Question: Consider a very simple symmetric block encryption algorithm, in which 64-bits blocks of plaintext are encrypted using a 128-bit key. Encryption is defined as C
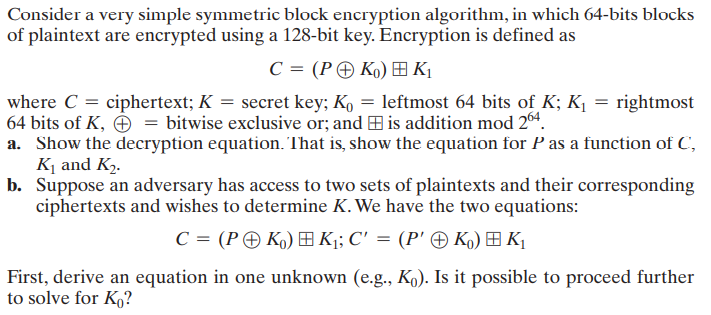
Consider a very simple symmetric block encryption algorithm, in which 64-bits blocks of plaintext are encrypted using a 128-bit key. Encryption is defined as C = ( PK) K1 where C = ciphertext; K = secret key; K, = leftmost 64 bits of K; K1 = rightmost 64 bits of K, = bitwise exclusive or; and #is addition mod 264. a. Show the decryption equation. That is, show the equation for P as a function of C, K and K. b. Suppose an adversary has access to two sets of plaintexts and their corresponding ciphertexts and wishes to determine K. We have the two equations: C = ( PK) #Ki;C' = (P' K) EK First, derive an equation in one unknown (e.g., K.). Is it possible to proceed further to solve for K
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


