Question: Consider a long thin structure under an axial load. A single beam finite element isused to represent this structure and to predict the critical buckling
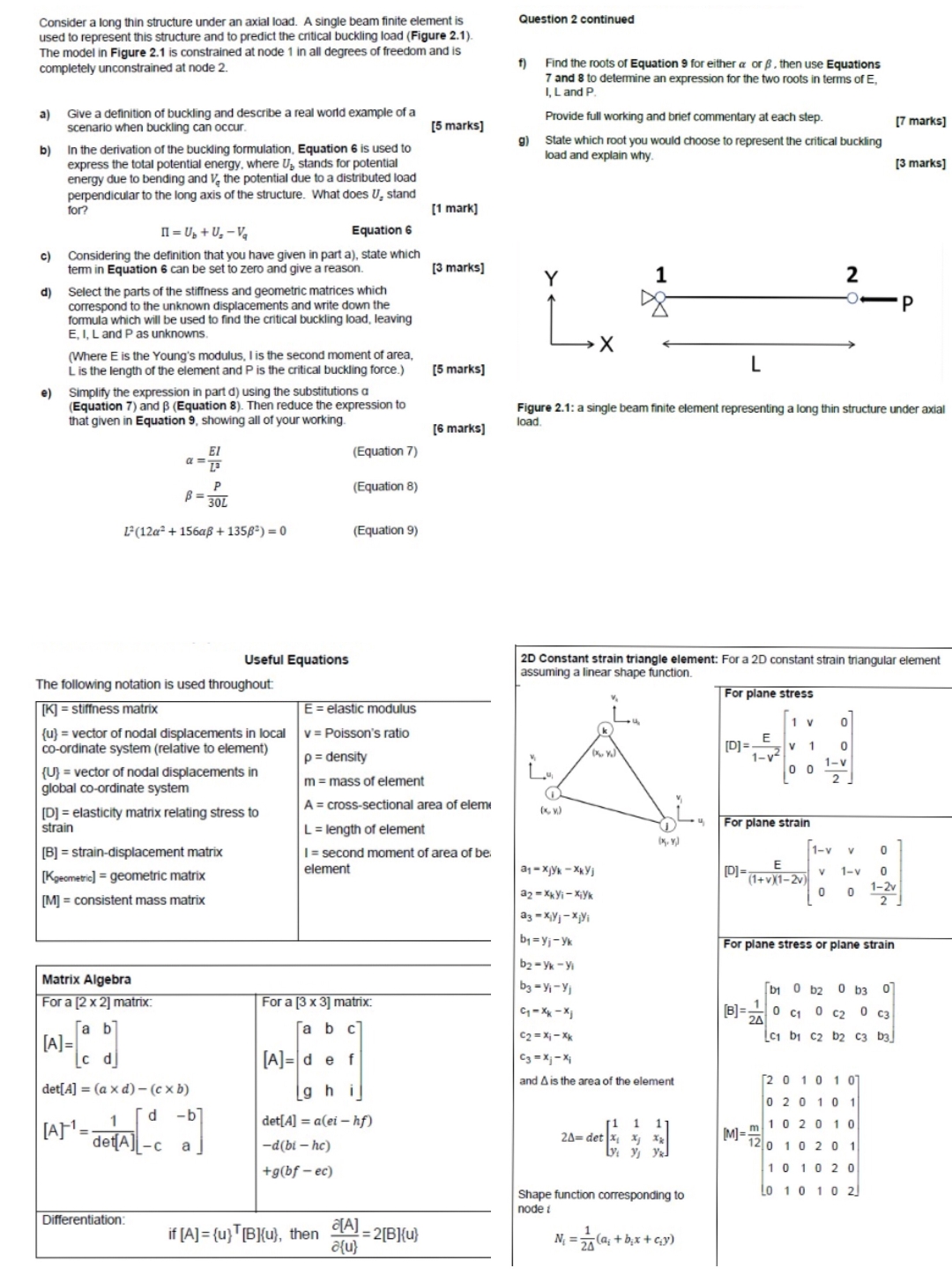
Consider a long thin structure under an axial load. A single beam finite element isused to represent this structure and to predict the critical buckling load Figure The model in Figure is constralned at node in all degrees of freedom and iscompletey unconstrained at node abceGive a definition of buckling and describe a real world example of aan cCur.Scenario when buckling canIn the derivation of the buckling formulation, Equation is used toexpress the total potential energy. where U stands for potentialenergy due to bending and V the potential due to a distributed loadperpendicular to the long axis of the structure. What does U standfor?ud Select the parts of the stiffness and geometric matrices whichcorrespond to the unknown displacements and write down thefomula which will be used to find the critical buckling load, leavingE, I, L and P as unknowns.Considering the definition that you have gven in pat a sta state whichten in Equation can be set to zero and give a reason.Where E is the Young's modulus, l is the second moment of area,Lis the length of the element andP is the critical buckling force.Simpity the expression in part d using the substitutions aEquation and B Equation Then reduce the expression tothat given in Equation showing all of your working.TK stiffness matrixThe following notation is used throughoutIUUVLadeg aU vector of nodal displacements inglobal coordinate systemMatrix AlgebraD elasticity matrix relating stress tostrainB straindisplacement matrixKgeometrc geometric matrixM consistent mass matrixFor a x matrix:Afa b vector of nodal displacements in localv Poisson's ratioOordinate system relative to elementc dBPdetAa xdcx bDifferentiation:dAT"detAcUseful EquationsbaEquation Eelastic modulusEquation Equation p densityEquation mmass of elementAd e fL length of elementFor a x matrix:a bdbi hcgbf ecA crosssectional area of elemif AJuBXu theng h i second moment of area of beelementdetA alei hfc marksAJ markBu marks marks marksQuestion continuedFind the roots of Equation for either a or B then use Equations and to detemine an expression for the twO roots in terms of EL and PProvide full working and briet commentary at each step.State which root you would choose to represent the critical buckingload and explain whywhyYLsXaz XiYkbyjFigure : a single beam finite element representing a long thin structure under axialloadD Constant strain triangle element: For a D constant strain triangular elementassuming a linear shape function.and A is the area of the elementnode tShape function corresponding toLNathr cyFor plane stressDEv VV For plane strainMvV vFor plane stress or plane strainb b bB c c cALCt b c b C b marksmLo J marksP
WILL GIVE GOOD REVIEW, IF YOU SOLVE CORRECTLY.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


