expect little-endian data, where the highest byte of a multi-byte value is stored in the highest address of its range of addresses.) 3. Write pseudocode for an 8-bit AVR function that will take the 16-bit number in $0111:S0110, subtract it from the 16-bit number in $0121:$0120, and then store the 16-bit result into $0101:S0100
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


