Question: Computer Science c++ program Recall, a Binary Search Tree (BST) data structure is a nonlinear data structure. A BST is traversed by starting at the
Computer Science c++ program
Recall, a Binary Search Tree (BST) data structure is a nonlinear data structure. A BST is traversed by starting at the root pointer. The root node is the first node inserted into the tree. Nodes are inserted into the tree such that all items to the left of the root node are less than, and all items to the right of the root are greater than its item. Also, this property holds true for any particular node in the tree. We will visualize a BST in the following way:
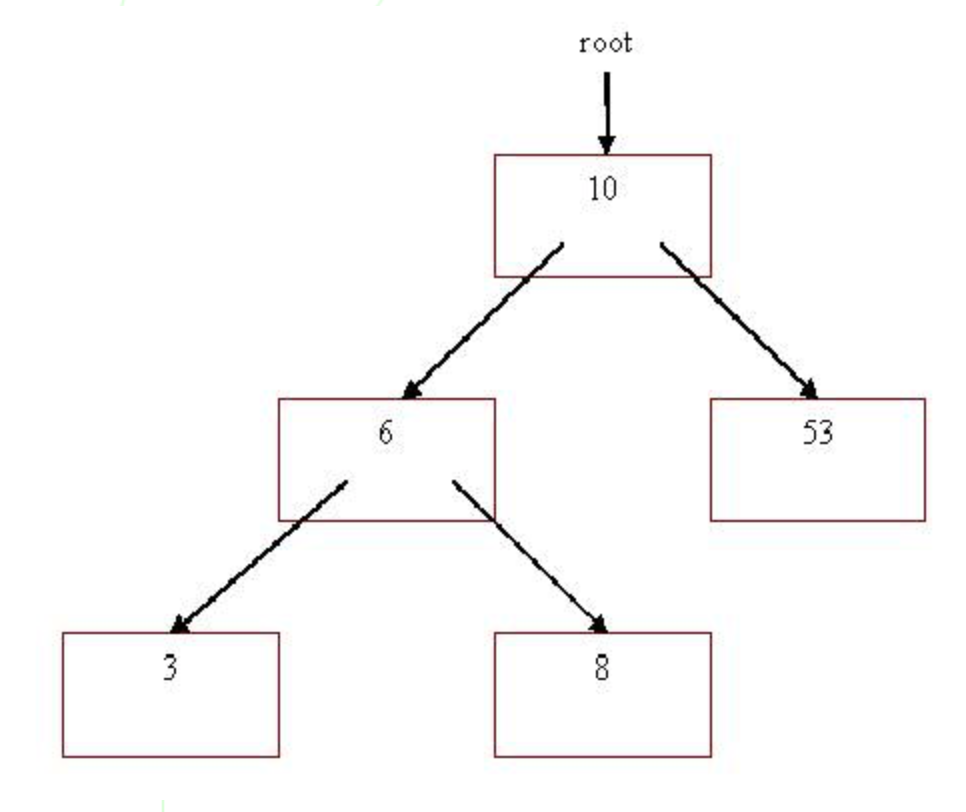
In this assignment you will be using a BST to convert English characters to Morse code strings. Morse code is a famous coding scheme that assigns a series of dots and dashes to each letter of the alphabet, each digit, and a few special characters. In sound-oriented systems, the dot represents a short sound and the dash represents a long sound. Other representations of dots and dashes are used with light-oriented systems and signal-flag systems (from Deitel and Deitel C How to Program).
1. (15 pts) Defining the BSTNode structure
For the first part of the assignment, you should start by designing the BSTNode class for the BST. Create a class for the BSTNode data that will have as its members a character and a string. The character will hold the English text character, and the string will hold the corresponding Morse code characters for that English text character. You should also define left and right child pointers that point to BSTNode objects. You must have a constructor that accepts arguments to set the English text character and Morse code string.
2. (50 pts) Create the BST code and create a Morse lookup BST
Next, you should be able to read in the Morse table from a file called MorseTable.txt. You should rearrange the Morse table in the file to make sure that your lookup tree is balanced. I recommend that you diagram a tree that provides a balanced tree so that you know how to order your MorseTable.txt file. Think about the order of insertions. However, the tree does not have to balance itself.
The tree should be built by the constructor for the BST. This means the constructor must open and read the file, create nodes for each character in the tree, insert the nodes into the tree (using an insert () function), and close the file. Note: the tree object could be declared as const, since all changes to it are being performed in the constructor. However, if you declare your object as a const, be sure to also declare your print () and search () functions as const. You should arrange the tree so that it is alphabetically ordered from left to right. Create a print ( ) function that uses recursion to traverse the tree in order (left most printed first). Also, build a search ( ) function that will return the Morse code string for each English character searched for. Do you need to return a found indicator from the search function? Should you use recursion? Finally, implement a destructor, which destroys the entire tree.
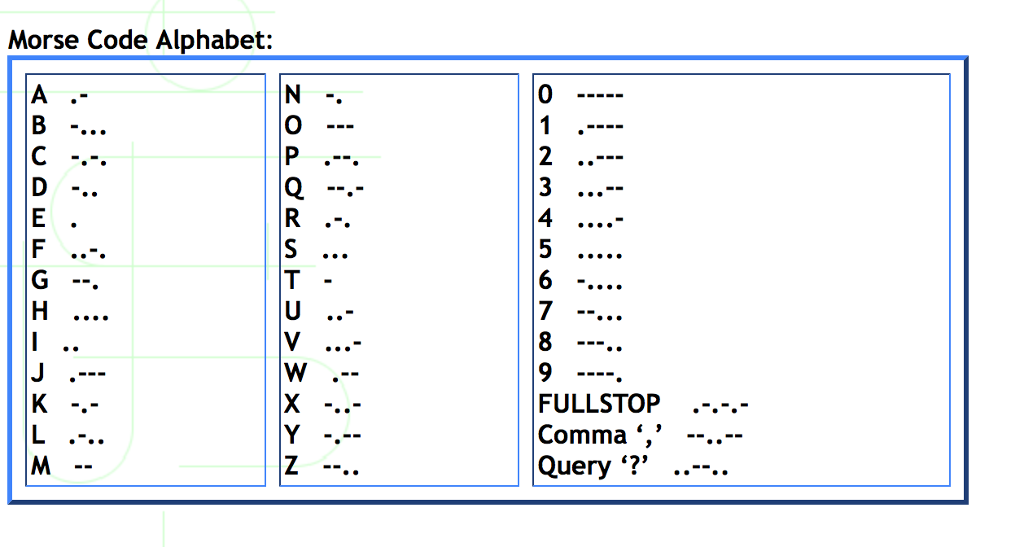
3. (30 pts) Putting the pieces together
First, print the current tree. Next, you must open a file called Convert.txt, which consists of English alphabetic characters, spaces, commas, and periods. You must look for each English character with a search ( ) function on the BST, and print the Morse code string for that character. For each character in Convert.txt, convert the character to a Morse code string. Each Morse character in the string will be separated by a space. Each complete Morse string will be separated by three spaces. Each newline character will be echoed to the screen. Note: you should convert any lowercase English characters to uppercase before processing the English text.
Below is an example test file (you should add more characters to test all conversions!):
(Convert.txt)
This is a test of the cpts 122
Morse code conversion tool.

root 10 53
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


