Question: Consider the Diamond - Samuelson model discussed in section 17.1 of the book. Change the lifetime utility function (17.1) to: A = U(CY, C+1),
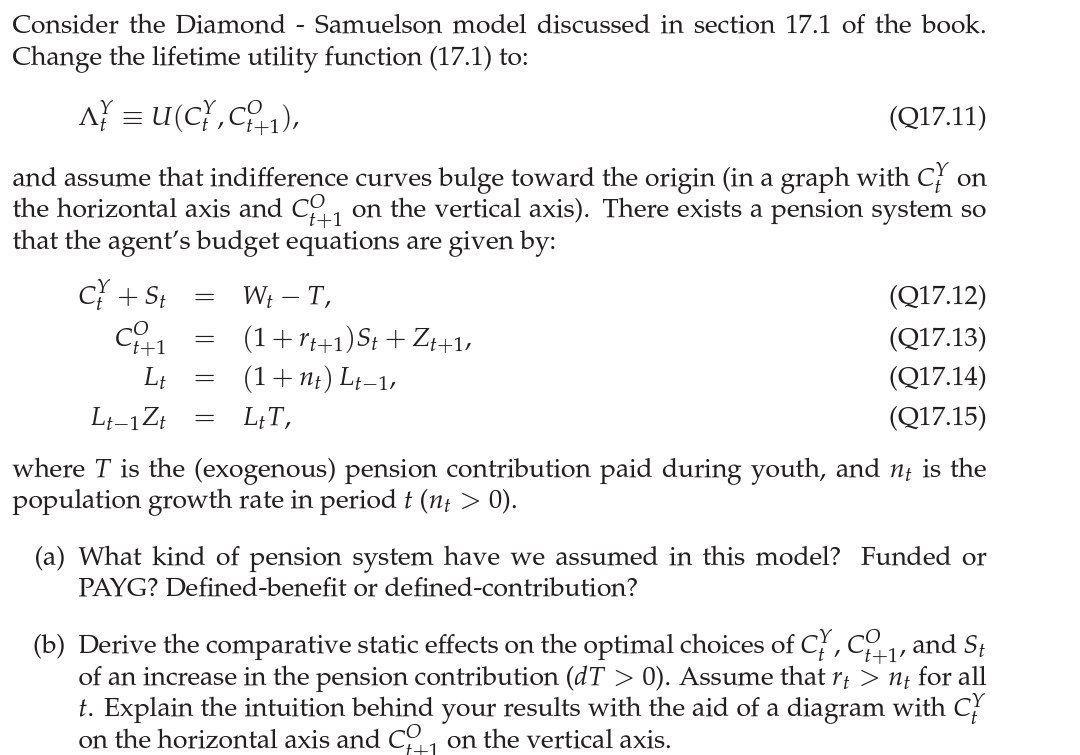
Consider the Diamond - Samuelson model discussed in section 17.1 of the book. Change the lifetime utility function (17.1) to: A = U(CY, C+1), (Q17.11) and assume that indifference curves bulge toward the origin (in a graph with CY on the horizontal axis and C on the vertical axis). There exists a pension system so that the agent's budget equations are given by: t+1 C + St t+1 Lt Lt-1 Zt = - = - Wt - T, (1 + rt+1) St + Zt+1, (1 + nt) Lt-1, LtT, (Q17.12) (Q17.13) (Q17.14) (Q17.15) where T is the (exogenous) pension contribution paid during youth, and nt is the population growth rate in period t (nt > 0). (a) What kind of pension system have we assumed in this model? Funded or PAYG? Defined-benefit or defined-contribution? (b) Derive the comparative static effects on the optimal choices of CY, C1, and St of an increase in the pension contribution (dT > 0). Assume that rt > nt for all t. Explain the intuition behind your results with the aid of a diagram with CY on the horizontal axis and C on the vertical axis.
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
This is a PAYG system The young pay for the pensions of the old Since T is exogenous and held constant this is a DC system If nt were to change then Z... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


