Question: Consider the following Bayesian network, where variables A through E are all Boolean valued. Note: there is a typo in the image, it should be
Consider the following Bayesian network, where variables A through E are all Boolean valued. Note: there is a typo in the image, it should be P(A = true) = 0.2 instead of P(D = true) = 0.2 .
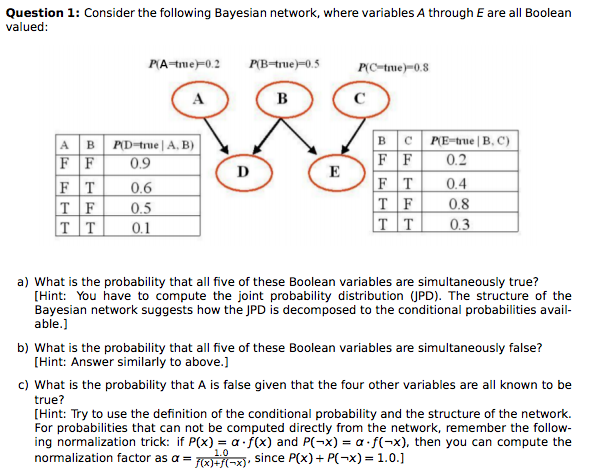
Question 1: Consider the following Bayesian network, where variables A through E are all Boolean valued PC-true)-0.8 B CPE true B, C) A B PD true A, B) FFI 0.9 FT0.6 FFI 0.2 0.4 TIF| 0.8 0.3 0.5 T?T| 0.1 a) What is the probability that all five of these Boolean variables are simultaneously true? [Hint: You have to compute the joint probability distribution PD). The structure of the Bayesian network suggests how the JPD is decomposed to the conditional probabilities avail- able.] b) What is the probability that all five of these Boolean variables are simultaneously false? [Hint: Answer similarly to above.] c) What is the probability that A is false given that the four other variables are all known to be true? [Hint: Try to use the definition of the conditional probability and the structure of the network. For probabilities that can not be computed directly from the network, remember the follow ing normalization trick: if P(x)a f(x) and P(-x)a f(-x), then you can compute the normalization factor as ?= since P(x)-P(-x) = 1.0.] Question 1: Consider the following Bayesian network, where variables A through E are all Boolean valued PC-true)-0.8 B CPE true B, C) A B PD true A, B) FFI 0.9 FT0.6 FFI 0.2 0.4 TIF| 0.8 0.3 0.5 T?T| 0.1 a) What is the probability that all five of these Boolean variables are simultaneously true? [Hint: You have to compute the joint probability distribution PD). The structure of the Bayesian network suggests how the JPD is decomposed to the conditional probabilities avail- able.] b) What is the probability that all five of these Boolean variables are simultaneously false? [Hint: Answer similarly to above.] c) What is the probability that A is false given that the four other variables are all known to be true? [Hint: Try to use the definition of the conditional probability and the structure of the network. For probabilities that can not be computed directly from the network, remember the follow ing normalization trick: if P(x)a f(x) and P(-x)a f(-x), then you can compute the normalization factor as ?= since P(x)-P(-x) = 1.0.]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


