Question: Consider the following differential equation. (A computer algebra system is recommended.) ( 1 + +2 ) y' + 4ty = (1 + +2)-2 (a) Draw
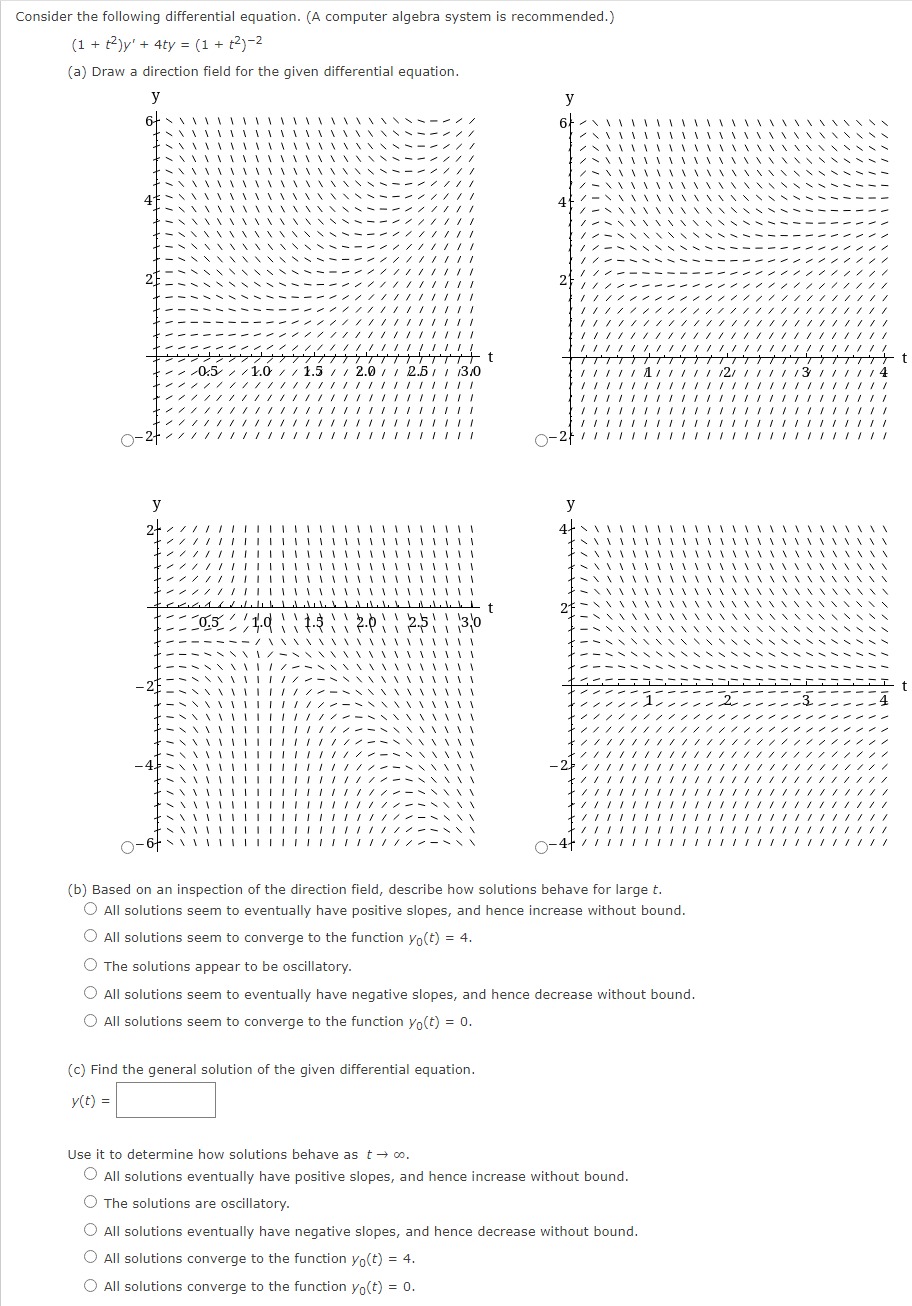
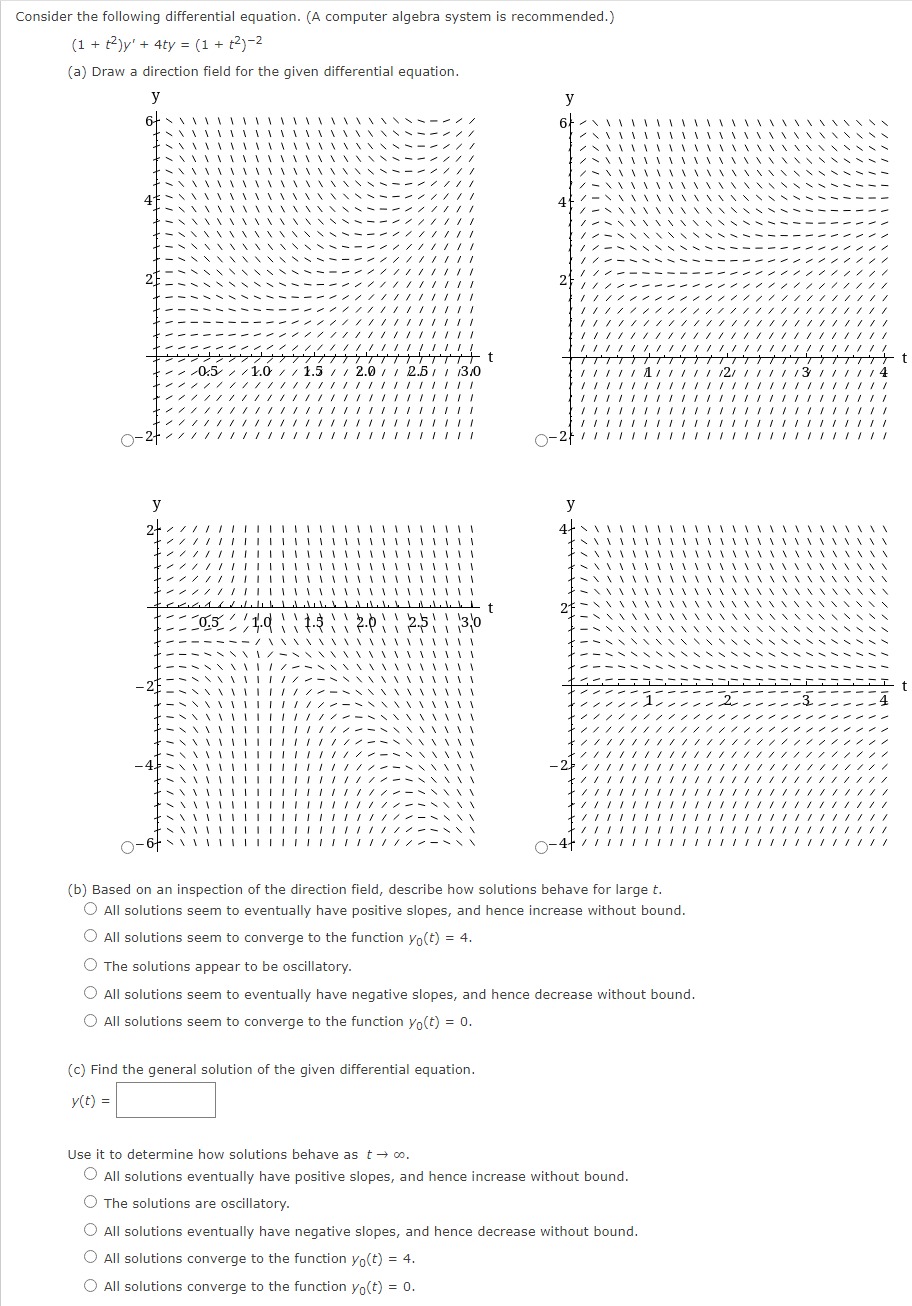
Consider the following differential equation. (A computer algebra system is recommended.) ( 1 + +2 ) y' + 4ty = (1 + +2)-2 (a) Draw a direction field for the given differential equation. 4 41 - t / 1.5 / / 2.0 / / 2.51 1 13/0 - t N 0.5 ' '10 \\ \\15 \\ \\20\\ \\25 30 (b) Based on an inspection of the direction field, describe how solutions behave for large t. All solutions seem to eventually have positive slopes, and hence increase without bound. All solutions seem to converge to the function yo(t) = 4. The solutions appear to be oscillatory. All solutions seem to eventually have negative slopes, and hence decrease without bound. All solutions seem to converge to the function yo(t) = 0. (c) Find the general solution of the given differential equation. y (t ) = Use it to determine how solutions behave as t + co. All solutions eventually have positive slopes, and hence increase without bound. The solutions are oscillatory. All solutions eventually have negative slopes, and hence decrease without bound. All solutions converge to the function yo(t) = 4. All solutions converge to the function yo(t) = 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


