Question: Consider an electrical heater made from a solid rod of thermal conductivity, k and rectangular crosssection (2Lx2H) as shown in the figure. The internal energy
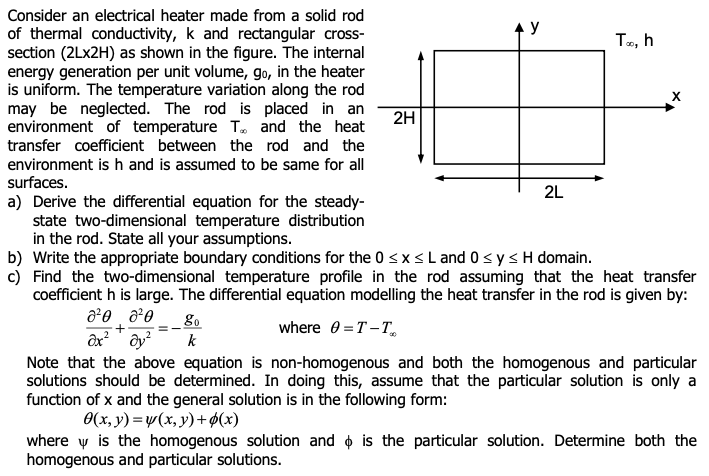
Consider an electrical heater made from a solid rod of thermal conductivity, k and rectangular crosssection (2Lx2H) as shown in the figure. The internal energy generation per unit volume, g0, in the heater is uniform. The temperature variation along the rod may be neglected. The rod is placed in an environment of temperature T and the heat transfer coefficient between the rod and the environment is h and is assumed to be same for all surfaces. a) Derive the differential equation for the steadystate two-dimensional temperature distribution in the rod. State all your assumptions. b) Write the appropriate boundary conditions for the 0xL and 0yH domain. c) Find the two-dimensional temperature profile in the rod assuming that the heat transfer coefficient h is large. The differential equation modelling the heat transfer in the rod is given by: x22+y22=kg0where=TT Note that the above equation is non-homogenous and both the homogenous and particular solutions should be determined. In doing this, assume that the particular solution is only a function of x and the general solution is in the following form: (x,y)=(x,y)+(x) where is the homogenous solution and is the particular solution. Determine both the homogenous and particular solutions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


