Question: Computer Science Python - Spring 2023 Concepts Class Diagram Implementation via OOP in Python Recursion Problem Specification You will be given a tree, i.e., an
Computer Science Python - Spring 2023
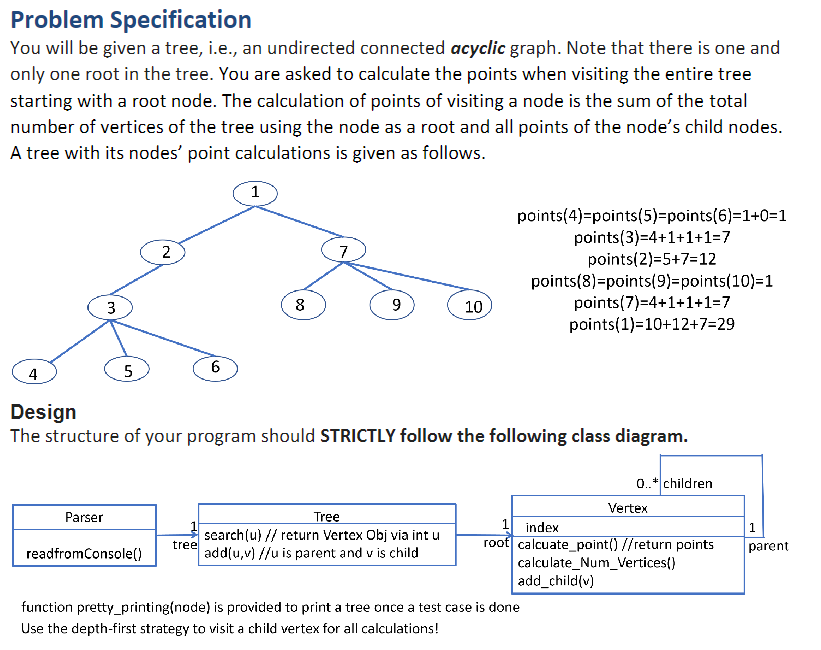
Concepts Class Diagram Implementation via OOP in Python Recursion Problem Specification You will be given a tree, i.e., an undirected connected acyclic graph. Note that there is one and only one root in the tree. You are asked to calculate the points when visiting the entire tree starting with a root node. The calculation of points of visiting a node is the sum of the total number of vertices of the tree using the node as a root and all points of the nodes child nodes. A tree with its nodes point calculations is given as follows. Design The structure of your program should STRICTLY follow the following class diagram.
Input The first line contains an integer, i.e., the total number of trees/test cases. For each tree/test case, first line contains the number of vertices in the tree/test case, say n. Then each of the following n-1 lines describes an edge of the tree. Edge is denoted by two integers and , the indices of vertices it connects (1 , , ). Examples: Input: 2 10 1 2 2 3 3 4 3 5 3 6 1 7 7 8 7 9 7 10 5 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 Output: Total from vertex = 29 Total from vertex = 11 Design Requirements Basic Structure Your program structure should follow the above class diagram. Also, you need to follow the principles we discussed in the class such as data hiding. DCG Strategy You MUST follow the DCG strategy by showing the base case and recursive case for the two calculate methods in Class Vertex. Testing Phase Some test cases will be provided. When grading, some hidden test cases might be used as well. Assignment Submission Generate a .zip file that contains all your files including: o Design document showing the base case & recursive case with the DCG Strategy (15pts) o Program (Structure Checking: 30 pts; Correctness 55 pts) Submit the .zip file to the appropriate folder on E-Learning.
The printTree() function is provided

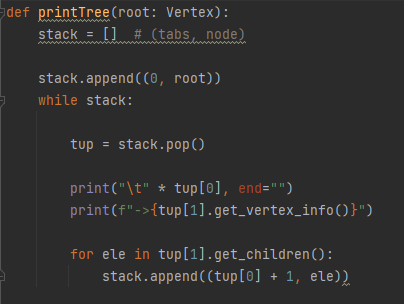
Must be in Python
Must follow the UML diagram
Here is a shell for the program to help:
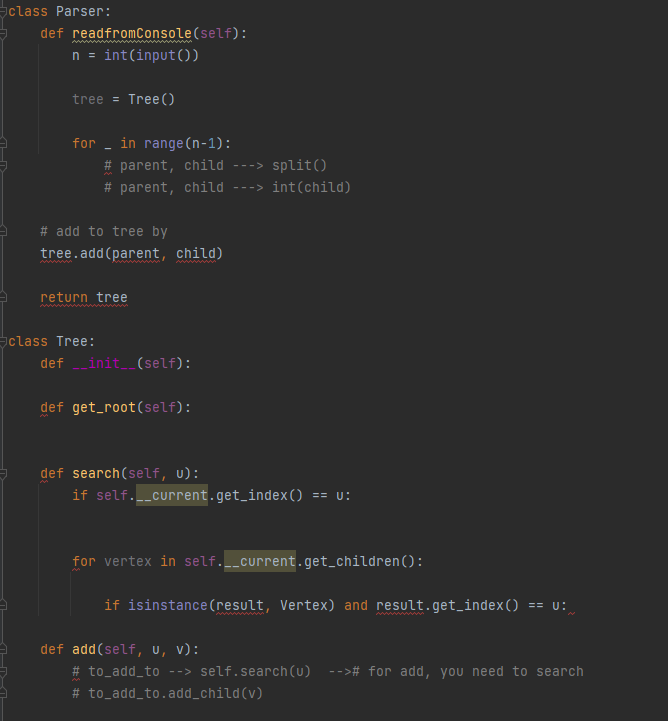
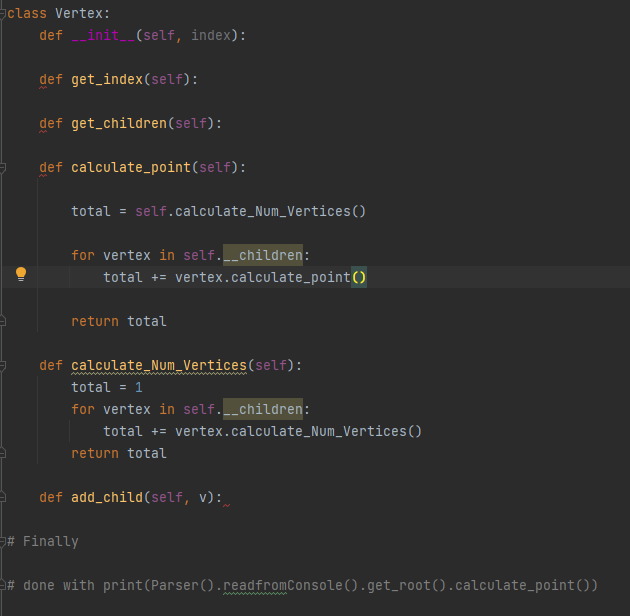
Problem Specification You will be given a tree, i.e., an undirected connected acyclic graph. Note that there is one and only one root in the tree. You are asked to calculate the points when visiting the entire tree starting with a root node. The calculation of points of visiting a node is the sum of the total number of vertices of the tree using the node as a root and all points of the node's child nodes. A tree with its nodes' point calculations is given as follows. Design The structure of your program should STRICTLY follow the following class diagram. function pretty_printing(node) is provided to print a tree once a test case is done Use the depth-first strategy to visit a child vertex for all calculations! Input The first line contains an integer, i.e., the total number of trees/test cases. For each tree/test case, first line contains the number of vertices in the tree/test case, say n. Then each of the following n1 lines describes an edge of the tree. Edge i is denoted by two integers ui and v, the indices of vertices it connects (1ui,vin,ui=vi). Examples: Input: 2101223343536177879710 5 12 13 24 25 Output: Total from vertex =29 Total from vertex =11 Problem Specification You will be given a tree, i.e., an undirected connected acyclic graph. Note that there is one and only one root in the tree. You are asked to calculate the points when visiting the entire tree starting with a root node. The calculation of points of visiting a node is the sum of the total number of vertices of the tree using the node as a root and all points of the node's child nodes. A tree with its nodes' point calculations is given as follows. Design The structure of your program should STRICTLY follow the following class diagram. function pretty_printing(node) is provided to print a tree once a test case is done Use the depth-first strategy to visit a child vertex for all calculations! Input The first line contains an integer, i.e., the total number of trees/test cases. For each tree/test case, first line contains the number of vertices in the tree/test case, say n. Then each of the following n1 lines describes an edge of the tree. Edge i is denoted by two integers ui and v, the indices of vertices it connects (1ui,vin,ui=vi). Examples: Input: 2101223343536177879710 5 12 13 24 25 Output: Total from vertex =29 Total from vertex =11
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


