Question: Consider the following class: class Greeter { String name; public void sayHello() { System.out, println(Hello + name); } Select the correct statement about generics in
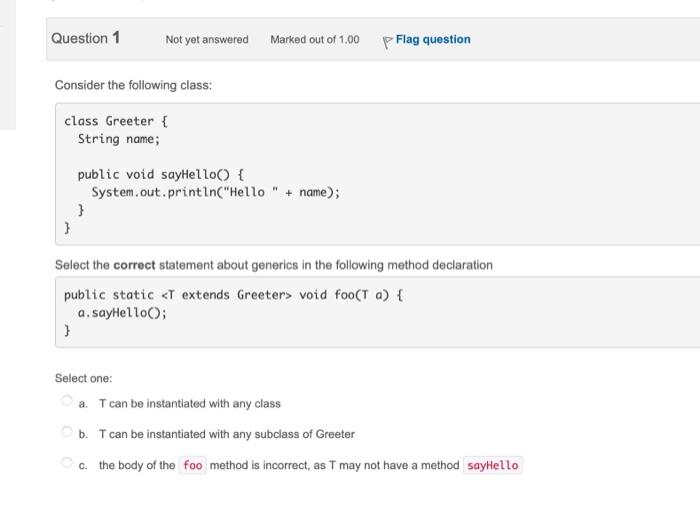
Consider the following class: class Greeter \{ String name; public void sayHello() \{ System.out, println("Hello" + name); \} Select the correct statement about generics in the following method declaration public static void foo(T a) \{ a.sayHello(); Select one: a. T can be instantiated with any class b. T can be instantiated with any subclass of Greeter c. the body of the method is incorrect, as T may not have a method
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


