Question: consider executing the following code on the pipelined datapath shown as the following figure: add $2, $3, $1 sub $4, $3, $5 add $5, $3,
consider executing the following code on the pipelined datapath shown as the following figure: add $2, $3, $1 sub $4, $3, $5 add $5, $3, $7 add $7, $6, $1 add $8, $2, $6 a. At the end of the fifth cycle of execution, which registers are being read and which register will be written? b. Explain what the forwarding unit is doing during the fifth cycle of execution. If any comparisons are being made, mention them. c. Explain what the hazard detection unit is doing during the fifth cycle of execution. If any comparisons are being made, mention them.
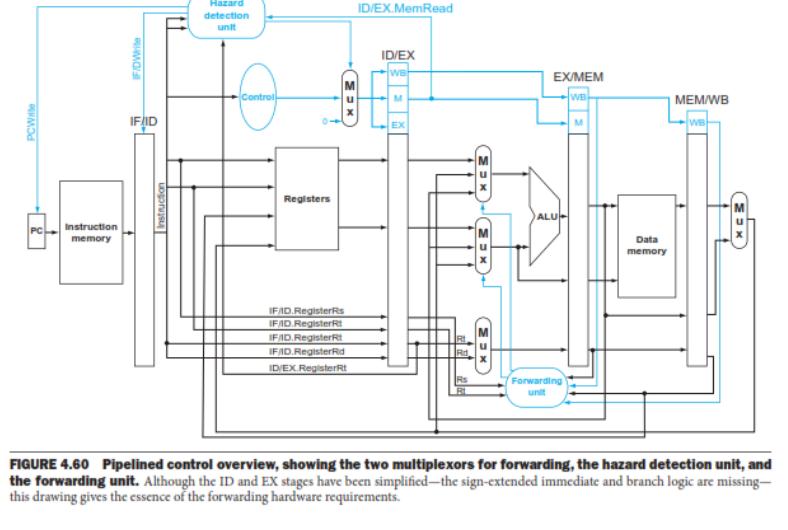
PCW Instruction memory IF/DWrite IF ID Instruction Hazard detection ID/EX.MemRead unit Registers IFAD.RegisterRs IFID.RegisterRt IFAID.RegisterRt IFAD.RegisterRd ID/EX RegisterRt ID/EX WE EX/MEM WB MEM/WB EX (Ex)-(X) ALU Data memory Forwarding FIGURE 4.60 Pipelined control overview, showing the two multiplexors for forwarding, the hazard detection unit, and the forwarding unit. Although the ID and EX stages have been simplified-the sign-extended immediate and branch logic are missing- this drawing gives the essence of the forwarding hardware requirements.
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (148 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To answer your questions we need to understand how instructions progress through a pipelined architecture and what happens in each pipeline stage The ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


