Question: Consider a central planning authority (like the former Soviet Union or Wal-Mart), who operates J firms with differentiable convex cost functions cj(qj) for producing good
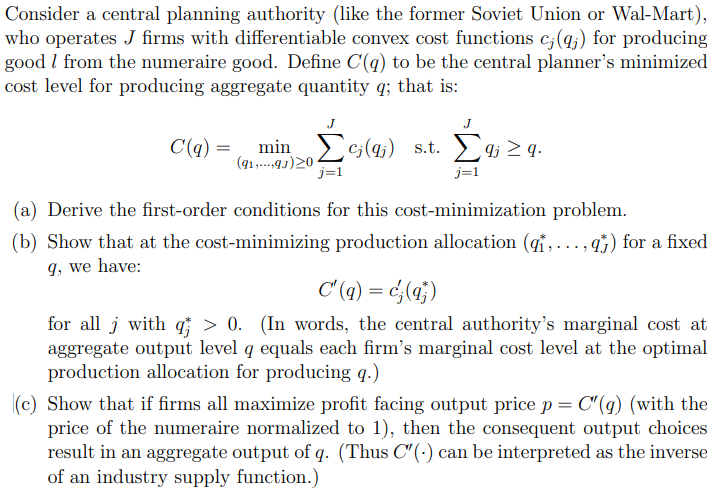
Consider a central planning authority (like the former Soviet Union or Wal-Mart), who operates J firms with differentiable convex cost functions cj(qj) for producing good l from the numeraire good. Define C(q) to be the central planner's minimized cost level for producing aggregate quantity q; that is: C(q)=min(q1,,qJ)0j=1Jcj(qj)s.t.j=1Jqjq. (a) Derive the first-order conditions for this cost-minimization problem. (b) Show that at the cost-minimizing production allocation (q1,,qJ) for a fixed g, we have: C(q)=cj(qj) for all j with qj>0. (In words, the central authority's marginal cost at aggregate output level q equals each firm's marginal cost level at the optimal production allocation for producing q.) (c) Show that if firms all maximize profit facing output price p=C(g) (with the price of the numeraire normalized to 1), then the consequent output choices result in an aggregate output of q. (Thus C() can be interpreted as the inverse of an industry supply function.) Consider a central planning authority (like the former Soviet Union or Wal-Mart), who operates J firms with differentiable convex cost functions cj(qj) for producing good l from the numeraire good. Define C(q) to be the central planner's minimized cost level for producing aggregate quantity q; that is: C(q)=min(q1,,qJ)0j=1Jcj(qj)s.t.j=1Jqjq. (a) Derive the first-order conditions for this cost-minimization problem. (b) Show that at the cost-minimizing production allocation (q1,,qJ) for a fixed g, we have: C(q)=cj(qj) for all j with qj>0. (In words, the central authority's marginal cost at aggregate output level q equals each firm's marginal cost level at the optimal production allocation for producing q.) (c) Show that if firms all maximize profit facing output price p=C(g) (with the price of the numeraire normalized to 1), then the consequent output choices result in an aggregate output of q. (Thus C() can be interpreted as the inverse of an industry supply function.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


