Question: Consider a U . S . Treasury bond that matures on Oct. 1 , 2 0 2 6 , has a par value of $
Consider a US Treasury bond that matures on Oct. has a par value of $ and makes semiannual coupon payments. The coupon rate is per year.
a On October after making its coupon payment, this bond was trading at $ What was the yield to maturity on the bond? As always, please state the YTM as an APR.
b Assume that you purchased the Treasury bond on October after it already paid its coupon at the market price of $ and that you are planning to hold the bond until maturity. Forecast the semiannual cash flows for this investment project and compute its IRR. After you find the semiannual rate of return IRR based on semiannual cash flows, state it as an APR to match the industry convention. Show that this IRR equals the YTM you found in part a
c This bond was issued at par value on October What was the yield to maturity YTM and the current yield CY at the time when the bond was issued?
d Now, consider a bond issued by the General Motors Acceptance Corporation GMAC The bond has a par value of $ matures on October carries an annual coupon rate of and makes semiannual coupon payments.
On October after the coupon payment the YTM on this bond was APR
i On this day, what was the yield spread over the Treasury bond in a What risk does this spread reflect?
ii What was the price of the GMAC bond?
iii. The GMAC bond was issued in October and market interest rates decreased from to Can you explain why the price of the bond likely fell below par despite the decline in market interest rates?
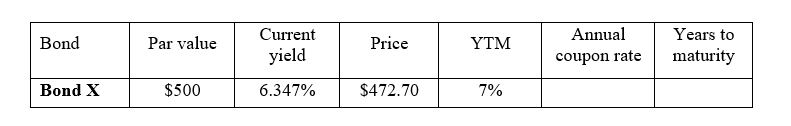
e Now, consider Bond X which makes semiannual coupon payments. The table below summarizes key information about this bond. As usual, YTM is stated as an APR.
Chart attached
i Please fill in the missing information in the table.
ii Between the GMAC bond and Bond X which bond has a higher interest rate risk? ie the price of which bond is more sensitive to discount rate fluctuations? To answer this question, vary the discount rate by a small percentage and see which bond has a higher percentage change in its price.
iii. Which characteristic of the respective bond explains its higher interest rate risk?
Bond Par value
Current yield
Price YTM
Annual coupon rate
Years to maturity
Bond X $ $
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


