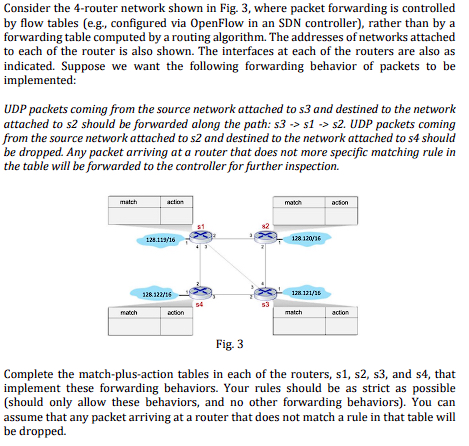
Question: Consider the 4 - router network shown in Fig. 3 , where packet forwarding is controlled by flow tables ( e . g . ,
Consider the router network shown in Fig. where packet forwarding is controlled by flow tables eg configured via OpenFlow in an SDN controller rather than by a forwarding table computed by a routing algorithm. The addresses of networks attached to each of the router is also shown. The interfaces at each of the routers are also as indicated. Suppose we want the following forwarding behavior of packets to be implemented:
UDP packets coming from the source network attached to and destined to the network attached to should be forwarded along the path: s UDP packets coming from the source network attached to and destined to the network attached to should be dropped. Any packet arriving at a router that does not more specific matching rule in the table will be forwarded to the controller for further inspection.
Complete the matchplusaction tables in each of the routers, s s s and s that implement these forwarding behaviors. Your rules should be as strict as possible should only allow these behaviors, and no other forwarding behaviors You can assume that any packet arriving at a router that does not match a rule in that table will be dropped.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


