Question: Conditional Independence . We can write down P(M). And then, since we know L is only directly influenced by M, we can write down the
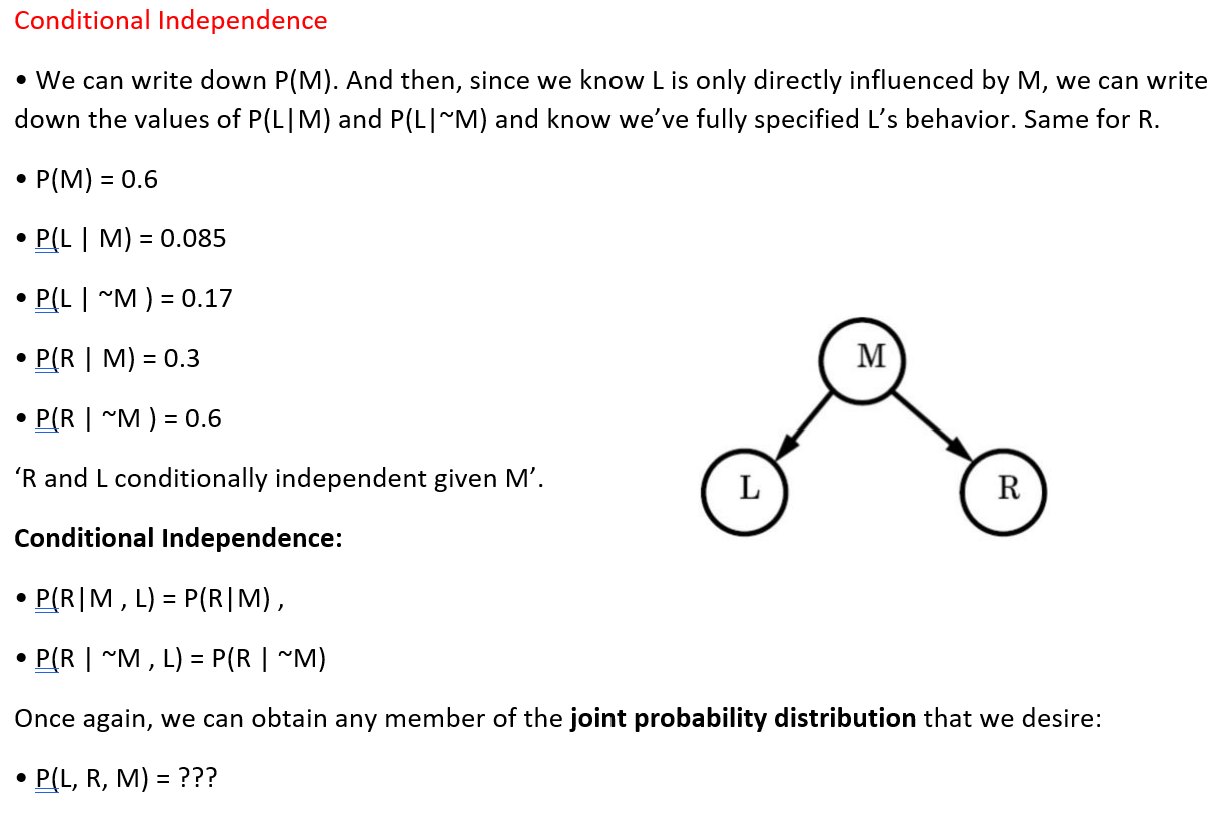
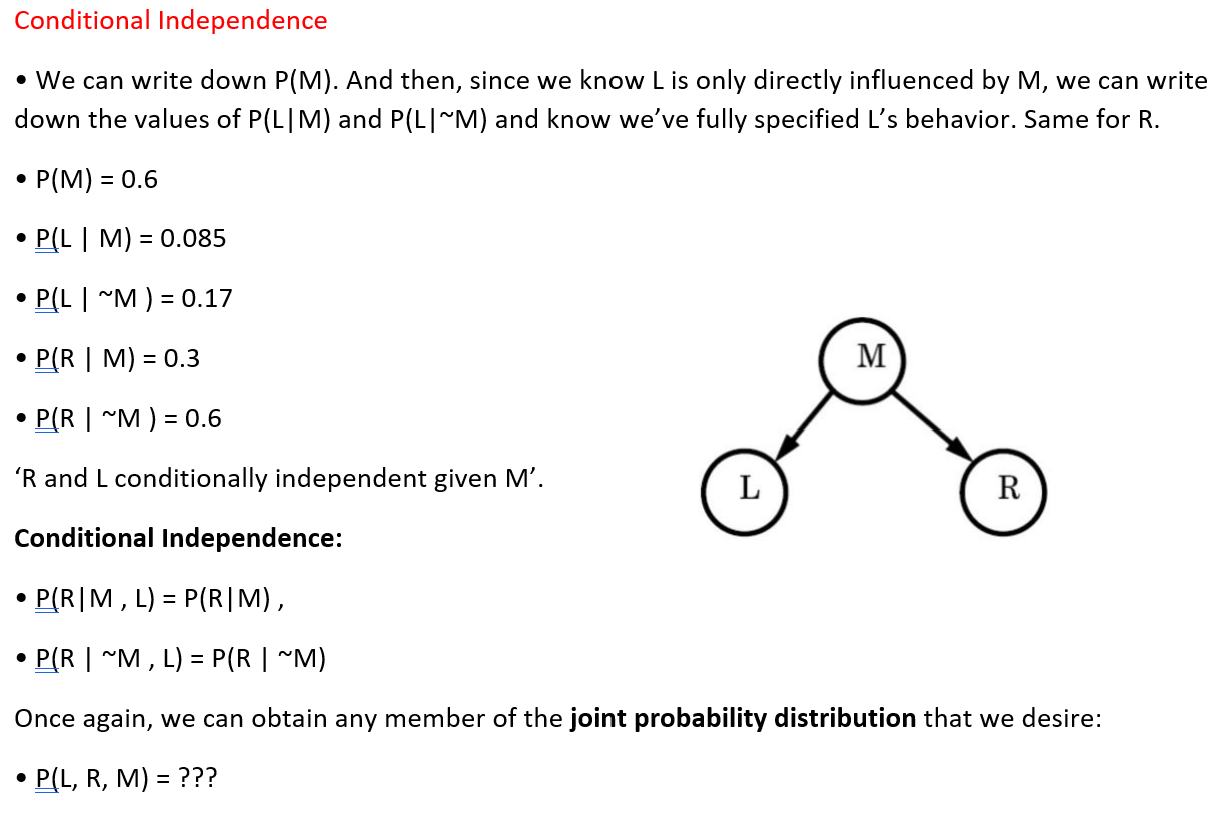
Conditional Independence . We can write down P(M). And then, since we know L is only directly influenced by M, we can write down the values of P(L| M) and P(L| ~M) and know we've fully specified L's behavior. Same for R. . P(M) = 0.6 . P(L | M) = 0.085 . P(L | ~M ) = 0.17 . P(R | M) = 0.3 M . P(R | ~M ) = 0.6 'R and L conditionally independent given M'. L R Conditional Independence: . P(R | M , L) = P(RIM) , . P(R | ~M , L) = P(R | ~M) Once again, we can obtain any member of the joint probability distribution that we desire: . P(L, R, M) =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


