Question: Consider a (binary) floating point system of the form (1.s182)2 x 2h where mE-31,32]. Calculate the relative error, with respect to oo-norm if we convert
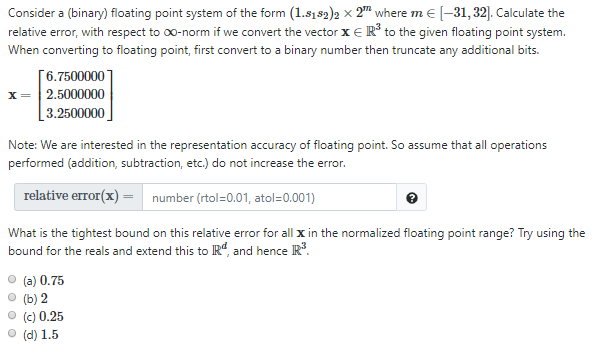
Consider a (binary) floating point system of the form (1.s182)2 x 2h where mE-31,32]. Calculate the relative error, with respect to oo-norm if we convert the vector x R3 to the given floating point system. When converting to floating point, first convert to a binary number then truncate any additional bits 6.7500000 x2.5000000 3.2500000 Note: We are interested in the representation accuracy of floating point. So assume that all operations performed (addition, subtraction, etc.) do not increase the error relative error(x)number (rtol-0.01, atol-0.001) What is the tightest bound on this relative error for all x in the normalized floating point range? Try using the bound for the reals and extend this to IRd and hence R3 O (a) 0.75 O (b) 2 (c) 0.25 O (d) 1.5 Consider a (binary) floating point system of the form (1.s182)2 x 2h where mE-31,32]. Calculate the relative error, with respect to oo-norm if we convert the vector x R3 to the given floating point system. When converting to floating point, first convert to a binary number then truncate any additional bits 6.7500000 x2.5000000 3.2500000 Note: We are interested in the representation accuracy of floating point. So assume that all operations performed (addition, subtraction, etc.) do not increase the error relative error(x)number (rtol-0.01, atol-0.001) What is the tightest bound on this relative error for all x in the normalized floating point range? Try using the bound for the reals and extend this to IRd and hence R3 O (a) 0.75 O (b) 2 (c) 0.25 O (d) 1.5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


