Question: Computer Science & Numerical Computation question. Python 3, JupyterNoteBook; fill the #your code here part. I will give thumb up, thank you! Question and test
Computer Science & Numerical Computation question. Python 3, JupyterNoteBook;
fill the #your code here part. I will give thumb up, thank you!
Question and test case:
Background infomation:
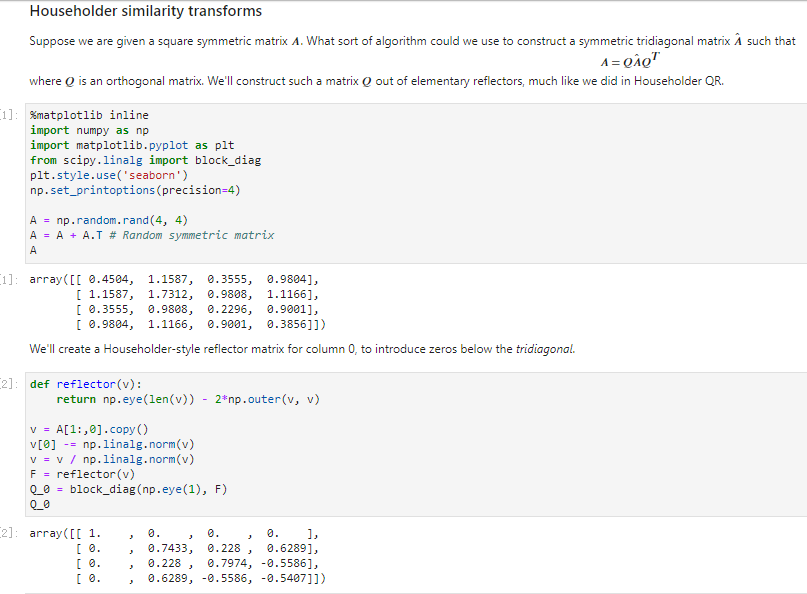
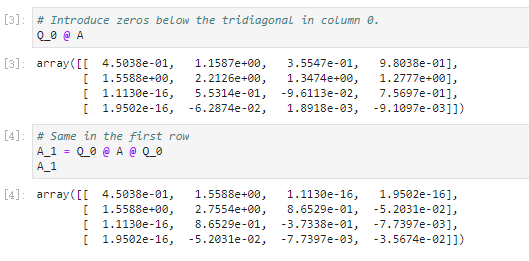
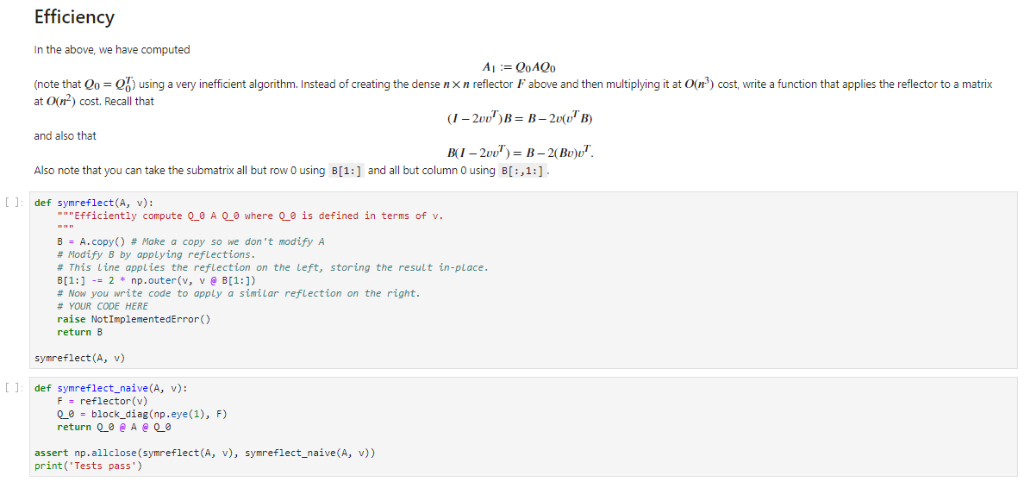
Efficiency In the above, we have computed (note that Qo Qa) using a very iner cent algorithm. Instead of creating the dense n n reflector F above and then multiplying it at 0 n3) cost, write a function that applies the reflector to a matrix at O(n2) cost. Recall that and also that Also note that you can take the submatrix all but row O using B[1:] and all but column 0 using B[:,1:] [ ] def synreflect(A, v): "Efficiently compute Q_0 A Q0 where Qe is defined in terms of v B -A. copy() # Make a copy so we don't modify A # Modify B by applying reflections # This line applies the reflection on the Left, storing the result in-place B[1:1-= 2 * np.outer(v, v @ B[1:1) # Now you write code to apply a similar reflection on the right # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError) return B symreflect(A, v) def symreflect_naive(A, v): F reflector(v) e block_diag (np.eye (1), F) return @ A @ assert np.allclose(symreflect(, print('Tests pass") v), synreflect-naive(A, v)) Householder similarity transforms Suppose we are given a square symmetric matrix A. What sort of algorithm could we use to construct a symmetric tridiagonal matrix A such that where O is an orthogonal matrix. We'll construct such a matrix O out of elementary reflectors, much like we did in Householder QR. A QAQ 1]: %matplot1ib inline import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.linalg import block_diag plt.style.use('seaborn') np.set_printoptions (precision-4) A np.random.rand(4, 4) A A + AT # Random symmetric matrix array( 0.4504, 1.1587, 0.3555, 0.9804], 1.1587, 1.7312, e.9808, 1.1166], 0.3555, 0.9808, 0.2296, 0.9001], 0.9804, 1.1166, 0.9001, 0.38561]) We'll create a Householder-style reflector matrix for column 0, to introduce zeros below the tridiagonal. 2]: def reflector(v): return np.eye(len(v)) - 2*np.outer (v, v) v A[ 1 : ,0].copy() vI0] np.linalg.norm(v) v = v / np. linalg"norm(v) F-reflector(v) block_diag (np.eye(1), F) 2] array([l 1. 0, 0.7433, 0.228, 0.6289], 0., 0.228, e.7974,-0.5586], , 0.6289, -0.5586, -0.540711) [3] # Introduce zeros below the tridiagonal in column e. Q0 @ A [3]: array(1 4.5838e-01, 1.1587e+00, 3.5547e-01, 9.8838e-01], 1.5588e+00,2.2126e+00, 1.3474e+00, 1.2777e+00], 1.1130e-16, 5.5314e-01, 9.6113e-02, 7.5697e-011, 1.9502e-16, -6.2874e-02, 1.8918e-03, 9.1097e-0311) [4]: # Same in the first row a_1 = Q0 @ A @Q_ ! 4]: array(1 4.5838e-01, 1.5588e+00, 1.1130e-16, 1.9502e-16, 1.5588e+, 2.7554e+90, 8.6529e-01, 5.2031e-02], 1.1130e-16, 8.6529e-01, 3.7338e-01, -7.7397e-03], 1.9502e-16, -5.2031e-02, 7.7397e-03, 3.5674e-0211) Efficiency In the above, we have computed (note that Qo Qa) using a very iner cent algorithm. Instead of creating the dense n n reflector F above and then multiplying it at 0 n3) cost, write a function that applies the reflector to a matrix at O(n2) cost. Recall that and also that Also note that you can take the submatrix all but row O using B[1:] and all but column 0 using B[:,1:] [ ] def synreflect(A, v): "Efficiently compute Q_0 A Q0 where Qe is defined in terms of v B -A. copy() # Make a copy so we don't modify A # Modify B by applying reflections # This line applies the reflection on the Left, storing the result in-place B[1:1-= 2 * np.outer(v, v @ B[1:1) # Now you write code to apply a similar reflection on the right # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError) return B symreflect(A, v) def symreflect_naive(A, v): F reflector(v) e block_diag (np.eye (1), F) return @ A @ assert np.allclose(symreflect(, print('Tests pass") v), synreflect-naive(A, v)) Householder similarity transforms Suppose we are given a square symmetric matrix A. What sort of algorithm could we use to construct a symmetric tridiagonal matrix A such that where O is an orthogonal matrix. We'll construct such a matrix O out of elementary reflectors, much like we did in Householder QR. A QAQ 1]: %matplot1ib inline import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.linalg import block_diag plt.style.use('seaborn') np.set_printoptions (precision-4) A np.random.rand(4, 4) A A + AT # Random symmetric matrix array( 0.4504, 1.1587, 0.3555, 0.9804], 1.1587, 1.7312, e.9808, 1.1166], 0.3555, 0.9808, 0.2296, 0.9001], 0.9804, 1.1166, 0.9001, 0.38561]) We'll create a Householder-style reflector matrix for column 0, to introduce zeros below the tridiagonal. 2]: def reflector(v): return np.eye(len(v)) - 2*np.outer (v, v) v A[ 1 : ,0].copy() vI0] np.linalg.norm(v) v = v / np. linalg"norm(v) F-reflector(v) block_diag (np.eye(1), F) 2] array([l 1. 0, 0.7433, 0.228, 0.6289], 0., 0.228, e.7974,-0.5586], , 0.6289, -0.5586, -0.540711) [3] # Introduce zeros below the tridiagonal in column e. Q0 @ A [3]: array(1 4.5838e-01, 1.1587e+00, 3.5547e-01, 9.8838e-01], 1.5588e+00,2.2126e+00, 1.3474e+00, 1.2777e+00], 1.1130e-16, 5.5314e-01, 9.6113e-02, 7.5697e-011, 1.9502e-16, -6.2874e-02, 1.8918e-03, 9.1097e-0311) [4]: # Same in the first row a_1 = Q0 @ A @Q_ ! 4]: array(1 4.5838e-01, 1.5588e+00, 1.1130e-16, 1.9502e-16, 1.5588e+, 2.7554e+90, 8.6529e-01, 5.2031e-02], 1.1130e-16, 8.6529e-01, 3.7338e-01, -7.7397e-03], 1.9502e-16, -5.2031e-02, 7.7397e-03, 3.5674e-0211)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


