Question: Consider the example of the Hydrogen atom. A simplified ( but very useful ) model for this atom ( typically called the Bohr model )
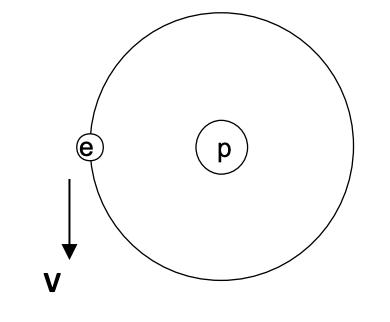
V e
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Direction of acceleration of the electron The direction of the acceleration of the electron is tow... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


