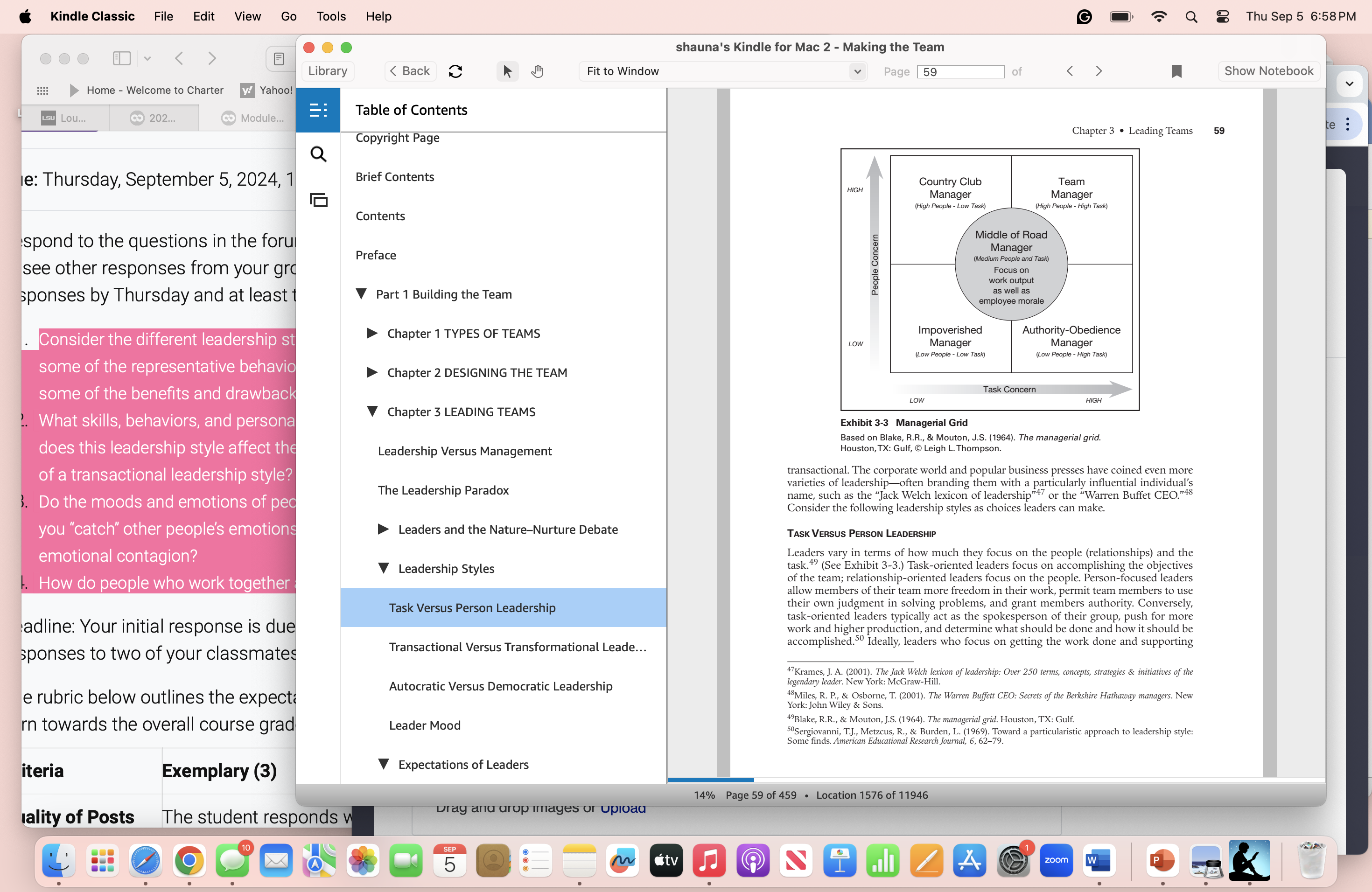
Question: Consider the different leadership styles outlined in this chapter 3 of the textbook. What are some of the representative behaviors associated with each style of
- Consider the different leadership styles outlined in this chapter 3 of the textbook. What are some of the representative behaviors associated with each style of leadership? What are some of the benefits and drawbacks to each particular style?
- What skills, behaviors, and personality traits are common to transformational leaders? How does this leadership style affect their teams, and how are those results different from those of a transactional leadership style?
- Do the moods and emotions of people around you influence your emotional state? How do you "catch" other people's emotions and "spread" your emotions? Why is this process called emotional contagion?
- How do people who work together as a team mutually shape one another's behavior?
All the questions have to be answered in paragraph formate and APA cites
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


